In today's global digital wave, the prototyping meaning has evolved from simple concept validation to the gain and loss of driving innovation. Rapid prototyping effectively constructs prototype models and translates product concepts into physical or digital forms, allowing the team to validate technical feasibility and market demand at an early stage.
From interactive interface testing in consumer electronics to performance validation of components for new energy vehicles, prototyped samples are reshaping manufacturing's the R&D logic. Businesses can use prototyping model to capture user pain points in advance, complete at least 5 iterations of optimization before product finalization, and improve the market fit of the final product by over 60%.
What is rapid prototyping?
Rapid prototyping is a method to quickly construct physical models or functional prototypes of products based on computer-aided design (CAD) data and advanced manufacturing technologies. 3D printing, CNC machining, silicone replication are commonly used, and materials (e.g. plastics, metals, etc.) and processes (e.g. photopolymerization, melt deposition, laser sintering, etc.) can be selected flexibly according to different needs. Its advantages include shorter product development and lower verification costs, as well as helping teams achieve early inspection functionality and user experience that accelerate product iteration and optimization and reduce production risks.
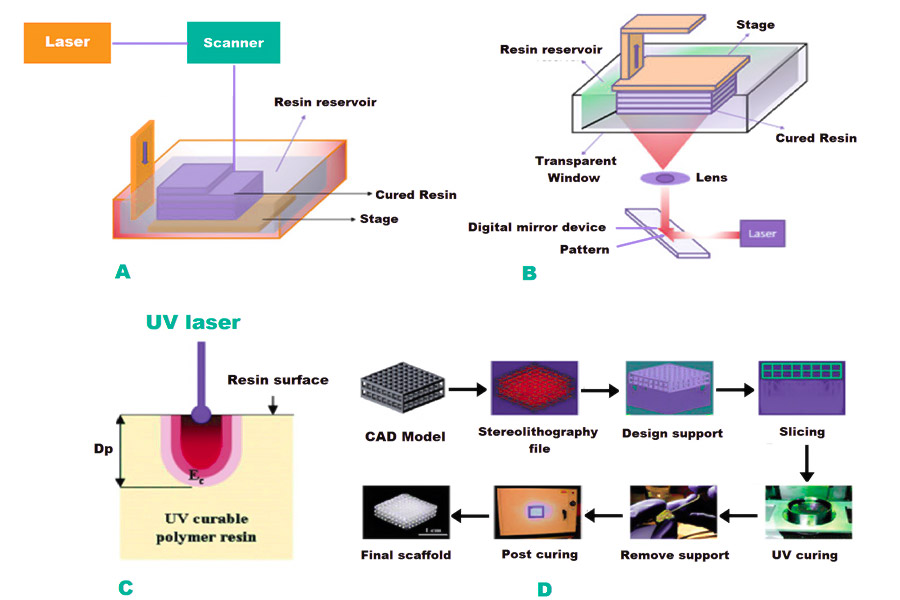
What are the technical paths for rapid prototyping?
1.3D printing technology (SLA/SLS/FDM)
Technical features:
- SLA(Stereolithography Apparatus): Liquid resin cured by laser, suitable for high precision and complex geometric structures such as jewelry and dental models.
- SLS (Selective Laser Sintering): Powder materials (nylon, metal) are formed by laser melting and are suitable for functional testing.
- FDM (fused deposition modeling): Hot melt is a kind of layered extrusion molding, low cost, fast speed, suitable for concept verification.
JS technology association:
JS supports the upload of uploading STL files with 3D printing to meet ±0.005mm precision requirements. In many cases, medical equipment and precision components use this technology for rapid delivery (1-2 weeks).
2.CNC precision machining
Technical features:
High-rigidity prototypes are achieved by cutting metal materials (aluminum, steel, titanium alloys) or plastics. Supports complex surface processing with high material utilization.
JS technology association:
JS's CNC equipment can handle STEP/IGES files with metal prototype accuracy ±0.005mm for automotive and aviation fields applications.
3.SLM Metal 3D Printing
Technical features: Metal laser direct melting, manufacturing high strength, lightweight metal components. Suitable for high-demand scenarios such as aerospace and medical implants.
JS technology association: With more than 50 materials processing experiences, JS can meet customer demand for high temperature and corrosion resistant components, helping some automotive customers shorten their R&D lead times by 15%.
4.Injection molding
Technical features: 3D printing or numerical control is used to make injection molds quickly, shortening the development cycle of traditional molds. Suitable for medium batch production (500-5000 pieces).
