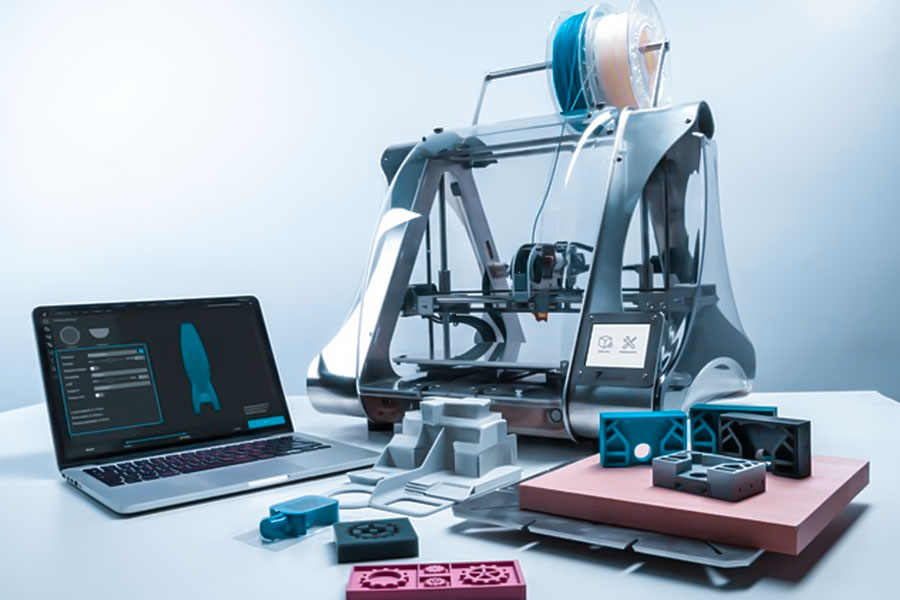
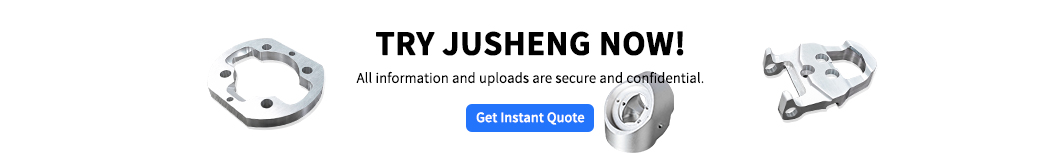
Quais são os tipos de tecnologias de impressão 3D?
1.fused modelagem de deposição (fdm)
- princípio: moldagem por deposição fundida, aquecendo a camada de fibra plástica por extrusão de camada.
- Recursos: baixo custo, Adequado para o protótipo rápido , o processo de produção eficiente do JS otimize.
2.tereolitography (sla)
- princípio: tecnologia de cura UV, a resina líquida é formada pela cura UV.
- Recursos: alta precisão (± 0,05 mm), superfície lisa, adequada para estruturas complexas, atende aos requisitos de fabricação de precisão de JS.
- como funciona: pó de nylon sinterizado a laser não requer estrutura de suporte.
- Recursos: Alta resistência, adequada para partes funcionais, a compatibilidade de material/composto de JS pode expandir sua faixa de aplicação.
- como funciona: fusão de leito a jato de a jato de tinta, solidificando o pó de nylon por camada por meio de fusão e aquecimento infravermelho.
- Features: High speed (3 times faster than SLS), high detail (±0.08mm), support for mass production of functional components, and the ability to adapt to JS Para produção rápida e otimização de custos.
5. data-pos = "2" data-len = "30" data-v-7b79c893 = ""> fusão seletiva a laser (slm)
- como funciona: fusão a laser em pó de metal para fabricação de ponta.
- Recursos: alta precisão (± 0,02 mm), alta resistência à temperatura, a tecnologia de usinagem de precisão da JS pode melhorar ainda mais a qualidade do produto.
src = "https://jsrpm.com/webSite_img/i/2025/04/24/ssmkx6-2.jpg" alt = "tipos de tecnologias de impressão 3D" width = "900" Height = "600">
Tipo de técnica
velocidade
custo
tipo de material
capacidade de processamento de complexidade
vantagens associadas da empresa js
fdm
médio
Low
plásticos como PLA e Abs.
★★★ ☆
Velocidade de otimização do processo de produção eficiente.
sla
rápido (dlp)
centro
resina fotossensível.
★★★★ ☆
JS ± 0,005 mm de alta precisão de alta precisão.
sls
médio
centro
nylon, tpu e outros pós.
