Sheet metal fabrication is the core process of turning metal sheets processing into precision industrial components. Cutting, bending sheets metal and precision assembly technology are widely used in automotive, electronics, construction and other fields. Whether producing galvanized sheet metal or lightweight aluminum sheet metal processing is inseparable from advanced equipment and technology. From initial design to final product, precise controls are required at every step to ensure that the product meets strict quality standards. Whether it is small precision parts or large equipment racks sheet metal processing has been an indispensable basic link in modern industry.
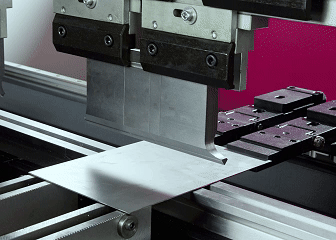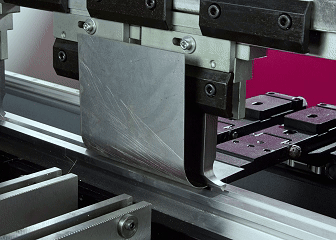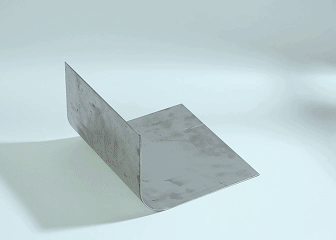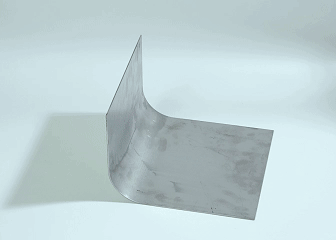
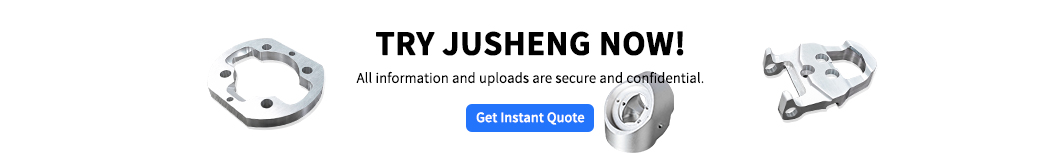
What is sheet metal fabrication?
Sheet metal fabrication refers to a precision machining technique of converting flat metal sheets into the desired shape through cutting, bending sheet metal, stamping, welding and other processes. The core is to use bending machine, die and other equipment to exert external force on metal sheets, achieve precision sheet metal bending, and manufacture structural parts to meet design requirements. Adopting compatible metal sheets and scientific bending process control, ideal forming effect can be achieved. The process is widely used in automobile parts, mechanical equipment casings, building components, etc. It has the advantages of high production efficiency and low cost.
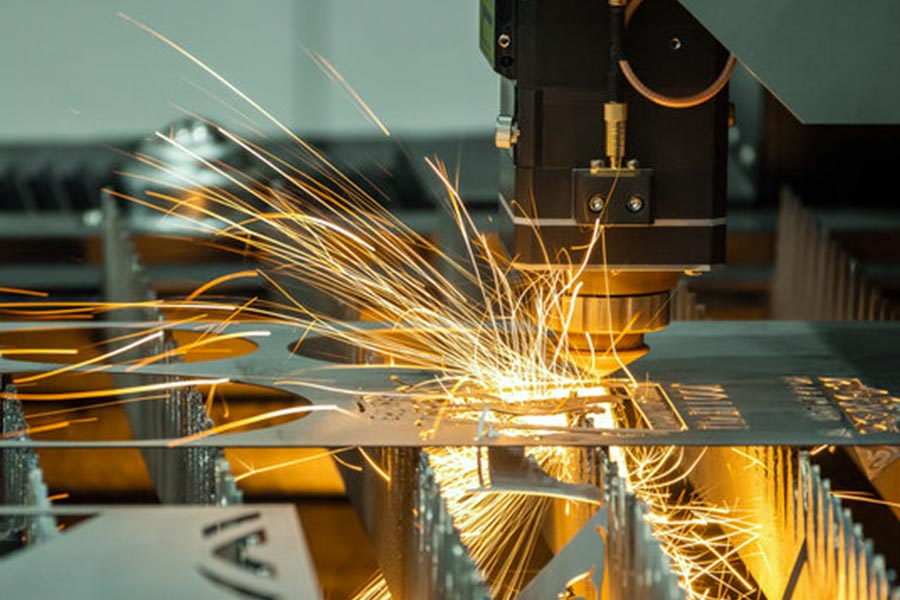

How to choose materials for sheet metal fabrication?