JS technology correlation: By combining CNC and 3D printing technology to achieve rapid mold manufacturing, industrial customers have reduced their lead time by 40%.
JS company through CNC machining, additive manufacturing, injection molding and other technologies, deep integration of a variety of materials. The introduction of rapid prototypes has resulted in a 15% reduction in the average project life of clients. JS's rapid prototyping service cover the entire process from concept design to functional verification and are particularly suited to project requirements that require high accuracy, efficiency and material performance.

What are the effects of different materials on rapid prototyping?
Effect of mechanical properties of materials on functional verification
1.Metal prototypes (e.g. aluminium and titanium alloys):
- Strengths: High strength, high temperature, corrosion resistance, suitable for prototypes requiring mechanical stress or complex working conditions (e.g. auto components, aerospace components, etc.).
- Challenge: It is difficult and costly to process and requires precision CNC or additive manufacturing techniques.
2.Plastic prototypes (e.g. ABS, nylon):
- Strengths: Low cost, light weight, easy to process, suitable for quick verification of appearance or simple functions (e.g. consumer electronics shell, toy prototypes).
- Limitations: poor heat resistance and rigidity, not suitable for high strength.
3.Composite materials (e.g. carbon fiber):
- Strengths: Light weight, high strength, suitable for high-end industrial or research prototypes (such as UAV structures).
- Challenge: High complexity of processing requires specialized equipment support.
Adaptability of material characteristics to processing process
1.Processability:
- Metal materials rely on high-precision CNC machine tools or laser cutting, processing cycle is long.
- Plastics and composites can be quickly molded using 3D printing techniques such as FDM/SLA, shortening the production cycle.
2.Surface accuracy:
- The tolerance of metal materials is ±0.005mm, suitable for precision assembly prototypes.
- The surface roughness of plastic prototypes is relatively high and requires to be polished or sprayed at a later stage.
Balance between material costs and lead times
- High-cost materials (e.g. titanium alloys): Prototype production costs have increased significantly, but they can directly mimic the performance of the final product and reduce the risk of repetition later.
- Low-cost materials (such as PLA plastics): Suitable for projects with limited budgets, but require a balance of precision and durability to meet requirements.
- Material supply stability: JS supports rapid procurement of more than 50 materials to ensure timely delivery of prototype materials and avoid delays.
Requirements for material reprocessing processes
- Metal prototyping: Need polishing, plating, anodic oxidation or other treatment to improve appearance or corrosion resistance.
- Plastic prototyping: Usually spray-painted, silk-screen printed or electroplated, with some materials requiring annealing to remove internal stress.
- Composites: Fiber exposure needs to be addressed to ensure a smooth surface.
Impact of material selection on sustainability
Naturally degradable plastics or recyclable metals, such as aluminium, can reduce environmental burden and are in line with green manufacturing trends. JS company reduces waste by 20% through material recycling technology.

What is the difference between Rapid Mockup and Rapid Prototyping?
1.Differences in core objectives
Rapid Mockup: A visual model used to construct the appearance, size, or interactive interface of a product design quickly. Its core objective is to verify aesthetic, human-machine interaction logic, or conceptual feasibility of the product design. Often not involving complex functional or physical performance tests, the focus is on providing intuitive form and operational experience. For example, prototype phone appearance and UI/UX interaction prototype.
Rapid Prototyping: Focuses on verifying product functionality, structural rationality, and technical feasibility through physical or digital models such as mechanical properties, assembly accuracy, or dynamic performance of mechanical components. It is necessary to simulate the actual use and test engineering indicators such as material strength and heat dissipation efficiency. For example, 3D-printed gear components and CNC machining electronic housing prototypes.
2.Technical means
| Dimension | Rapid Mockup | Rapid Prototyping |
| Tools/Technology | Manual modeling (clay, foam), 2D/3D modeling software (SketchUp, Figma). | CNC machining, 3D printing (SLA/FDM), silicone mold casting. |
| Material | Non functional materials (cardboard, plastic sheets, wood). | Functional materials (metals, engineering plastics, composite materials). |
| Complexity | Low (only appearance or basic structure). | High (to meet mechanical, thermal and other performance requirements). |
3.Application stage
| Stage | Rapid Mockup | Rapid Prototyping |
| Early-stage | ✔️ Concept validation (e.g. product styling review). | ❌ Usually after Mockup. |
| Midium-stage | ❌ | ✔️Functional testing (e.g. buttons and waterproofing). |
| Later-stage | ❌ | ✔️Small batch trial production (e.g. final confirmation before production). |
The core difference between a Rapid Mockup and a Rapid prototype is the target phase and application phases. The Mockup is quickly conceptualized through low-cost materials and is suitable for early design review. Rapid prototyping, which verifies core structural strength and assembly accuracy through precision manufacturing, is commonly used for intermediate testing and mass production preparation.
