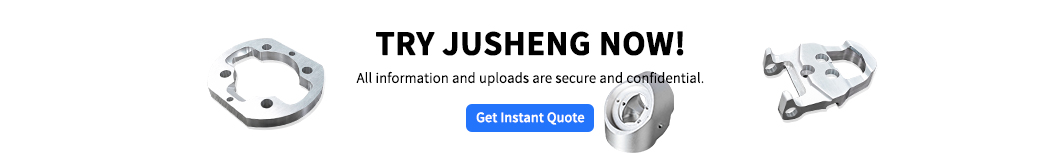
3D 인쇄 기술은 디지털 제조로 생산 논리를 재구성하고 있습니다. 디자인과 제작 사이의 링크, 3D 인쇄 모델은 유효한 도구가 생성됩니다. JS는 FDM, SLA, SLS 및 Metal Printing Processes , 프로토 타입 개발에서 소규모 배치 생산에 이르기까지 모든 것을 지원하고 혁신을 돕습니다.

3D 프린팅 기술의 유형은 무엇입니까?
1. 1
- 원리 : 층 압출에 의해 플라스틱 섬유 층을 가열하여 용융 증착 몰딩.
- 특징 : 저비용, 빠른 프로토 타입 , JS의 효율적인 생산 과정 > > > > > > > > > > > > > > > > > >.
2.stereolithography (SLA)
- 원리 : UV 경화 기술, 액체 수지는 UV 경화에 의해 형성됩니다.
- 기능 : 높은 정확도 (± 0.05mm), 매끄러운 표면, 복잡한 구조에 적합하며 JS 정밀 제조 요구 사항을 충족합니다. .
3. data-len = "32"data-v-7b79c893 = "" "> 선택적 레이저 소결 (SLS)
- 작동 방법 : 레이저 소결 나일론 파우더는지지 구조가 필요하지 않습니다.
- 기능 : 고강도, 기능적 부품에 적합한 JS의 금속/복합 재료 호환성은 응용 범위를 확장 할 수 있습니다. .
< "> mjf)
- 작동 방법 : inkjet 파우더 베드 퓨전, 용융 및 적외선 가열을 통한 층에 의한 나일론 분말 층을 굳히는 방법. .
- 특징 : 고속 (SLS보다 3 배 더 빠른 3 배), 높은 세부 사항 (± 0.08mm), 빠른 생산 및 비용 최적화를위한 JS.
5. data-pos = "2"data-len = "30"data-v-7b79c893 = "" "> 선택적 레이저 용융 (SLM)
- 작동 방법 : 고급 제조를위한 금속 파우더 레이저 용융.
- 기능 : 높은 정확도 (± 0.02mm), 고온 저항, JS의 정밀 가공 기술은 제품 품질을 더욱 향상시킬 수 있습니다. >.
< "> 3D Printing의 비교 DATA-V-7B79C893 =" "" "" "" "" "" "" ""PAR DATA-V-7B79C893 = "" 기술
<테이블 스타일 = "Border-Collapse; Collapse; 너비 : 99.9046%; 테두리-width : 1px; 국경 색 : #000000; 높이 : 439.938px;" Border = "1">- 빠른 전달은 MJF 기술을 사용하여 1-2 주 동안 달성 될 수 있으며, 이는 기존 SLS에 비해 생산 효율성을 최대 3 배까지 향상시킬 수 있습니다. .
- MJF, SLA 및 JS의 조합 ± 0.005mm 정밀 기계 기능 는 Aerospace, Medical 및 Medical 및 기타의 Components를 충족시킵니다. 필드.
- MJF 기술은 배치 소결을 통해 재료 폐기물을 줄입니다. 이는 JS의 프로세스 최적화와 결합하여 평균 20%의 평균 비용을 감소시킵니다.