The core of sheet metal processing lies through cutting, stamping, sheet metal bend and other processes will be sheet metal processing into structural parts, the choice of materials directly affect the performance and cost of the finished product. Here are the main selection principles:
1.Material characteristics and bending properties
- Strength and ductility: Steel is tough but brittle and requires more bending force, aluminum is soft and easy to shape for complex bending (e.g. air conditioning fins).
- Surface treatment adaptability: Galvanized sheet has rust resistance, but tends to appear white edge after bending, while stainless steel has corrosion resistance, but requires high rebound compensation.
- Sheet metal bend process considerations: Material thickness directly affects mold selection (e.g. 1mm aluminum plate requires V-groove 88 degree match).
2.Application scenario requirements
- Lightweight requirements: Electronic casings and drone drone components best made with aluminum and Aluminum magnesium alloy, with a balance of strength and weight ratio.
- Weather resistance requirements: Outdoor equipment (such as lampposts) should be made of galvanized sheet or stainless steel to resist corrosion and oxidation.
- Conductivity scenario: Copper is the preferred material for circuit circuit board heat, which takes into high conductivity and heat dissipation efficiency.
3.Optimization of process adaptability
- Precise control of sheet metal bend: Use a CNC bending machine preset rebound value (such as 1-2 degrees of stainless steel compensation) to ensure accuracy of angle.
- Mould-plate match: For thin plates (≤2mm), sharp cutting tools are used to reduce burr, for thick plates (≥ 5mm), step bending is required to avoid cracking.
4.Cost-benefit savings
- Material cost comparison: Ordinary carbon steel the lowest price, titanium alloy has the highest cost, and needs to take into account performance and budget.
- Processing Loss Rate: For irregular parts, strong plasticity materials (such as copper foil) should be preferred to reduce waste rates.
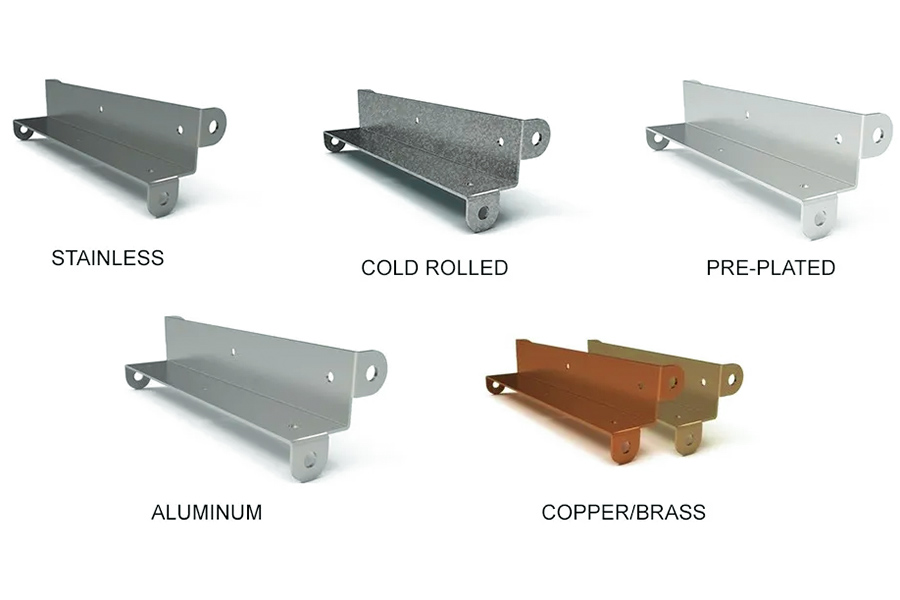
What is the process of sheet metal fabrication?
1.Digital design and analogue
- Complete 3D modeling using specialized software such as SolidWorks/Inventor.
- Accurate engineering drawings are generated through AutoCAD (support uploads in formats such as STEP/IGES).