How to match suitable processing techniques in rapid prototyping?
1.Clarify requirements and objectives
First, the purpose of the prototype (such as functional testing, appearance display or structural verification) needs to be determined, as well as the requirements for accuracy, strength, surface quality, etc. For example, rapid prototype can prioritize 3D printing (such as FDM or SLS) if rapid verification of a mechanical structure is required, or CNC machining or silicone replication if high-precision appearance models are required.
2.Material compatibility Analysis
Process selection is based on the characteristics of the prototype material, such as high temperature resistance, flexibility or electrical conductivity. For example, metal parts require selective laser melting (SLM), while transparent parts can be made using resin photopolymerization (SLA) or CNC cutting.
3.Process matching principles
- Complex structure: Priority is given to adding manufacturing (3D printing), such as PolyJet, to achieve multi-material mixing.
- Mass Rapid Iteration: Combining CNC and 3D printing hybrid technology to balance efficiency and economy.
- Small batch production: Vacuum replication or laser sintering (SLS) balances cost and delivery cycle.
4.Cost and time balance
Low-complexity prototypes can use low-cost processes (such as desktop FDM), while high-precision requirements require investment in industrial-grade equipment (such as five axis CNC). At the same time, it is necessary to assess post-treatment time, such as the need for cleaning and secondary curing of SLA.
5.Technical validation and iteration
The feasibility of the design is verified by rapid sampling and the process parameters are adjusted according to the test results. For example, metal casting prototypes require multiple adjustments to the mold, while 3D printing can quickly modify model files.
6.Technology integration and automation
Combining CAD/CAM software to optimize processes such as topologically optimized CNC machining paths directly generated, or AI algorithms to predict 3D printing the deformation and compensate in advance.
Will Rapid prototyping replace traditional engineering design thinking?
The core value of traditional engineering design is irreplaceable
1.Systematic design framework:
Traditional engineering follows a systematic process of requirements analysis, conceptual design, detailed design, and verification testing to ensure the integrity and reliability of the product from concept to implementation. For example, car airbags must be designed in strict compliance with collision testing standards, and rapid prototyping alone cannot replace rigorous simulation and verification.
2.Risk control capability:
Traditional engineering avoids design defects through multiple rounds of reviews, fail-pattern analysis (FMEA), and other processes, while relying solely on rapid iterations can lead to key issues (such as compliance risks for medical devices) being overlooked.
Rapid prototyping overcomes limitations of traditional engineering
1.Accelerated validation and iteration:
Rapid prototyping shorten the validation process from a few weeks to a few days by quickly creating physical or digital models.
2.Reducing trial and error costs:
In traditional engineering, design errors can lead to higher die scrap costs; waste of resources can be avoided by pre-verifying low-cost prototypes,such as FDM plastic parts. JS company has helped customers detect structural strength issues through prototype testing, saving 30% on late rework costs.
Synergistic application scenarios for both
| Stage | Traditional engineering design | Rapid prototyping |
| Concept validation | Requirement documents, sketches, preliminary simulations. | Handmade models, low-cost 3D-printed parts. |
| Functional verification | Detailed design, engineering drawings and testing of key components. | CNC machining prototype, silicone mold casting. |
| Mass production preparation | Full size inspection, process curing, supplier audit. | Small batch trial production production, material certification. |
Rapid prototyping is an accelerator, not a substitute for conventional engineering thinking. It helps engineers validate innovative ideas faster by shortening iteration cycles and reducing trial and error costs, but core design logic, safety standards, and system processes still rely on traditional engineering thinking. The combination of the two is the key to efficient innovation and reliable implementation in modern manufacturing.

Why choose JS as your prototype partner?
1.Full chain rapid prototyping solution
- CNC precision machining: Supports ±0.005mm of ultra-precision tolerances and can process materials such as metals and plastics quickly to meet the structural and functional verification requirements of high-complexity prototypes.
