3D-Druck ist eine fortschrittliche Fertigungstechnik, die digitale Modelle in feste Objekte umwandelt, indem sie sie übereinander verlegen, auch als additive Herstellung bekannt. 3 d drucken generiert 3D-Entitäten direkt aus CAD-Entwurfsmodellen oder Computerdesigns wie 3D-Scan-Daten, reduzierende Produktionszyklen und die Kosten für die Entwicklungskosten. Zu den Kerntechnologien gehören Photopolymerisation (SLA), Molten Deposition Modeling (FDM) und selektives Lasersintern (SLS). Flexibel für Kunststoffe, Metalle, Keramik und sogar Biomaterialien. Es wird häufig in industriellen Prototypen, medizinischen Modellen, Luft- und Raumfahrtkomponenten und personalisierten Konsumgütern verwendet.
JS Company ist seit vielen Jahren in 3D-Druckdienste intensiv und bietet Kunden One-Stop-Lösungen. Ob es die Nachfrage nach Präzisions-3D-Modelldruck oder die Herstellung komplexer struktureller funktionaler Komponenten ist, kann JS Company eine hohe Qualität und effiziente Anpassung erreichen.
Was ist 3D-Druck?
Es werden 3D-Modelle nach CAD-Design oder 3D-Scan erstellt. Anschließend formen Kunststoffe, Metalle und andere Materialienschichten für Schicht in feste Objekte. . href = "https://jsrpm.com/3dprinting"> Fertige komplexe geometrische Strukturen schnell hergestellt wie Hohlgitter und unregelmäßige Oberflächen.
3D-Printed-Modelle werden verwendet, um die Knochen oder Titanlegierungsgelenke für die präzise Anpassung zu drucken. kleine Stapel von Komponenten , wie aerospace-Leuchten
Wie wähle ich 3D-Druckmaterialien aus?
Kombinieren Sie gemeinsame industrielle Anwendungsszenarien und technische Eigenschaften, die folgenden Empfehlungen für die Auswahl von 3D-Druckmaterialien:
1. Materielle Selektion nach Technologie-Typ
| Technischer Typ | häufig verwendet | Features | Typische Anwendungsszenarien |
| fdm | PLA, ABS, PETG, Nylon | Niedrige Kosten, bequemer Betrieb und mäßige Genauigkeit. | Rapid Prototyping , Grundfunktionenkomponenten. |
| SLA | Photosensitives Harz (hart/flexibel) | Die Oberfläche war glatt und nuanciert. | precision-Teile, medizinische Modelle . |
| SLS | Nylon (PA12/PA6), TPU | Hochtemperaturwiderstand, hohe Festigkeit, ohne Unterstützung. | Funktionale Komponenten, leichte Konstruktion. |
| Metalldruck | Edelstahl, Titanlegierung, Aluminiumlegierung | hohe Festigkeit, korrosionsresistente, leitende und hitzebedingte. | aerospace und Automotive-Säfen . |
2.Choose nach den Eigenschaften des Materials
| Materialtyp | Kernstärken | Präventive Maßnahmen | ||||||
| pla | Umgebungsschutz, ungiftig, kostengünstig. | Schlechter Temperaturwiderstand (<60 ° C). | ||||||
| ABS | Stoßfest, Plattierung. | Während des Druckprozesses gibt es einen Geruch und die Plattform muss erhitzt werden. | ||||||
| Nylon (PA) | Wear-Resistant Self-Subrication. | Feuchtigkeitsabsorption, feuchtigkeitsdes Lagerung ist erforderlich. | ||||||
| TPU | Gute Flexibilität, nicht leicht zu reißen. |
| Photosensitive Harz |
In hochauflösenden, transparenten/semi-transparenten Optionen verfügbar. |
UV-Sicht beim Speichern. |
Metallpulver |
Es kann mit hoher Festigkeit und komplexer Struktur hergestellt werden. |
Nachbehandlung ist komplex (Defat, Sintern). |
|
3. Keey-Selektionsdeterminanten
Mechanische Eigenschaften
- Kraftanforderungen: Nylon und Metall bevorzugt.
