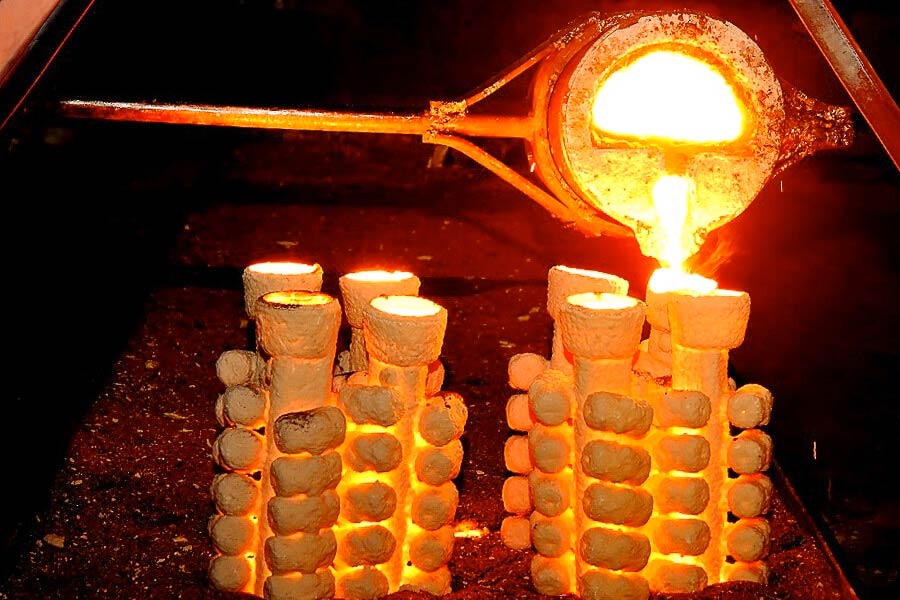
Metal casting is a common method used in the production process to produce parts by melting metal and pouring it into a mold. Common casting methods are sand casting, die casting, and investment casting. Sand casting is inexpensive and suitable for mass production, and die casting is high-precision and suitable for components with complex shapes.
In recent years, the jet cooling light metal casting industry has developed rapidly. This process of metal casting utilizes the employment of high-speed airflow to accelerate cooling, with the effect being the improvement of casting strength, as well as surface quality. All these casting processes have their own characteristics, and the selection has to be made based on material, performance, and cost factors. This understanding of the processes will help in the future to optimize production process and product quality.
What are the common metal casting processes?
1.Sand casting
Sand casting is one of the most common metal casting operations. It uses sand as a mold and is suitable for large or complex-shaped components. It is often used to manufacture large parts such as bases for machine tools and engine blocks. The casting can range from a few kilograms to hundreds of tons in weight. Sand casting equipment is simple and low-cost, with high surface roughness and medium precision. Sand casting molds are often used only once.
2.High-pressure casting
High-pressure casting is another important metal casting operations. It pushes the molten metal into the metal mold under high pressure (normally 10-200MPa). The advantages of high-pressure casting are high productivity, fast molding speed (filling time 0.01-0.2 seconds), part surface smooth and precise size. The disadvantage is high cost of mold and it is suitable for mass production. High-pressure casting is extensively used for alloys such as aluminum and zinc. It is widely used in automotive parts (e.g., gearbox housing) and 3C product housing, and the pressure is usually 50-150MPa.
3.Low-pressure casting
The casting pressure of low-pressure casting is low (usually 0.01-0.05MPa). It forces the molten metal in the bottom to flow into the mold. Low-pressure casting has the benefit of high metal utilization and less pores, which is utilized to manufacture components with higher quality requirements. The disadvantage is that the filling is slow (about 1-10 seconds), and the production efficiency is not as good as high-pressure casting.
4.Investment casting
Investment casting is also known as lost wax casting. It first makes a model in wax, then covers it with refractory material, and finally heats it to let the wax melt and flow out. The advantages of investment casting are high precision, good surface quality, and can be applied to parts that have complex shapes. The disadvantages are high cost and long production cycle. It is used mainly for small high-accuracy castings such as aerospace blades and medical instruments, and the weight of the casting usually does not surpass 50kg.
5.Die casting
Die casting is a type of high-pressure casting, yet it typically refers to the rapid prototyping of non-ferrous metals. It uses metal molds and higher pressures (up to 100MPa or higher). The advantages of die casting are extremely high production efficiency ( hundreds of pieces per hour are possible) and suitable for thin-walled parts (wall thickness can be as small as 0.5mm). The disadvantage is that it can only be used for low-melting point metals such as aluminum, magnesium, zinc, etc., and the mold is expensive.
