In the modern industrial system, the molding meaning not only reflected in the precise realization of product form, but also in the efficiency support and cost control ability of large-scale production. Injection molding is the rapid molding of complex structural plastics moldings by injecting high-pressure molten plastics into precision molds, cooling and curing them.
The choice of material directly determines the performance of the product, and the characteristics of different materials (e.g. temperature resistance, strength, elasticity) need to be accurately matched to the function and process requirements of the product. This paper aims to systematize the classification and selection principles of injection molding materials, provide practical guidance to engineers and designers, help optimize design process, reduce production cost and promote green manufacturing practice.
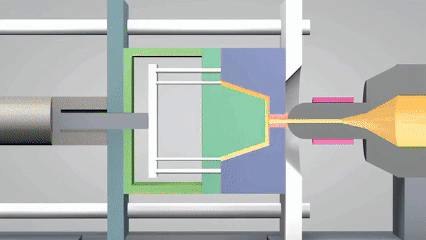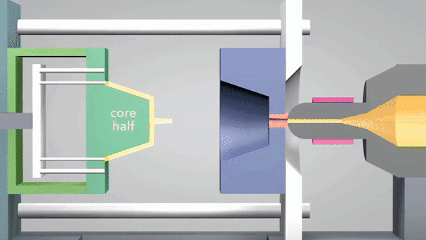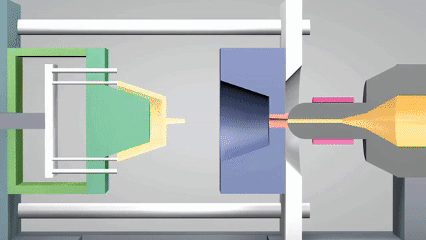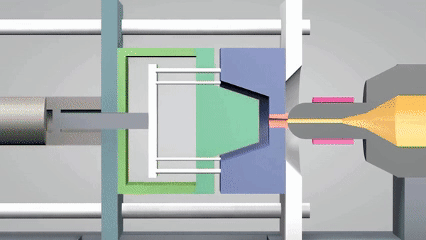
What is the definition of injection molding?
Injection molding is an efficient processing technology widely used in plastics molding field. The core principle is to melt plastic material through a heating device and inject it into precisely designed molds,such as silicone molding or metal molds, to be used in high-pressure environments. When the material is cooled and solidified, it will form a product with a specific shape.
The process can not only accurately replicate complex geometrical structures, but also has the characteristics of high production efficiency and material utilization, especially suitable for large-scale production of industrial products such as electronic casings and automobile parts. In recent years, silicone molding have been widely used to produce injection molds or small batch customization parts for their excellent temperature resistance and flexibility, further expanding the application scenarios of this technology.
What are the types of injection molding technologies?
1.Plastic injection molding
One of the core processes of plastic molding is injection molding, which involves heating and melting thermoplastic or thermoset plastic particles, injecting them into precision mold cavity at high pressure before cooling and solidifying.
Core Technology:
- Heat flow system: By optimizing the flow path of melt, reduce material waste and improve injection-molding efficiency.
- Multi cavity mold design: Realize the production of the first mold of many parts, suitable for a large quantity of standardized products (such as grocery stores, packaging containers, etc.).
Application scenario: Mass production of general plastic products, such as plastic bottles, stationery, household appliance, etc.
2.Overmolding
In the field of plastic molding, overmolding is an advanced technology that combines different materials through two injection molding processes.
Type of technology:
- Color injection molding: Combine Hard Rubber (ABS) and Soft Rubber (TPE) for handles, for example, to balance slip resistance and aesthetics.
- Encapsulation molding: Injection-molding involves wrapping plastic around a metal frame to strengthen the structure (such as tool handles).
Advantages: Reduce assembly steps, improve product functionality and aesthetics, widely used in automotive interiors, consumer electronics and other fields.
Insert molding is a key technique in plastic moldings, which involves metal/ceramic inserts being pre-placed in a mold and injected into the mold along with plastic.
Key elements:
- High-precision positioning: Die structure or robotic arm ensures precise insertion position (deviation <0.01mm).
- Material compatibility: Supports composite molding of metals, ceramics and plastics such as PA and PC.
Application: Automotive electronic connector (high temperature resistance, plug and pull resistance), home appliance knob (metal shaft+plastic shell).
4.Mold Technology for Plastics molding
Mold is the core carrier of injection process, which directly affects the accuracy and efficiency of plastic molding.
Mold design and type:
- Heat runner mold: Reduce sprue condensation and improve material utilization (save 30%).
- Stacking molds: Injection-molding of upper and lower molds at the same time, multiplying efficiency (e.g. food packaging boxes).
Core processes:
- Gate optimization: Control the direction of melt filling to avoid weld marks and shrinkage marks.