- Temperaturwiderstand: ABS (80-100 ° C) gegen PA (120 ° C+).
Kostenkontrolle
- schnelle Überprüfung: PLA/FDM empfohlen.
- Präzisionsproduktion: Optionales photosensitives Harz oder SLS Nylon .
Postanforderungen verarbeitet
- Keine Farbe: Metall/Keramik.
- Farbanpassung: Multicolor-ABS/PLA-Filament.
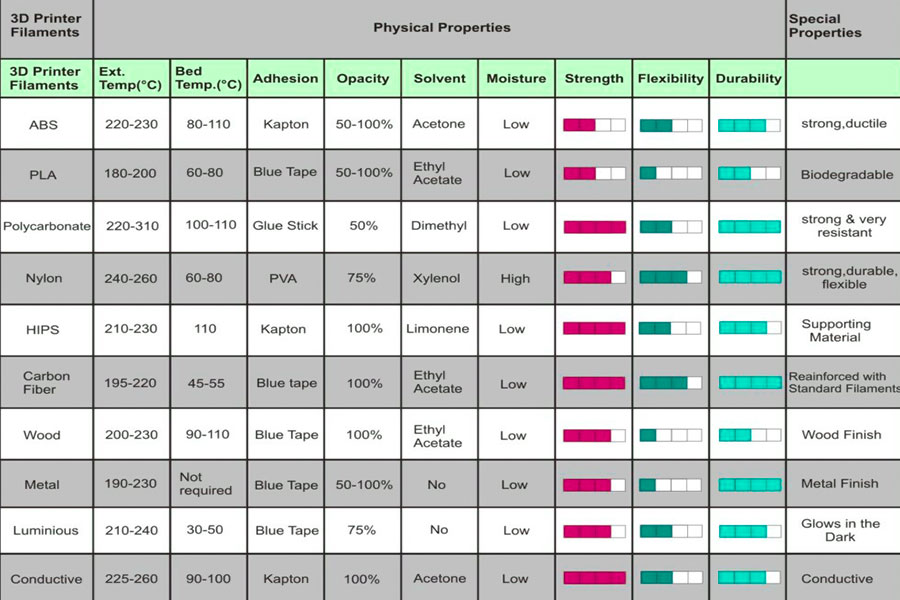 Was sind die Unterschiede zwischen verschiedenen Arten von 3D-Drucktechnologien?
Was sind die Unterschiede zwischen verschiedenen Arten von 3D-Drucktechnologien?
Hier ist ein Vergleich der Kernunterschiede zwischen den drei Mainstream 3D-Drucktechnologien :
1. Data-V-7B79C893 = ""> Vergleich der Kernverfahren
| Technischer Typ | Bildungsprinzip | Materialtyp | Genauigkeitskontrolle | Oberflächenqualität |
| FDM | Heiß geschmolzen ist extrudiert. | Thermoplastik (PLA/ABS). | hängt von der Düsegenauigkeit ab (± 0,1-0,5 mm). | grob (erfordert Polieren). |
| SLA | UV-Laser-Härtung flüssiger photosensitiver Harz. | Photosensitives Harz. | hohe Präzision (± 0,05 mm). | glatt ( in der Nähe von Injektionsformen ). |
| SLS | Lasersintern von Nylon/Metallpulver. | Engineering Plastics/Metals. | Mäßige Genauigkeit (± 0,1-0,3 mm). | porous struktur ( Beschichtung ). |
2. Data-V-7B79C893 = ""> Vergleich technischer Vor- und Nachteile
| FDM | SLA | SLS | |
| Vorteil | kostengünstige, weite Materialumfang, große Druckgröße . | Hochauflösende, hohe Detailleistung. | hohe Festigkeit, keine Stützstruktur erforderlich. |
| Nachteil | Oberflächenrauheit und begrenzte Genauigkeit. | Harze sind spröde und komplex zu handhaben. | teure Geräte und störende Pulververarbeitung. |
 Was sind die grundlegenden Designprinzipien, denen das 3D-Druckmodell folgen muss?