What are the major process flows of furnace metal casting?
1.Metal smelting
This is the first step of furnace metal casting. Metal raw materials (aluminum, iron, copper, etc.) are placed in a furnace and heated at high temperature until completely melted. The melting point differs according to the type of metal, such as, aluminum melts at around 660°C, while iron requires about 1538°C.
Key points:
- Temperature has a direct impact on the quality of molten metal and requires real-time control to avert oxidation or gas mixing.
- Choice of type of smelting furnace: Electric arc furnace for metal with a high melting point (e.g. steel), and gas furnace for metal with a low melting point such as aluminum alloy.
2.Melt treatment
Purify the molten metal. Remove impurities and gases to improve the quality of the metal. Some practices that are normally carried out are the introduction of refining agents, inert gas stirring or passing.
3.Mold preparation
Select the mold according to the casting process. Use sand molds for sand casting, metal molds for die casting; and ceramic molds for investment casting. The mold must be dry and clean so that it cannot affect the quality of the casting.
Key points:
- Sand molds are cheap to produce but are imprecise. Metal molds can be reused but need to be heat-resistant in design to withstand the high temperature of the molten metal.
- In furnace metal casting, a preheated mold prevents defects caused by excessive rapid cooling of the molten metal.
4.Pouring
The liquid metal in the furnace is poured into the mold cavity through a ladle or automatic conveying system. The pouring temperature and speed need to be well controlled. Too fast will cause bubbles, and too slow will lead to non-solidification of the metal.
Key points:
- Pouring temperature must be 50-100°C higher than the melting point of the metal (e.g. pouring temperature of aluminum alloy is about 700-750°C).
- The gate design affects the flow of molten metal, and pores or cold shut defects are to be avoided.
5.Cooling and solidification
The metal is left to cool in the mold naturally to create a solid casting. The time it takes to cool will depend on the size of the casting and the metal. The larger castings will take a few hours. The rate at which it cools must be regulated. Too fast will make it brittle, and too slow will be ineffective.
6.Demolding and cleaning
After the casting is solid, it is removed from the mold. Sand casting requires the mold to be broken, whereas metal molds can be reused. The surface of the casting may be with burrs or residual sand, and the metal molds may be reused once they have been cleaned.
7.Post-processing
The casting may require going through other processes such as cutting, grinding, and heat treatment, etc., for improving accuracy and performance.

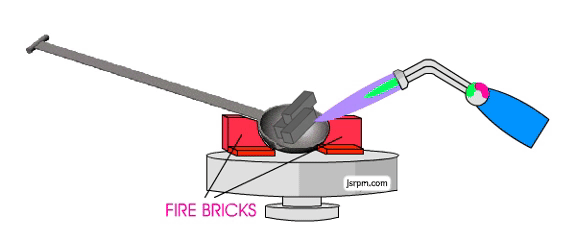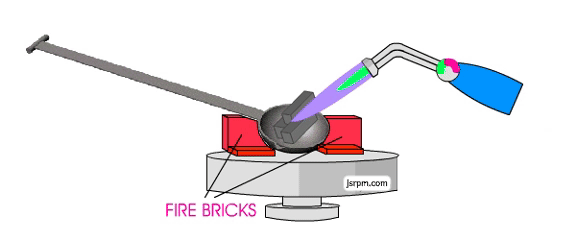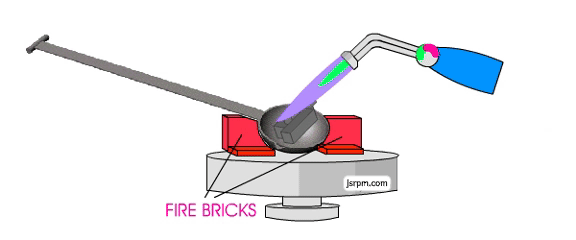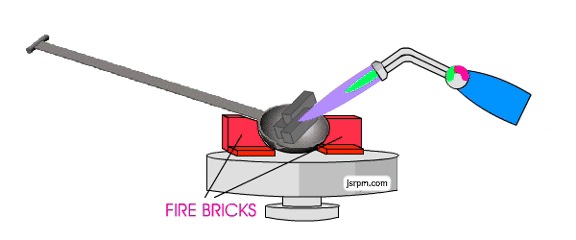
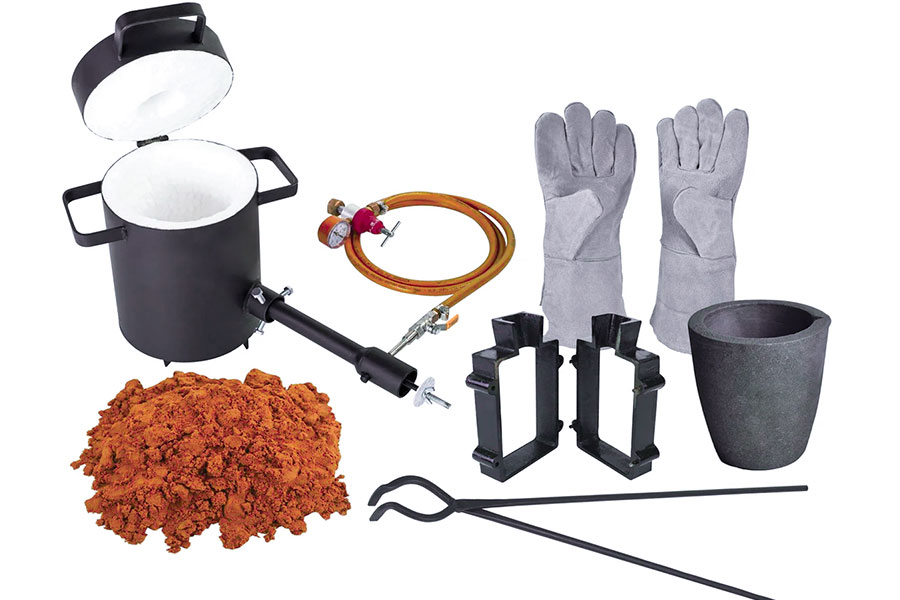
How to use plaster molds to achieve simple aluminum casting?
1.Prepare materials and tools