- Cooling system design: Reduction of molding cycle (e.g. cooling time of thin-walled parts<30 seconds).
5.Technical comparison and application selection
| Technical type | Applicable scenarios | Advantages | Typical materials |
| Plastic injection molding | Standardized mass production. | Low cost, high efficiency. | ABS、PP、PE. |
| Overmolding | Functional integration or exterior decoration. | Less assembly, more texture. | PC+TPU、ABS+TPE. |
| Insert molding | Structural reinforcement or functional integration. | The combination of metal and plastic. | Metal inlay+PA66. |
| Plastic injection mold | High-precision or complex structural components. | Size stability, long service life. | Precision electronic components, automotive parts. |
What are the classifications of injection molding materials?
Plastic materials
1.Engineering plastics
- Typical materials: ABS, PC (polycarbonate), PA (nylon), POM (polyoxymethylene), PPO/PSU (polyphenylene ether/polysulfone).
- Features: High strength, high temperature resistance, impact resistance, suitable for automotive, electronic, medical and other fields.
- JS company can meet the high precision requirements of engineering plastics complex structures such as precision parts for medical equipment.
2.General plastics
- Typical materials: PP, PE (polyethylene), PVC.
- Features: Low cost, easy to process, suitable for daily necessities, packaging and other lightweight scenarios.
- JS reduces costs by 20% through process optimization and is suitable for large orders such as home appliance casings and containers.
3.Special engineering plastics
- Typical materials: PEEK, PI, LCP.
- Features: High temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, excellent insulation, aerospace and semiconductor equipment.
- JS has successfully processed 50+material types and has experience in processing high abrasionresistant materials such as PEEK aviation components.
Metallic materials
1.Metal injection molding materials
- Typical materials: stainless steel (316L, 17-4PH), copper alloy, titanium alloy.
- Features: Flexibility of plastic injection molding combined with metal strength, suitable for precision parts such as watch gears.
- JS achieves mass production of complex metal parts through adhesive spraying technology, shortening the production cycle by 15%.
2 Lightweight alloys
- Typical materials: aluminum alloy, magnesium alloy.
- Features: High strength, low density, used in auto components and consumer electronics.
- JS provides customized surface treatment (such as anodization) to improve corrosion resistance.
Composites materials
1.Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastic (CFRP)
- Features: Ultra-high strength, lightweight, suitable for high-end sports equipment and drone construction.
- JS technology: Supports multi material composite molding to ensure dimensional stability (tolerances ± 0.02mm).
2.Glass Fiber Reinforced Plastic (GFRP)
- Features: High temperature resistance, creep resistance, used in automobile mold and industrial components.
- JS technology association: Adopt high pressure injection molding process to improve material fluidity and filling effect.
Other innovative materials
1.Biobased materials: PLA, PHA
- Uses: Environmentally friendly packaging, disposable medical supplies.
- JS works with sustainable development strategies to provide low-carbon emissions solutions.
2.Conductive/Thermal Conductive Plastic
- Purpose: Sensor casing, heat dissipation components.
- JS Company's integrated nanofiller technology optimizes the material's electrical/thermal properties.

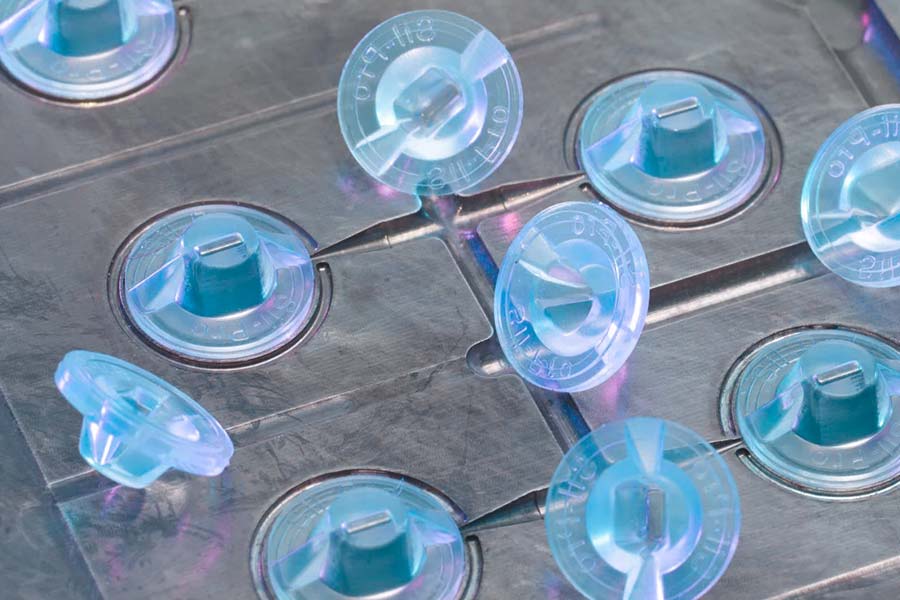
What are the advantages of thermoplastic in injection molding?