- 3D printing: Compatible with FDM, SLA, SLS, Metal printing, and other technologies, enables rapid prototyping prototyping of complex internal structures or lightweight prototypes.
2.Rapid delivery and iteration capability
- Standardized process: From design to finished product in 1-2 weeks, emergency orders can be compressed to 3-5 days to speed up product launch.
- Digital collaboration: Supports online file upload, real-time progress tracking and remote collaboration to reduce communication delays.
- Quick feedback mechanism: Technical solutions and offers are provided within 24 hours, engineers are involved in design optimization and iteration costs reduced.
3.Precise investment and resource optimization
- Process intelligence matching: Recommended optimal process solutions through AI algorithms, saving an average of 20% in manufacturing costs.
- Small-batch trial production: 10-50 units can be produced at low-cost cost, avoiding the risk of large-scale production.
4.Quality reliability verification
- High-precision detection: Equipped with coordinate measuring instrument, spectrometer and other equipment to ensure that prototype size and material properties meet standards.
- Functional test support: It can simulate real working conditions (such as waterproofing, earthquake resistance, temperature resistance) to verify the reliability of the prototype.
- Compliance assurance: Complies with ISO 9001 and industry standards, especially in more demanding areas such as healthcare and automotive.
5.Sustainable development
- Energy conservation: Using renewable energy and closed-loop recycling systems can reduce carbon emissions by 20%.
- Environmentally friendly material options: Provide green prototype solutions such as bioplastics and biodegradable materials.
6.Recognition of success stories
- Automotive: Rapid production of a prototype electric vehicle battery pack for an automotive company, verification of heat dissipation and structural strength, and reduction of the R&D cycle by 40%.
- Consumer electronics: The prototype of metal shell case of the smartwatch with CNC machining has achieved a precision of 0.02mm, guaranteeing 98% compliance with the mass production target.
Summary
Rapid Prototype is a fast method to visualize product concepts and validate functions. At its core, abstract ideas can be quickly turned into interactive physical or digital samples utilizing techniques such as 3D printing and CNC. Whether in industrial manufacturing, consumer electronics, or healthcare, Rapid prototyping not only shortens the life cycle of a product from concept to market, it also promotes interdisciplinary collaboration and innovative thinking. With the continuous advancement of technology, Rapid prototyping will continue to be an important engine of product innovation, enabling all industries to break through the boundaries of traditional development models.
Disclaimer
The content of this page is for informational purposes only.JS SeriesNo representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, are made as to the accuracy, completeness or validity of the information. It should not be inferred that the performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features,material quality and type or workmanship that the third-party supplier or manufacturer will provide through the jusheng network. This is the responsibility of the buyerAsk for a quote for partsto determine the specific requirements for these parts.please Contact us Learn more information.
JS Team
JS is an industry-leading companyFocus on custom manufacturing solutions. With over 20 years of experience serving more than 5,000 customers,we focus on high precisionCNC machining,Sheet metal fabrication,3D printing,Injection molding,metal stamping,and other one-stop manufacturing services.
Our factory is equipped with more than 100 state-of-the-art 5-axis machining centers and is ISO 9001:2015 certified. We provide fast, efficient and high-quality manufacturing solutions to customers in more than 150 countries around the world. Whether it's low-volume production or mass customization, we can meet your needs with the fastest delivery within 24 hours. chooseJS TechnologyIt means choosing efficiency, quality and professionalism.
To learn more, please visit our website:jsrpm.com
FAQs
1.Why the rapid prototyping?
Rapid prototyping saves time and costs by quickly validating design concepts, identifying potential problems in advance, reducing development risks, promoting team collaboration and user feedback, and avoiding direct investment in developing immature products.
2.Does rapid prototyping require repeated modification?
need. Repeatedly modify the verification function and adjust the design to ensure that the final product meets the requirements while improving development efficiency and user experience and avoiding large-scale rework in the later stages.
3.What are the advantages of 3D printing in rapid prototyping?
The advantages of 3D printing in rapid prototyping are: mold free rapid prototyping, support for single-use molding of complex structures, wide material selection (plastics, metals, resins, etc.), low cost and time saving, especially for small batch trial production and design iteration optimization.
4.What common problems do rapid prototype encounter during production?
Insufficient accuracy (error ±0.05mm or more), surface roughness requiring secondary processing, limited material strength, additional support for complex structures, high small batch costs, poor design adaptability, short lead times, fragile structures requiring advance planning of processes and material selection.