Materials:
Gypsum powder (best is refractory gypsum).
Water (mixing ratio of gypsum to water is about 1: 1.3).
Aluminum materials (aluminum trash cans, aluminum blocks, etc. for smelting).
Tools:
Smelting container (cast iron crucible or steel tank with a thick wall).
Heat source (propane spray gun, small furnace).
Mold prototype (can be wax, wood or 3D printed model).
Protective equipment (goggles, masks, high heat-resistant gloves).
Safety protection is the initial operation of DIY metal casting aluminum, and protection equipment must be worn.
2.Make a plaster mold
Make a prototype:
Carve out the desired aluminum form (e.g., keychain or small statue) using wax or wood.
The prototype must be smooth in texture and not contain any sharp edges (to prevent cracking upon demolding).
Prepare the plaster slurry:
Slowly add the plaster powder to the water and mix until it becomes a paste that is thick with no particles.
Plaster slurry should be applied within 10 minutes (it dries faster).
Casting the plaster mold:
Position the prototype in a container and pour over the plaster slurry to give the prototype a covering thickness of at least 2 cm.
Gently shake the container to eliminate air bubbles and allow it to stand for 1-2 hours to harden completely.
Dry the mold:
The plaster mold must be dried entirely (can dry naturally for 1-2 days, or be baked at temperature 100°C for 4 hours).
After drying out, remove the mold from the prototype and retain the cavity to be casted.
In DIY metal casting aluminum, the plaster mold must be dry entirely, otherwise it will burst when facing hot-temperature aluminum liquid.
3.Melting and pouring aluminum liquid
Melting aluminum material:
- Put the scrap aluminum into the crucible and melt it to 660-700°C using a propane torch or furnace (the melting point of aluminum is about 660°C).
- When the aluminum liquid develops a silvery white color, stir it with a steel rod to remove impurities.
- Preheating of the mold: Put the plaster mold into the oven and warm it to a temperature of 150-200°C (for reducing defects created due to fast cooling of aluminum liquid).
Filling of aluminum liquid:
- Take the crucible in a tongs crucible and fill slowly the aluminum liquid into the cavity of the mold not to splatter.
- Regulate the hands while filling and make sure aluminum liquid flows through all the corners.
In alumalloy metal casting, pouring speed needs to be maintained slow to avoid bubbles.
4.Cooling and post-processing
- Natural cooling: After pouring, leave it to stand for 20-30 minutes until the aluminum liquid solidifies fully (the exterior temperature of the mold falls below 50°C).
- Demolding and stripping off the casting: Carefully tap open the plaster mold and strip off the aluminum parts (plaster is brittle and has a low reuse rate).
- Cleaning and polishing: File or sand off burrs and rough surfaces.
- Polishing surface: Grind smooth with fine sand or electric grinder.
Aluminum products heat-transfer rapidly, therefore avoid coming into direct contact with cold water during cooling (to prevent deformation or cracking).