★★★★ ☆
suportando a expansão de aplicações de metal/composto.
mjf
extremamente rápido
médio-alto
nylon (PA12/PA11).
★★★★★
Melhoria da eficiência da produção em lote para entrega rápida.
slm
lento
Tall
metal em pó (titânio, aço inoxidável).
★★★★★
Tecnologia de usinagem de precisão garante alta complexidade das peças.
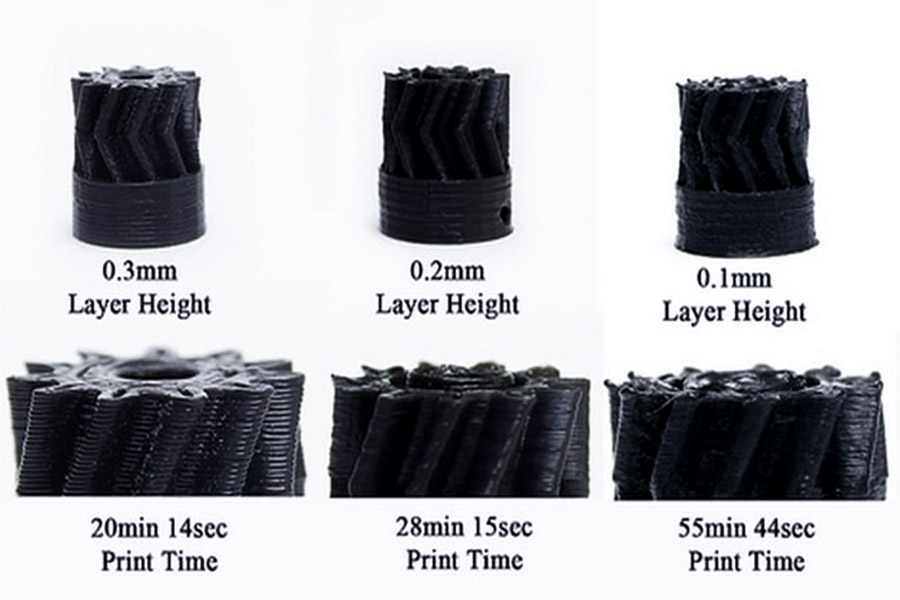
Qual é o efeito da espessura da camada de impressão FDM na força?
1. mais espessa a camada, quanto mais fraca a adesão intercalante
- na impressão FDM, cada camada de plástico fundido precisa ser completamente ligado à camada anterior.
- sugestão de otimização: a empresa JS padrão é uma fina espessura da camada de 0,1-0.2mm no serviço de impressão para Área de contato entre camadas.
2. mais espessa a camada, a estrutura densa
- menor espessura da camada, como 0,05 mm, reduz a lacuna entre as camadas, tornando a superfície mais suave e a estrutura interna mais uniforme.
- js caso: Durante a impressão Serviço de peças aeroespaciais, JS controla a espessura da camada de impressão o nível do micrômetro para garantir que os componentes atendam aos padrões de força aeroespacial.
equilíbrio entre a espessura da camada e as propriedades do material 1. Camadas do chão salvar material, mas sacrificar força 2. camadas finas adicionam força, mas levam mais tempo para imprimir seleção de espessura da camada em aplicações reais 1. Peças funcionais vs. Exibir peças 2. Adaptação da propriedade de material

Quais parâmetros determinam a resolução de impressão do SLA?
1. tipo de fonte de luz e tamanho de mancha
- Fonte de luz do laser: o diâmetro do ponto é geralmente de 10 a 100 mícrons, adequado para jóias, odontologia e outros modelos li-li-cish = https://jsrpm.com/3d-printing "> href =" Href = "https://jsrpm.com/3d-printing"> li-li- li-cys.
- Fonte de luz DLP: Uma mancha de luz é projetada através de um projetor digital e o tamanho do pixel determina a resolução (por exemplo, 50-100 mícrons para projeção 2K/4K).
- impacto: quanto menor o tamanho da mancha, melhor os detalhes do eixo x/y, mas o tempo de impressão pode aumentar.
- Fonte de luz DLP: Uma mancha de luz é projetada através de um projetor digital e o tamanho do pixel determina a resolução (por exemplo, 50-100 mícrons para projeção 2K/4K).
- Quanto mais lenta a velocidade de varredura, maior a energia de exposição por unidade de área, mais profunda a cura; Se a varredura for muito rápida, a cura pode estar incompleta.
- direção de otimização: ajuste dinâmico da velocidade de varredura (por exemplo, redução da velocidade de varredura de detalhes) com base na complexidade do modelo.