Was sind die grundlegenden Designprinzipien, denen das 3D-Druckmodell folgen muss?
Optimizing support structure
- Suspensionswinkelgrenze: Zusätzliche Unterstützung ist erforderlich, wenn die Suspensionswinkel 45 Grad überschreiten. -Sleiche-Materials. Das schälen leicht und hinterlässt keine Spur nach der Verarbeitung.
- komplexe interne Strukturen Kann den Materialverbrauch durch Habenunterstützung reduzieren, und JS-Algorithmen können automatisch effiziente Support-Lösungen generieren.
structure optimization
Photosensitive resin: LED matrix partition exposure technology increases SLA curing speed by three times.
3.Post processing efficiency improvement plan As an important branch of 3D printing, Ink jet printing has become a key technology in complex structure manufacturing, personalized customization and high performance parts production through precise control of micro-nozzles and multi-material compatibility. Its importance is reflected in the following: 1.High precision and meticulous performance 2.Integration of multiple materials and colors 3.Efficient production and rapid iteration 4.Physical diversity and innovation 5.Technical constraints and improvement directions Technology Strength Assessment 1.Advanced equipment 2.Material adaptability Service Capability Verification 1.Design support 3.Post processing support Quality control system 1.Accuracy verification 2.Reliability testing Cost transparency 1.Quotation details 2.economies of scale Priority should be given to service providers with more than 100,000 hours of printing per year (JS has a large-scale production line that reduces marginal costs). Cases and reputations 1.Industry case studies 2.Client reviews Viewing user feedback through industry forums or third-party platforms such as G2 focuses on on-time product delivery and aftermarket response (JS official website shows 98%% customer satisfaction). 1.Industrial-grade precision manufacturing: Equipped with SLA light curing equipment (±0.02mm accuracy), industrial FDM (±0.05mm), SLS nylon printing supports 100% density to 20% crystal lattice free adjustment with 40% weight loss and constant strength. 2.Comprehensive material compatibility: Includes engineering plastics (ABS/PLA), metals (titanium alloys), ceramics, biodegradable materials and conductive silver ink, supporting parameterized material selection (e.g. PEEK resistance to temperatures below 300°C). 3.Cost optimization and small batch customization: By combining 3D printing and injection molding processes, large-scale production costs can be reduced to 60% of traditional methods, especially for small orders of 100-1000 pieces. Water-soluble auxiliary materials can reduce reprocessing costs by 70% and delivery cycles by 30%. 4.Full Chain Digital Services: From CAD modeling to finished product inspection, 18 node data loops ensure 100% restoration of design intent. 5.Global Service Network: We provide 3D printing services to a number of countries worldwide. For small orders (≤100 pieces), delivery can be made as soon as 48 hours. For medical emergencies, we promise 24-hour fast delivery. The bilingual engineering team provides remote assistance such as model restoration and parameter optimization. 