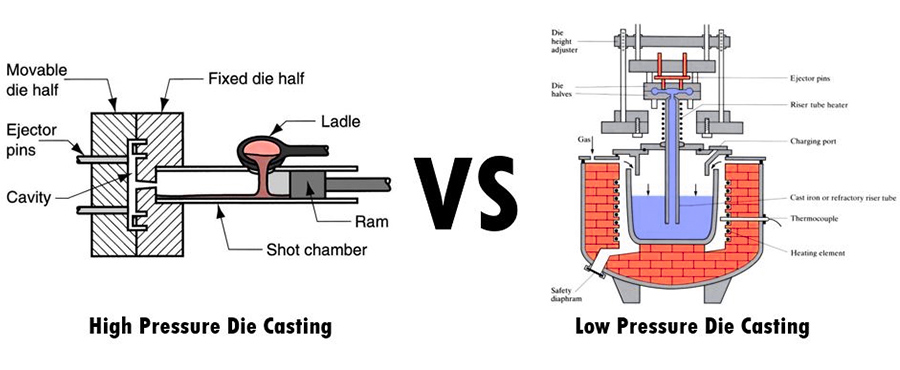
What are the process parameters differences between high-pressure casting and low-pressure casting?
Low-pressure casting and high-pressure casting are two mainstream processings in aluminum metal casting:
1.Core process parameter comparison
| Parameters | Low-pressure casting (LPDC) | High-pressure casting (HPDC) |
| Filling pressure | 0.5~5 bar (lower pressure). | 70~1000 bar (Ultra High Pressure). |
| Charging speed | 0.5~2 m/s (slow filling). | 5~15 m/s (high speed filling). |
| Mold temperature | 200~300℃ (lower temperature). | 250~400°C (high temperature). |
| Casting wall thickness | 2-8 mm (uniform wall thickness). | 0.5~4 mm (thin-walled complex parts). |
| Mold lifespan | 50,000~200,000 times (low mold wear). | 100,000~500,000 times (high mold loss). |
| Typical application | Structural components such as car wheels and engine cylinders. | Lightweight thin-walled parts such as cell phone shells and automobile coverings. |
2.Technical applicability of JS
JS Precision Manufacturing combines low-pressure and high-pressure techniques extensively in the field of aluminum-magnesium alloy casting, relying on the following technical capabilities to meet the requirements of high-end customers:
High-precision control:
JS employs a closed-loop pressure control system to adjust the fluctuation of the filling pressure of low-pressure casting to ±0.5%, and adopts hot mold correction technology to achieve casting dimensional accuracy of ±0.02mm, exceeding industry standards (±0.05mm). Its high-pressure casting equipment is also equipped with a real-time pressure monitoring system to ensure the thin-walled part filling uniformity, and has been implemented in a successful project of a new energy vehicle battery pack shell.
Material adaptability:
In low-pressure casting of aluminum-magnesium alloy, JS has developed a special coating system to enhance the mold life of low-pressure casting to 1.5 times the industry average (up to 300,000 times). At the same time, with the optimization of the injection curve in high-pressure casting, the rate of sticking is controlled below 0.3%. Recent cases show that the tensile strength of its aluminum-magnesium alloy wheel hub has increased by 12%, and the elongation has been over 8%.
Green Manufacturing:
We uses an inert gas protection device in low-pressure casting to reduce oxide inclusions by 20%. The high-pressure casting machine utilizes a waste heat recovery system to reduce unit energy consumption by 18%. Both processes follow ISO 14001 environmental certification, which aligns with ours green casting policy.
Quick response:
With the help of digital simulation technology, JS shortened the development cycle time for low-pressure casting molds by 60% of the traditional model and improved process parameters for high-pressure casting by 40%. Recently, we developed a shaped bracket for an aerospace customer, and it took only 28 days from design to delivery of the first piece, which is 35% faster than the industry average.
3.Process selection strategy
| Scenario Requirements | Recommended processes | JS technical support |
| Require high strength/complex internal cavity structure | Low pressure casting | Hot top gating + step pressurization technology. |
| Pursuit of lightweight/high-volume production | High pressure casting | Multi-point pressure injection + vacuum exhaust system. |
| Material utilization sensitive projects | Low pressure casting (anti-gravity mode) | Adaptive liquid level control system, scrap rate<8%. |
| High value-added precision parts | High pressure casting + Localized extrusion | Real-time pressure, speed double closed-loop adjustment, surface roughness Ra<0.8μm. |
What are the differences between die casting and sand casting?