1.Repeatability of processing
Thermoplastics melt and flow when heated, solidify after cooling, and can be heated and cooled repeatedly indefinitely. This property enables molding plastic waste to be recycled directly, greatly reduces production costs and minimizes resource waste.
2.Efficient molding cycle
Thermoplastic materials often have faster crystallization or cooling rate, which can shorten the injection molding cycle. Thin-walled products, for example, can be filled and cooled in seconds, greatly increasing productivity. In addition, it has good fluidity and can be further accelerated by optimizing molding design to reduce energy consumption.
3.High dimensional stability
Many thermoplastic materials,such as ABS and PC, contract low and controllably after cooling, ensuring high accuracy of complex structures during injection-molding process. It avoids warping and distortion due to uneven cooling.
4.Diversified material properties
Thermoplastic plastics cover a wide range of types from general purpose plastics to high performance plastics such as:
- ABS: Resilience combined with surface gloss, suitable for home appliance housing.
- PA (nylon): high abrasion and tensile strength for gears and bearings.
- PC: High temperature resistant, transparent, for bulletproof glass or lighting fixtures.
This diversity enables plastic molding to adapt flexibly to the functional requirements of different products and further improve performance through modification techniques.
5.Environmental compatibility
The recyclability of thermoplastic materials is in line with global environmental trends and reduces the environmental impact of injection molding production production chains. For example, replacing raw materials with recycled plastics (such as rPET) would not only reduce carbon emissions, but would also meet limits on harmful substances imposed by EU regulations such as RoHS. In addition, some thermoplastic materials,such as PLA polylactic acid, are biodegradable and suitable for single-use medical supplies or food packaging, reducing white pollution.
What is the core basis for selecting injection molding materials?
1.Product functional requirements drive material selection
Application scenarios: Temperature resistance (e.g. engine components requiring 200 °C heat resistance), bearing capacity (e.g. mechanical parts), sealing performance (e.g. medical catheters), etc.
Functional requirements: Electrical conductivity (electronic components), antimicrobial properties (everyday products), transparency (lighting fixtures), etc.
JS technology:
- Material database: Covers performance parameters (tensile strength, hot deformation temperature, etc.) of various plastics (e.g. PA, PC) and silicone (LSR), supporting online screening.
- Customized modification: By adding fiberglass, nano fillers, or color masterbatch, customized conductive ABS (surface resistance <10³Ω) can be achieved.
2.Matching material performance adaptability
Mechanical properties: Tensile strength (e.g. high toughness required for car bumpers), abrasion resistance (e.g. gears).
Thermal properties: Temperature resistance range (e.g. PEEK 300 °C), thermal conductivity (e.g. heat dissipation components).
Chemical stability: Acid-base resistance (chemical equipment), biocompatibility (medical implants).
JS technology:
- Special Materials Supply: We offer high performance plastics such as PEI and PPS, as well as liquid silicone (LSR) injection molding services to meet extreme working conditions.
- Simulation system: Optimize gate design by analyzing the shrinkage rate and warpage deformation of the material by means of modulus flow (35% reduction in warpage rate of an automotive component).
3.Compatibility guarantee of processing technologies
Fluidity: Thin-walled parts require high plastic fluidity (e.g. ABS) and thick-walled parts can be selected for low viscosity PP.
Shrinkage control: Precision parts (such as phone frames) require low shrinkage materials (such as POM).
Mold lifespan: Corrosive materials such as PVC require chrome molds, while silicone injection molding requires a high temperature resistant coating.
JS technology:
- Thermal flow channel system: Multi-cavity die heat flow channel with tolerance of ±0.02mm supports 96-cavity injection molding.
- Silicone secondary injection molding: Develop flexible cooling water channels and multi-stage vulcanization process for seamless integration of soft and hard rubber (silicone+plastic) such as handle grip.
4.Balance between costs and mass production efficiency
Material costs: The price difference between virgin and recycled plastics.
Waste rate: Scrap recycling rate (95% by granulation technology).
Production cycle: Rapid prototyping requirements (such as daily orders requiring 72 hours of delivery).
JS technology:
- Cost optimization solution: 30% fiberglass enhanced PA6 is recommended instead of pure PA6, reducing costs by 25% while maintaining strength.
- Flexible production line: Supports small-scale pilot production (at least 100 units), mass production of millions of units per month, shortening a customer's production cycle by 60 days.
5.Environmental compliance requirements
Recyclability: Whether the material supports physical/chemical recycling (e.g. PCR recycling of plastics).
Limit Hazardous Substances: Follow RoHS, REACH and other regulations (toys must be phthalate-free, for example).