- CAE software used to simulate bending rebound compensation (setting core parameters of sheet metal bending).
- JS technology Highlights: With 20 years of experience, our engineering team provides parameter optimization suggestions to reduce trial and error costs.
2.Precise selection of materials
- Conventional Material: SPCC/SGCC cold-rolled plate, SUS stainless steel, AL5052 aluminum plate, and more than 50 others.
- Special requirements: Copper materials, titanium alloys, composite plate customization supply.
- JS Advantage: 98% of orders are delivered on time and inventory turnover is industry-leading.
3.Efficient cutting and shaping
- Laser cutting (accuracy ±0.02mm).
- CNC punching machine (3mm thick plate).
- Water jet cutting (for parts with complex shapes).
- JS technology: Self-developed nested algorithm improves material utilization by 92%.
4.Precision bending
- Fully automatic bending unit (3T-300T tonnage).
- V-groove adaption system (minimum curved edge 1.5mm).
- Real-time pressure monitoring system (±0.01mm repeatability accuracy).
- JS core technology: Develop the Bend rebound compensation Database independently to ensure sheet metal bending tolerance ±0.005mm.
5.Automated welding integration
- Robot MIG/TIG welding workstation.
- Laser weld tracking system.
- Welding deformation control process package.
- JS characteristics: Automobile grade welding standard, weld strength test pass rate of 100%.
6.Surface Treatment Process
- Electrophoretic coating (salt spray test ≥500 hours).
- Powder coating (color customization).
- Nickel coating (thickness can be controlled between 0.0001-0.002mm).
- JS Environmental Measures: 85% water paint usage rate, 60% reduction in VOC emissions.
What are the differences in bending parameters between galvanized sheet and aluminum sheet?
Comparison of bending parameters differences galvanized sheet and aluminum sheet
| Parameters/Materials | Galvanized sheet metal | Aluminum sheet metal |
| Rebound tendency | Small rebound (galvanized layer increases material rigidity). | The rebound is large (compensation value needs to be increased). |
| Recommended bending radius | Minimum radius ≥0.5T (T is plate thickness). | Minimum radius ≥1.0T (to avoid cracking). |
| Temperature sensitivity | Cold bending is stable. | High temperature bending softens easily (room temperature treatment is best). |
| Mould wear rate | The friction loss of galvanized layer shortens the service life of die by about 20%. | Aluminum shavings adhere easily to molds (require to be cleaned regularly). |
| Bend angle control | The recommended rebounding compensation is 0°-1°. | The rebound compensation value should be reserved at 1°-3°. |
| Difficulty treating burrs | The zinc layer burrs are prone to detachment. | Aluminum burrs need to be finely polished. |
| Differences in ductility | Low ductility (easy to break). | High ductility (for complex shapes). |
| Corrosion resistance treatment | Passivation and rust immediately after bending. | Anodized or sprayed protection is required. |
Detailed description of key process parameters
1.Rebound compensation control
- Galvanized sheet: Due to the hardening effect of galvanized plate, the rebound amount is generally between 0.5° and 1.5°, bending machine needs to predetermine the reverse compensation angle.
- Aluminum plate: Aluminum alloy (e.g. 3003) can bounce up to 2°-5° and mold angle need to be dynamically adjusted through trial bending.
2.Mold gap adaptation
- Galvanized sheet: The recommended spacing is 8%-12% of the thickness of the sheet (e.g. 0.08-0.12mm for 1mm sheets).
- Aluminum plate: Gaps need to be increased to 12%-15% to avoid mold wear caused by aluminum chip adhesion.
3.Choice of bending direction
- Galvanized sheet: Prefer bending along rolling direction to reduce the risk of flaking of galvanized layer.
- Aluminum sheet: Avoid bending perpendicular to the fiber direction, so as not to reduce cross-sectional strength.