1.Type and material of the mold
- Die casting: Reusable metal molds (e.g. steel or aluminum alloy) are utilized, and mold life is long, which is suitable for high-precision complex structures. For example, the knife mold for metal casting used by JS for die casting is precision tool parts, and high-hardness mold materials (e.g. H13 steel) are used to ensure molding stability and surface finish.
- Sand casting: Through the use of disposable sand molds, low accuracy but inexpensive, suitable for single or large part production. JS enhances the process by digital sand mold design and shortens the development cycle.
2.Production efficiency and cost
- Die casting: High initial mold cost, but suitable for mass production (e.g. automotive parts). JS achieves daily production capacity of thousands of pieces by automated production lines.
- Sand casting: Low mold cost, but long production time for a single piece, suitable for small batches or making prototypes.
3.Precision and surface quality
- Die casting: Tolerance can reach ±0.005mm (JS company technical standard), surface roughness Ra≤1.6μm, especially suitable for knife mold for metal casting needed edge sharpness and size consistency.
- Sand casting: General tolerance ±0.5mm, surface roughness Ra ≥12.5μm, requires follow-up processing.
4.Application scenarios
- Die casting: High complexity, thin-walled parts (e.g. electronic housing, tools), JS company adds multi-material compatibility (aluminum/zinc/ magnesium alloys) for meeting light-weighting requirements.
- Sand casting: Large components (e.g. machine tool bases), one-piece customization or low-complexity parts.
Summary
Sand casting, die casting, investment casting, centrifugal casting, and other technologies in metal casting together constitute the core technology system of the manufacturing industry. Sand casting has become the preferred solution for big structural parts with its low cost and versatility, and die casting provides a high-precision solution for thin-wall complex components on the basis of high-pressure rapid prototyping technology.
In recent years, with the growing demand for green and light manufacturing, new processes such as jet cooling technology and moldless casting have emerged one after another, further expanding the boundaries of casting technology. At the metal casting company where you work, you need to achieve a double breakthrough in yield improvement and energy saving. Send us your specific demand documents, and we will provide metal casting services to you within a short time. JS's technical accumulation and engineering capabilities can provide you with key support.
Disclaimer
The content on this page is for general reference only. JS Series makes no express or implied warranties regarding the accuracy, timeliness, or applicability of the information provided. Users should not assume that the product specifications, technical parameters, performance indicators, or quality commitments of third-party suppliers are completely consistent with the content displayed on this platform. The specific design feature, material standards, and process requirements of the product should be based on the actual order agreement. It is recommended that the purchaser proactively request a formal quotation and verify product details before the transaction. For further confirmation, please contact our customer service team for professional support.
JS Team
JS is an industry leading provider of customized manufacturing services, dedicated to providing customers with high-precision and high-efficiency one-stop manufacturing solutions. With over 20 years of industry experience, we have successfully provided professional CNC machining, sheet metal manufacturing, 3D printing, injection molding, metal stamping and other services to more than 5000 enterprises, covering multiple fields such as aerospace, medical, automotive, electronics, etc.
We have a modern factory certified with ISO 9001:2015, equipped with over 100 advanced five axis machining centers to ensure that every product meets the highest quality standards. Our service network covers over 150 countries worldwide, providing 24-hour rapid response for both small-scale trial production and large-scale production, ensuring efficient progress of your project.
Choosing JS Team means choosing manufacturing partners with excellent quality, precise delivery, and trustworthiness.
For more information, please visit the official website: jsrpm.com
FAQs
1.What is metal casting?
Metal casting involves pouring liquid metal into a mold and letting it cool to obtain the desired shape. Metal casting is employed for making complex or large parts, such as engine parts, industrial tools, etc., with both productive efficiency and economic advantages.
2.What are the advantages of investment casting?
Investment casting (lost wax process) uses disposable wax mold to achieve high-precision complex parts molding with a surface finish of up to Ra1.6μm, and can be used for processing difficult-to-machine materials such as titanium alloy. It is especially suitable for producing small lots of precision components in aerospace, medical, and other fields.
3.How fast is high-pressure casting?
High-pressure casting can fill molds with a maximum speed of 20-60 m/s, and can fill complex molds in 0.02-0.2 seconds. It is suitable for thin-walled parts (e.g. car cylinder blocks), and one cycle takes about 30-90 seconds, taking into account both precision and productivity.
4.Is DIY casting safe?
Do-it-yourself casting is dangerous with potential for high heat and metal splashing, requires rigorous protection (goggles, gloves, ventilation), and makes it impossible to use wet material or molds. It is safely possible under regular operation, but professional guidelines must be followed.
Resource