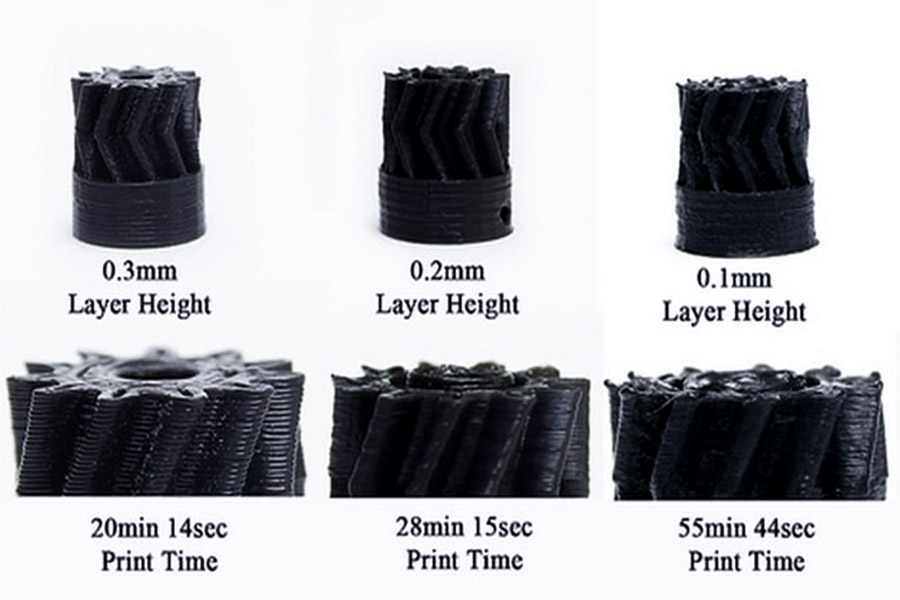
FDM 인쇄층 두께가 강도에 미치는 영향은 무엇입니까?
<"> 강도
1. 층이 두꺼워 질수록 인터레이어 접착력이 약할수록>
- FDM 인쇄에서는 용융 플라스틱의 각 층이 이전 층에 완전히 결합되어야합니다. 더 많은), 층과 층 사이의 접촉 영역은 감소하여, 특히 힘의 방향이 층의 패턴 (예 : 인장 테스트)과 평행 할 때 접착력이 감소 할 수있다. .
- 최적화 제안 : JS 회사는
층의 두꺼운 층, 더 밀도가 높은 구조
- 0.05mm와 같은 작은 층 두께는 층 간의 간격을 줄여 표면이 더 매끄럽고 내부 구조를 더욱 균일하게 만듭니다. 약점, 따라서 충격 저항이 증가합니다.
- js 사례 : 인쇄 중 <스팬 클래스 = "sentence"data-translateid = "59dae278e1d0d222c543269d4997239c"data-len = "0"219 "" "219" Data-V-7B79C893 = ""> 서비스 항공 우주 부품의 JS는 인쇄층의 두께를 제어하여 마이크로 미터 레벨을 제어하여 구성 요소가 항공 우주 강도 표준을 충족하도록합니다.
.
- FDM 부분의 강도는 이방성입니다. 즉, 인쇄 방향 (Z 축)은 일반적으로 수직 방향 (XY 축)보다 강합니다.
- 솔루션 : JS의 전문 엔지니어링 팀은 인쇄 방향 및 두께를 권장합니다.
층 두께와 재료 특성 사이의 균형
1. 층층은 재료를 절약하지만 강도
- 두꺼운 레이어는 빠르게 인쇄하여 소모품을 적게 사용하여 빠른 프로토 타이핑에 적합하지만 층간 결함으로 인해 강도가 부족할 수 있습니다. 예를 들어, ABS 플라스틱을 0.3mm 층 두께로 인쇄 할 때 인장 강도는 0.1mm 층 두께보다 15% -20% 낮을 수 있습니다.
- 비용 최적화 : JS의 인쇄 서비스는 지능형 알고리즘을 에 사용하여 가장 경제적 인 계층 두께 솔루션을 자동으로 권장합니다 강도를 보장하면서 고객에게 재료 비용의 30% 이상을 절약합니다.