-
A espessura da camada varia de 25 a 100 microns. - por exemplo, 50 mícrons para protótipo rápido e 25 microns para peças de precisão.
5. data-translateid="4182065a6f414abb77c054c39fa7ebeb" data-pos="3" data-len="25" data-v-7b79c893="">Model geometry complexity Comparação de parâmetros e tabela de sugestões de otimização By properly selecting parameter combinations, the 3D printing model can achieve precise manufacturing from concept verification to functional prototypes. 1.3D printing of metallic materials (high temperature environment preferred) SLM/DMLS (selective laser melting/sintering) 2.Ceramic 3D printing technology (ultra-high temperature resistance potential) SLA/DLP (light-curing ceramics) 3.High-Performance engineering plastic 3D Printing FDM (Molten deposition modeling) SLS (selective laser sintering) Technology selection recommendations for high temperature scenarios Ink jet printing technology is by layering liquid material on top of each other to create three-dimensional objects. Its core lies in high high-precision jetting and curing control. Specific implementation steps and key technologies are as follows: 1.Preparation of materials: Adaptation of liquid media 2.Ink jet print head: Precision droplet injection Piezoelectric drive or thermal foaming technology: 3.Layer by layer stacking: droplet solidification molding 4.Post-treatment: enhancement and surface optimization 1.Structural adaptation principle Overhang structure (>45°): Bridge structure (long span): 2.Matching and separation of materials Easy peel combination: Chemical dissolution combination: ABS+HIPS: Lemonin is needed to dissolve the scaffold and is suitable for complex internal parts such as gear components. 3.Actual performance requirements 4.Post-treatment efficiency Quick removal: Environmental Protection Plan: It is advisable to select biodegradable scaffolds (e.g. PBDE-based biodegradable materials) to reduce waste liquid treatment costs. 5.Printer adaptation FDM equipment: SLA/DLP equipment: 1.Multi-material printing technology support JS's 3D printing services include MJF and composite metal/ceramic printing technologies, which can switch different materials (e.g. metal-ceramic, carbide-polymer) during the same printing process to achieve continuous or segmented gradient changes in material composition. 2.Material compatibility and gradient design Through JS's 3D printing services, customers can choose from a variety of material combinations, including metals, ceramics and composites, and freely design the microstructure of functional gradient components (such as abrasionresistant + substrate layer). 3.Process optimization and performance assurance JS's industrial-grade equipment supports thickness control (±0.005mm) and temperature management to ensure uniform interface bonding strength and gradient transition across different materials and meet extreme working conditions such as high temperature and pressure. 4.Customized solutions For areas such as aerospace and medical devices, JS's team can provide a full range of services, from material selection and gradient structure design to reprocessing, such as: As a disruptive technology, 3dprinting continues to drive change in manufacturing with its diverse process types (e.g. FDM, SLA, metal printing, etc.) and a wide range of application scenarios (from industrial manufacturing to medical innovation). Whether it is the efficient production of complex functionally gradient parts or the rapid iteration of custom models, 3D printing services demonstrate irreplaceable flexibility and economy. Technology service providers represented by JS have further lowered the technology threshold by integrating multi-material printing, precision process control and industry-wide chain support, allowing businesses to focus on design innovation and value creation. The content on this page is for general reference only. JS Series makes no express or implied warranties regarding the accuracy, timeliness, or applicability of the information provided. Users should not assume that the product specifications, technical parameters, performance indicators, or quality commitments of third-party suppliers are completely consistent with the content displayed on this platform. The specific design feature, material standards, and process requirements of the product should be based on the actual order agreement. It is recommended that the purchaser proactively request a formal quotation and verify product details before the transaction. For further confirmation, please contact our customer service team for professional support. JS is an industry leading provider of customized manufacturing services, dedicated to providing customers with high-precision and high-efficiency one-stop manufacturing solutions. With over 20 years of industry experience, we have successfully provided professional CNC machining, sheet metal manufacturing, 3D printing, injection molding, metal stamping and other services to more than 5000 enterprises, covering multiple fields such as aerospace, medical, automotive, electronics, etc. We have a modern factory certified with ISO 9001:2015, equipped with over 100 advanced five axis machining centers to ensure that every product meets the highest quality standards. Our service network covers over 150 countries worldwide, providing 24-hour rapid response for both small-scale trial production and large-scale production, ensuring efficient progress of your project. Choosing JS Team means choosing manufacturing partners with excellent quality, precise delivery, and trustworthiness. 1.Does SLS printing require support? SLS printing usually does not require support. The unsintered nylon powder will naturally envelop the model to avoid collapsing in the air. Only a few complex designs require a small amount of ancillary support, which greatly simplifies the reprocessing process. 2.Which technology is suitable for printing transparent parts? SLA technology is suitable for printing transparent parts. It uses photosensitive resin that hardens under UV luz. The surface is smooth and transparent. Suitable for making high precision transparent model (such as optical parts). 3.What does the layer thickness of FDM affect? The thickness of FDM layer influences surface smoothness, printing time and printing strength. The thicker the layer, the more visible the pattern, the faster the printing, but the intensity may be reduced. 4.How big a part can 3D printing make? Industrial-grade 3D-printing devices can manufacture large parts of meters (such as aerospace parts), while desktop devices are usually limited to a few dozen centimeters and are suitable for small models or prototypes.