Biodegradability: Medical or packaging materials shall conform to EN 13432.
JS technology association:
- Environmental material certification: Provides FDA food grade, UL flame retardant certification and other reports to ensure product compliance.
- Recycled plastics: An electronics brand has achieved 92% material recycling rate and zero landfill target through JS solution.
What defects can occur when the temperature of silicone injection molding is too high?
1.Pyrolysis of materials and residual volatile compounds
- Defect manifestation: Too high a temperature can cause strands of silicone molecules to break, releasing low-molecular substances (such as acidic byproducts), form bubbles, silver lines on the surface or corroding molds.
- JS adopts a special temperature control system for silicone molding to monitor and regulate screw temperature (accuracy ±1℃) in real time to avoid local overheating.
2.Uneven color and yellowing phenomenon
- Defect manifestation: High temperature will accelerate the oxidation of pigments or additives, resulting in product color difference or overall yellowing, affecting the consistency of appearance.
- Precision color masterbatch measuring device is embedded in injection molding to ensure uniform dispersion of chromophore at high temperature.
3.Uncontrolled size shrinkage and deformation
- Defect manifestation: Excessive vulcanization leads to abnormal cross-linking density silicone gel, shrinkage rate deviates from the design value, causing product warping or assembly failure.
- Dynamic feedback of mold sensors vulcanization degree, optimization of silicone molding process parameters, so as to shorten the cooling time by 20%.
4.Mechanical deterioration
- Defect manifestation: high temperature will destroy the molecular structure of silicone gel, resulting in a decrease in tensile strength and tear strength, affecting the durability of the product.
- JS has developed high-strength silicone composites,such as fiberglass reinforced ones, that increased the tensile strength of industrial sealing ring engineering by 30%.
5.Mold thermal damage and shorter service life
- Defect manifestation: High temperature will accelerate the oxidation of mold steel, clog or deform the nozzle of the heat channel, increase the frequency and cost of maintenance.
- JS technology association: The die has a DLC diamond coating (HRC 60+), a high temperature and corrosion resistant heat flow system with independent temperature field control (± 0.5℃ accuracy) to prevent overheating in the nozzle area and a 30% reduction in maintenance frequency.

Summary
In the field of injection molding, material selection is the core factor that determines product performance and cost. From basic plastic molding to high performance engineering plastics to special silicone molding, different materials meet the diverse needs of automotive, medical and electronics industries due to their high temperature resistance, strength, elasticity and environmental protection. With increasing environmental regulations, the application of biodegradable plastics (such as plastics) and recycled materials has become a trend, promoting green manufacturing practices.
In this process, JS maximizes the potential of injection molding technology through precision die design, intelligent temperature control systems and modification technology. In the future, injection molding will continue to play a key role in lightweight, functionally integrated, and sustainable development as materials science and manufacturing technologies are deeply integrated.
Disclaimer
The content of this page is for informational purposes only.JS SeriesNo representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, are made as to the accuracy, completeness or validity of the information. It should not be inferred that the performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features,material quality and type or workmanship that the third-party supplier or manufacturer will provide through the jusheng network. This is the responsibility of the buyerAsk for a quote for partsto determine the specific requirements for these parts.please Contact us Learn more information.
JS Team
JS is an industry-leading companyFocus on custom manufacturing solutions. With over 20 years of experience serving more than 5,000 customers,we focus on high precisionCNC machining,Sheet metal fabrication,3D printing,Injection molding,metal stamping,and other one-stop manufacturing services.
Our factory is equipped with more than 100 state-of-the-art 5-axis machining centers and is ISO 9001:2015 certified. We provide fast, efficient and high-quality manufacturing solutions to customers in more than 150 countries around the world. Whether it's low-volume production or mass customization, we can meet your needs with the fastest delivery within 24 hours. chooseJS TechnologyIt means choosing efficiency, quality and professionalism.
To learn more, please visit our website:jsrpm.com
FAQs
1.What is the difference between plastic and silicone in injection molding?
Plastic (such as ABS) is low-cost, easy to process and suitable for large-scale production. Silicone (LSR) is soft and heat resistant and suitable for soft or medical-grade products such as pacifiers.
2.Are environmental friendly materials widely used in injection molding?
More and more! Biodegradable plastics (PLA) and recycled plastics (rPET), commonly used in packaging and car components, comply with environmental regulations.
3.Does material cost have a big impact on injection molding production?
Material costs directly affect production costs. Reasonable material selection can reduce costs by 30%, but performance and process requirements must be taken into account.
4.How do material properties affect product quality?
The quality of the material properties directly affects the quality of the products. For example, PA has high strength and abrasion resistance, whereas PC is transparent and heat resistant. It is easy to crack, deform or corrode due to Improper material selection, which determines the service life and safety of the product.