2. data-len = "55"data-v-7b79c893 = "" "> 얇은 레이어는 강도를 추가하지만 인쇄하는 데 시간이 더 걸리지 만
- 얇은 층 인쇄는 강도를 향상시킬 수 있지만 인쇄 시간은 분명히 증가합니다. 0.3mm 층의 길이.
- 인쇄 서비스 시간 보장 : JS는 산업용 멀티 노즐 프린터 클러스터를 사용하므로 초 약속의 레이어를 선택하더라도 약속 된 1-2 주 내에 배송 할 수 있습니다. .
실제 애플리케이션에서의 두께 선택
1. 기능 부품 대 표시 부품
- 기능 부품 (공구 핸들, 기계적 부품 등) : 강도와 효율을 모두 고려하여 0.1-0.2mm 층 두께가 권장됩니다.
- 디스플레이 부품 (예 : 모양 모델) : 0.3mm 층 두께를 선택하여 비용을 줄이고 배송 속도를 높일 수 있습니다.
- 맞춤형 서비스 : js는 무료 기술 상담을 제공하고 고객 요구에 따라 계층 두께 매개 변수를 동적으로 조정합니다.
2. 재산 적응
- PLA/ABS : 기존 층 두께는 0.1-0.3mm이며 얇은 층은 세부 성능을 향상시킬 수 있습니다.
- 나일론/복합 재료 : 강인성을 향상시키기 위해 0.05-0.15mm 층 두께가 권장됩니다.
- 인쇄 서비스 자료 라이브러리 : JS는 50+ 재료의 인쇄를 지원하며 각 재료는 최적의 강도 성능을 보장하기 위해 층 두께에 대해 테스트되었습니다.

SLA 인쇄 해상도를 결정하는 매개 변수는 무엇입니까?
"span Class ="Sentence " data-translateid = "67a9aa2de38208c3575fd6cdde054b37"data-pos = "0"data-len = "49"data-v-7b79c893 = "">
광원 유형 및 스펙 클 크기 유형
- 레이저 광원 : 스팟 직경 : 스팟 직경은 일반적으로 10-100 미크론이며, 보석류, 치과 및 기타 dlp light source : 빛의 반점은 디지털 프로젝터를 통해 투사되고 픽셀 크기는 해상도를 결정합니다 (예 : 2K/4K 프로젝션의 경우 50-100 미크론).
- 충격 : 스펙 클 크기가 작을수록 x/y 축 세부 사항이 더 좋을 수 있지만 인쇄 시간이 증가 할 수 있습니다.
2. Data-TranslateId = "9C8D0C9D004D7EAA4D3D8DB94A4466E7"Data-POS = "3"Data-Len = "32"Data-V-7B79C893 = "" "> < data-translateid = "7B77520B706CA48488BA88AC33DFB23B"data-pos = "3"data-len = "35"data-v-7b79c893 = ""> Resin Properties < 매개 변수 비교 및 최적화 제안 테이블 By properly selecting parameter combinations, the 3D printing model can achieve precise manufacturing from concept verification to functional prototypes. 1.3D printing of metallic materials (high temperature environment preferred) SLM/DMLS (selective laser melting/sintering) 2.Ceramic 3D printing technology (ultra-high temperature resistance potential) SLA/DLP (light-curing ceramics) 3.High-Performance engineering plastic 3D Printing FDM (Molten deposition modeling) SLS (selective laser sintering) Technology selection recommendations for high temperature scenarios Ink jet printing technology is by layering liquid material on top of each other to create three-dimensional objects. Its core lies in high high-precision jetting and curing 제어. Specific implementation steps and key technologies are as 다음 : 1.Preparation of materials: Adaptation of liquid media 2.Ink jet print head: Precision droplet injection Piezoelectric drive or thermal foaming technology: 3.Layer by layer stacking: droplet solidification molding 4.Post-treatment: enhancement and surface optimization 1.Structural adaptation principle Overhang structure (>45°): Bridge structure (long span): 2.Matching and separation of materials Easy peel combination: Chemical dissolution combination: ABS+HIPS: Lemonin is needed to dissolve the scaffold and is suitable for complex internal parts such as gear components. 3.Actual performance requirements 4.Post-treatment efficiency Quick removal: Environmental Protection Plan: It is advisable to select biodegradable scaffolds (e.g. PBDE-based biodegradable materials) to reduce waste liquid treatment costs. 5.Printer adaptation FDM equipment: SLA/DLP equipment: 1.Multi-material printing technology support JS's 3D printing services include MJF and composite metal/ceramic printing technologies, which can switch different materials (e.g. metal-ceramic, carbide-polymer) during the same printing process to achieve continuous or segmented gradient changes in material composition. 2.Material compatibility and gradient design Through JS's 3D printing services, customers can choose from a variety of material combinations, including metals, ceramics and composites, and freely design the microstructure of functional gradient components (such as abrasionresistant + substrate layer). 3.Process optimization and performance assurance JS's industrial-grade equipment supports thickness control (±0.005mm) and temperature management to ensure uniform interface bonding strength and gradient transition across different materials and meet extreme working conditions such as high temperature and pressure. 