parâmetros
impacto na resolução
direção de otimização
valor típico
tipo de fonte de luz
laser> dlp (o laser tem maior precisão na mesma resolução).
Escolha o laser para modelos de precisão e DLP para produção em massa.
laser: 50μm / dlp: 100μm
tamanho de ponto
menor o local, mais claros os detalhes.
Use cabeças a laser de alta precisão ou projeção 4K DLP.
50μm (laser)
Scanning speed
The slower the speed, the more complete the curing.
Reduce speed in fine areas (e.g. 0.1mm/s) and speed up in large areas.
50-200mm/s
Layer thickness
The layer thickness is halved and the Z-axis resolution is increased by 4 times.
Use thin layers (25μm) for precision parts and thick layers (100μm) for speed increase.
50μm (standard)
Resin viscosity
Low viscosity improves fluidity and detail filling ability.
Use special resins (e.g. transparent resins with viscosity ≤1500cP).
500-2000cP
Model overhang angle
If the angle is too small, dense support is required, and blocking the light affects the curing.
Avoid <45° overhangs or add auxiliary supports in the design.
≥60° (unsupported)
Which printing technology is more stable in high temperature environments?
Scene temperature
Recommended Technology
Core advantages
Key capabilities of printing shops
600-1000℃
Metal SLM/DMLS.
High strength and creep resistance.
Laser equipment, vacuum environment, heat treatment.
1000-1500℃
Ceramic SLA/DLP.
Ultra high temperature resistance and corrosion resistance.
Specialized ceramic materials and high-temperature sintering process.
200-600℃
PEEK FDM, Nylon SLS.
Economy and lightweight.
Industrial grade equipment and material modification.
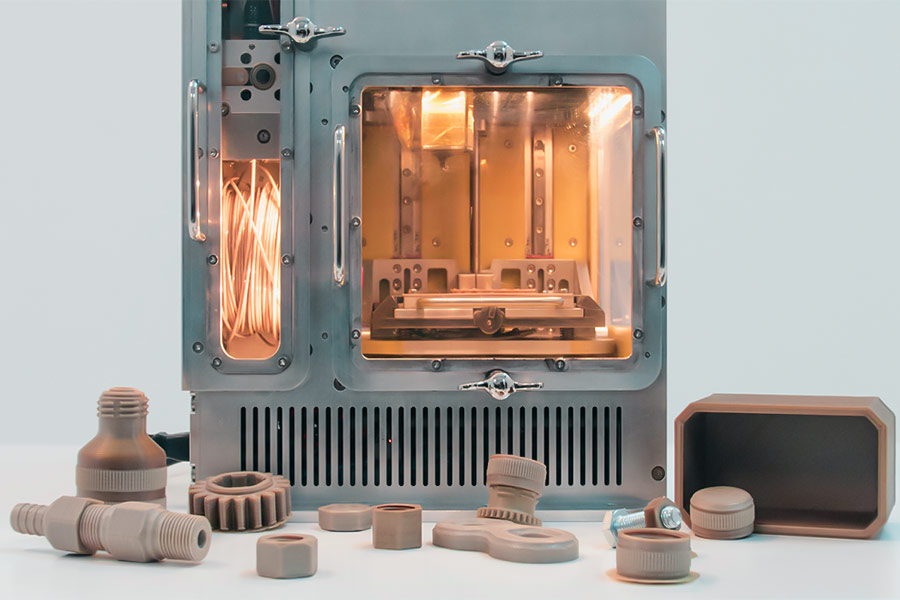
How to achieve layered stacking in 3D ink jet printing?
How to choose supporting materials for complex 3D printing models?
Can JS achieve functionally graded components through multi material 3D printing?
Summary
Disclaimer
JS Team
For more information, please visit the official website: jsrpm.comFAQs
Resources