3D printing, at the heart of additive manufacturing, is reshaping global manufacturing landscape. It overcomes the limitation of traditional subtractive manufacturing processes, and enables numerous fields with its advantages of high precision, flexibility and low cost. From biocompatible implants to lightweight aerospace components, from personalized consumer electronics to complex industrial prototypes, 3D printing not only accelerates product iteration, but also facilitates frontier expansion in innovative design and functionality. In the future, 3D printing will continue to drive industrial upgrading as smart manufacturing and green manufacturing are deeply integrated. JS helps enterprises achieve personalized, efficient, low-carbon manufacturing and redefine global industry chain values through multi-material collaborative printing and hybrid manufacturing. The content of this page is for informational purposes only.JS SeriesNo representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, are made as to the accuracy, completeness or validity of the information. It should not be inferred that the performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features,material quality and type or workmanship that the third-party supplier or manufacturer will provide through the jusheng network. This is the responsibility of the buyerAsk for a quote for partsto determine the specific requirements for these parts.please Contact us Learn more information. JS is an industry-leading companyFocus on custom manufacturing solutions. With over 20 years of experience serving more than 5,000 customers,we focus on high precisionCNC machining,Sheet metal fabrication,3D printing,Injection molding,metal stamping,and other one-stop manufacturing services. 1.How can 3D printing reduce material waste? Traditional manufacturing often requires cutting and engraving, with a waste rate of 30% -50%. 3D printing is additive manufacturing, which involves printing only the parts needed, with a material utilization rate of over 90%. It is particularly suitable for small or complex production. 2.What is the best FDM printing layer thickness setting? The prototype is rough, with layers of 200-300 microns (0.2-0.3 mm) thick, fast but rough on the surface. The model is excellent, with layers 50-100 microns (0.05-0.1 mm) thick, better detail and longer processing time. 3.Are SLS-printed powder materials reusable? SLS-printed powder material can be reused, but after repeated use, its flowability decreases and their strength decreases slightly. The recovery rate of metal powder can be over 90%, and the number of uses needs to be controlled according to the material type to ensure performance. 4.Is 3D printing expensive? Small plastic printers for home use range from $280 to $1,400, and are suitable for DIY and small batch production. Mass production relies on industrial-grade metal/high-performance printers, requiring tens of thousands to millions.
Wie können Sie die Effizienz und Genauigkeit zwischen Schichtdicke und Druckgeschwindigkeit ausgleichen?
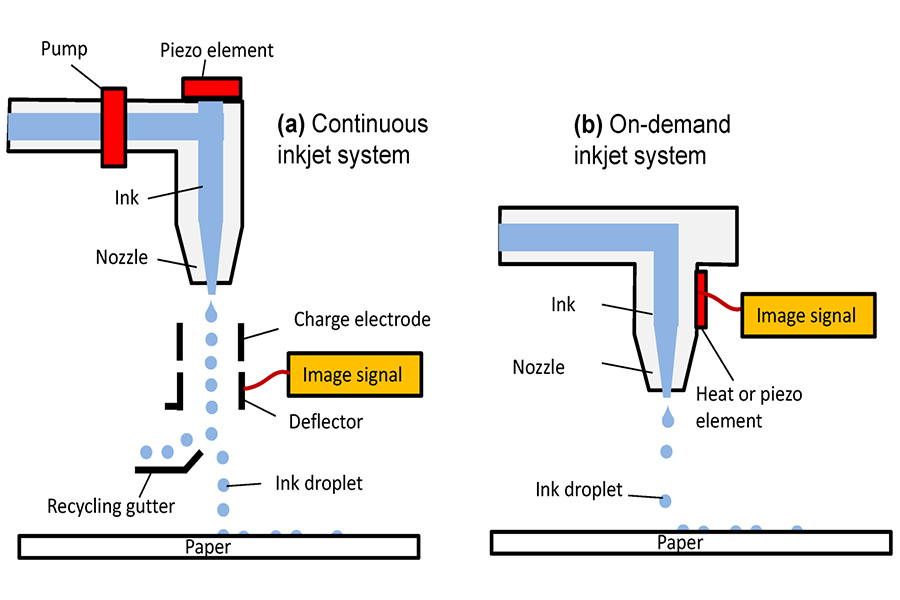
What is the importance of ink jet printing in 3D printing?
How to evaluate the professionalism of a 3D printing shop?
Five reasons to choose JS company's 3D printing services
Summary
Disclaimer
JS Team
Our factory is equipped with more than 100 state-of-the-art 5-axis machining centers and is ISO 9001:2015 certified. We provide fast, efficient and high-quality manufacturing solutions to customers in more than 150 countries around the world. Whether it's low-volume production or mass customization, we can meet your needs with the fastest delivery within 24 hours. chooseJS TechnologyIt means choosing efficiency, quality and professionalism.
To learn more, please visit our website:jsrpm.comFAQs
Resources