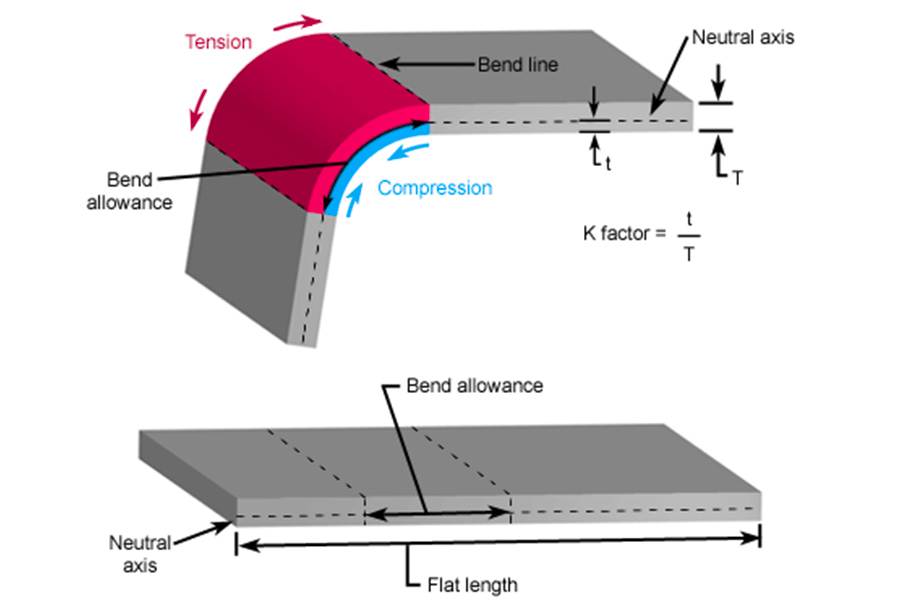
What tools are crucial for sheet metal fabrication?
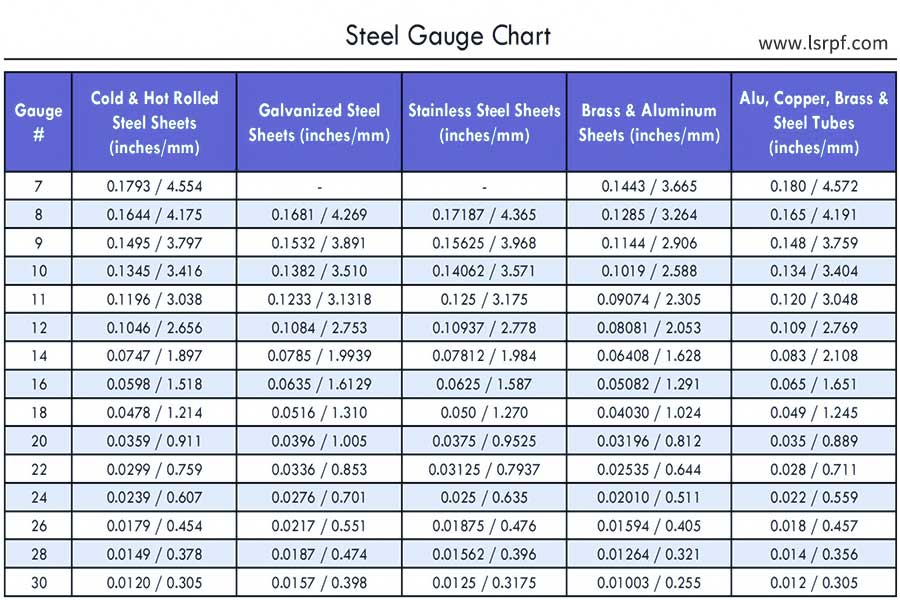
The following are the basic tools and techniques of sheet metal processing, combining the guidance of the sheet metal gauge chart:
Metal Sheet Forming Tools and techniques
1.Cutting Tools
- Laser Cutting Machine: Suitable for thin plates (≤6mm) with accuracy ±0.02mm. See thickness chart for power and focus selection.
- CNC punch: For medium thickness plates (1-8mm), the thickness map parameters (e.g. punch spacing, plate thickness ratio, etc.) are matched through the mold library.
- Plasma/waterjet cutting: applies to thick plates (>8mm), adjusting cutting speed and air pressure through thickness chart to reduce thermal deformation.
2.Bend tools
- Bend machine: Adjust the opening angle of the V-shaped groove according to the sheet metal gauge chart (e.g. 1.5mm aluminum plate requires an opening angle of 88° for V-shaped groove).
- The gap between the lower molds should be set according to the formula (gap= thickness * coefficient) to prevent the galvanizing layer from peeling or aluminum from cracking.