4.Customized solutions For areas such as aerospace and medical devices, JS's team can provide a full range of services, from material selection and gradient structure design to reprocessing, such as: As a disruptive technology, 3dprinting continues to drive change in manufacturing with its diverse process types (e.g. FDM, SLA, metal printing, etc.) and a wide range of application scenarios (from industrial manufacturing to medical innovation). Whether it is the efficient production of complex functionally gradient parts or the rapid iteration of custom models, 3D printing services demonstrate irreplaceable flexibility and economy. Technology service providers represented by JS have further lowered the technology threshold by integrating multi-material printing, precision process control and industry-wide chain support, allowing businesses to focus on design innovation and value creation. The content on this page is for general reference only. JS Series makes no express or implied warranties regarding the accuracy, timeliness, or applicability of the information provided. Users should not assume that the product specifications, technical parameters, performance indicators, or quality commitments of third-party suppliers are completely consistent with the content displayed on this platform. The specific design feature, material standards, and process requirements of the product should be based on the actual order agreement. It is recommended that the purchaser proactively request a formal quotation and verify product details before the transaction. For further confirmation, please contact our customer service team for professional support. JS is an industry leading provider of customized manufacturing services, dedicated to providing customers with high-precision and high-efficiency one-stop manufacturing solutions. With over 20 years of industry experience, we have successfully provided professional CNC machining, sheet metal manufacturing, 3D printing, injection molding, metal stamping and other services to more than 5000 enterprises, covering multiple fields such as aerospace, medical, automotive, electronics, etc. We have a modern factory certified with ISO 9001:2015, equipped with over 100 advanced five axis machining centers to ensure that every product meets the highest quality standards. Our service network covers over 150 countries worldwide, providing 24-hour rapid response for both small-scale trial production and large-scale production, ensuring efficient progress of your project. Choosing JS Team means choosing manufacturing partners with excellent quality, precise delivery, and trustworthiness. 1.Does SLS printing require support? SLS printing usually does not require support. The unsintered nylon powder will naturally envelop the model to avoid collapsing in the air. Only a few complex designs require a small amount of ancillary support, which greatly simplifies the reprocessing process. 2.Which technology is suitable for printing transparent parts? SLA technology is suitable for printing transparent parts. It uses photosensitive resin that hardens under UV 빛. The surface is smooth and transparent. Suitable for making high precision transparent model (such as optical parts). 3.What does the layer thickness of FDM affect? The thickness of FDM layer influences surface smoothness, printing time and printing strength. The thicker the layer, the more visible the pattern, the faster the printing, but the intensity may be reduced. 4.How big a part can 3D printing make? Industrial-grade 3D-printing devices can manufacture large parts of meters (such as aerospace parts), while desktop devices are usually limited to a few dozen centimeters and are suitable for small models or prototypes.
매개 변수
해상도에 대한 영향
최적화 방향
전형적인 값
광원 유형
Laser> DLP (레이저는 동일한 해상도에서 정밀도가 높습니다).
정밀 모델은 레이저를 선택하고 대량 생산을 위해 DLP를 선택하십시오. .
레이저 : 50μm / dlp : 100μm < / td>
스팟 크기
지점이 작을수록 세부 사항이 명확 해집니다.
고정밀 레이저 헤드 또는 4K DLP 프로젝션 사용.
50μm (레이저)
스캔 속도
속도가 느리면 경화가 더 완료됩니다. .
미세한 영역 (예 : 0.1mm/s)에서 속도를 줄이고 넓은 지역에서 속도를 높이십시오.
50-200mm/s
레이어 두께
층 두께는 절반으로 줄어들고 z 축 분해능이 4 배 증가합니다.
정밀 부품에는 얇은 층 (25μm)과 속도 증가를 위해 두꺼운 층 (100μm)을 사용합니다.
50μm (표준)
수지 점도
낮은 점도는 유동성과 세부 사항 충전 능력을 향상시킵니다. .
Use special resins (e.g. transparent resins with viscosity ≤1500cP).
500-2000cP
Model overhang angle
If the angle is too small, dense support is required, and blocking the light affects the curing.
Avoid <45° overhangs or add auxiliary supports in the design.
≥60° (unsupported)
Which printing technology is more stable in high temperature environments?
Scene temperature
Recommended Technology
핵심 장점
Key capabilities of printing shops
600-1000℃
Metal SLM/DMLS.
High strength and creep resistance.
Laser equipment, vacuum environment, heat treatment.
1000-1500℃
Ceramic SLA/DLP.
Ultra high temperature resistance and corrosion resistance.
Specialized ceramic materials and high-temperature sintering process.
200-600℃
PEEK FDM, Nylon SLS.
Economy and lightweight.
Industrial grade equipment and material modification.
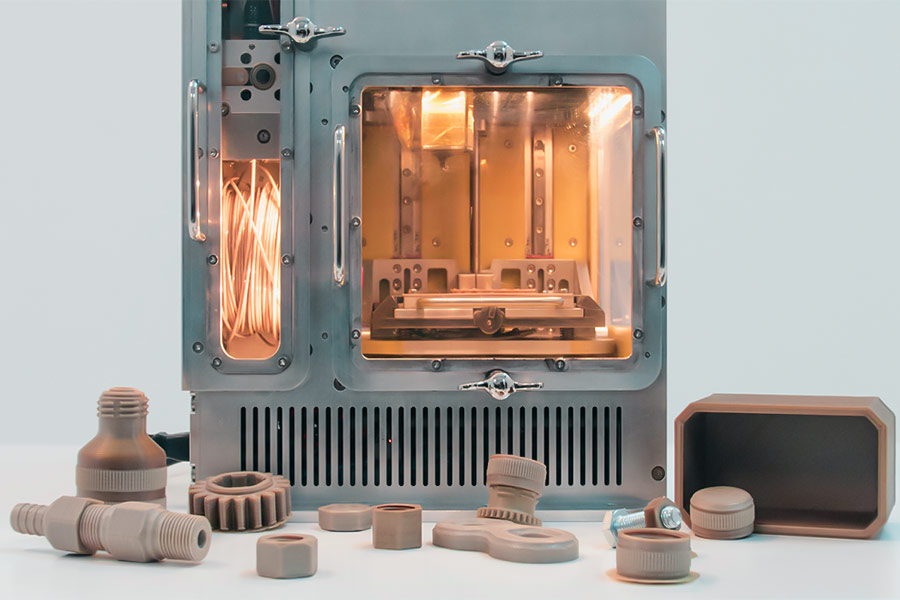
How to achieve layered stacking in 3D ink jet printing?
How to choose supporting materials for complex 3D printing models?
Can JS achieve functionally graded components through multi material 3D printing?
Summary
Disclaimer
JS Team
For more information, please visit the official website: jsrpm.comFAQs
Resources