- Roll bending machine: For cylindrical/curved parts, choose roller spacing and feed speed according to thickness diagram.
3.Forming mold
- Stretch molds: For deep presses (such as car coverings), mold fillet radius (≥1.5T is selected based on thickness diagram).
- Round rolling die: When rolling a sheet (≤2mm), pre-lubricating oil is needed to reduce friction coefficient.
Metal plate connection tools and techniques
MIG/TIG welding machine:
- Thin plates (≤3mm) are welded with pulses to avoid burnout (current range 50-150A).
- The thickness plate (>3mm) is welded in several layers and the temperature and weld spacing between the layers are determined in accordance with the thickness diagram.
Laser welding: Precision components,such as electronic components, require adjustment of spot diameter and focus.
2.Riveting tools
- Rivet gun: Select rivet diameter to match plate thickness.
- Hydraulic riveters: Calibration pressure values (≥8 tons for 3mm plates) are required for heavy duty plates (e.g. stainless steel).
3.Adhesive technology
- Epoxy resin adhesives: For sheet adhesives (such as electronic device casings), the thickness of the adhesive layer (0.1-0.3mm) should be controlled.
- Structural adhesive: When splicing thick plate, it must be combined with the curing schedule.
What do sheet metal fabricators do?
Core players in the industry
1.Key links in the industrial chain
- Upstream undertaking: Coordination of steel, non-ferrous metals and other raw material suppliers to ensure stable supply of plate.
- Downstream support: Precision metal components for automotive, electronics, home appliances, aerospace and other industries are fundamental to manufacturing supply chain.
2.Technology Transformation Hubs
- Translating customer requirements (e.g. CAD drawings, samples) into scalable production process solutions.
- Combine materials science and mechanical engineering knowledge to solve complex structural design and processing problems.
3.Customized solution providers
- According to the demand of different industries, the development of differentiated products and high-end, environmental protection industries, automobile covering parts, medical equipment casings, communication base station sheet metal accessories and so on have set up pilot projects.
- Provides flexible manufacturing capabilities from prototype design to mass production.
4.Standardization promoters
- Compliance with ISO, ASTM and other international standards to ensure product quality consistency.
- Promote industry process standardization (such as bending tolerance, welding specifications, etc.) to improve overall manufacturing level.
Core responsibilities of the industry
1.Quality and safety assurance
- Strict control material inspection (e.g. chemical composition inspection, mechanical performance inspection).
- Implement full process quality control (e.g. size accuracy, surface defect detection) to ensure that products meet safety standards (e.g. compressive strength, corrosion resistance).
2.Driven by technological innovation
- Advanced laser cutter and robot bending system are introduced to improve processing efficiency and accuracy.
- Development of green manufacturing processes (such as lead-free soldering and environmentally friendly surface treatment) to reduce energy consumption and pollution.
3.Cost and efficiency optimization
- Reduce cardboard waste (typically utilization rate ≥85%) through intelligent typesetting software.
- Optimize production processes (such as automatic loading and unloading, process linkage), shorten delivery cycles.
4.Responsibility for sustainable development
- Promotion of circular economy (e.g. waste recycling, waste heat recovery, etc.).
- Reduction of carbon emissions (e.g. use of EDM instead of traditional flame cutting).
How do global and local factors affect sheet metal fabrication?
1.Global drivers
- Technological innovation: Automation (robotic bending), promotion of new materials (aluminium/titanium alloy), improvement of accuracy and efficiency.
- Economic volatility: Raw material prices and tariff policies,such as the U.S.-China trade friction that has caused North American sheet metal companies to turn to local or Southeast Asian suppliers, have forced supply chain localization to localize.
- Environmental pressure: Global carbon reduction targets promote green manufacturing, such as requiring sheet metal companies in the Los Angeles area to adopt solar powered equipment and waste recycling systems. The rental for sale model, which requires manufacturers to design detachable and recyclable sheet metal components, is being promoted in the European market.
2.Key local elements
- Cost and skills: Developed countries tend to automate (Los Angeles has higher labor costs), while developing countries,such as Southeast Asia, rely on low-cost labor.
- Industry clusters: Los Angeles's automotive and aviation industry clusters driving sheet metal manufacturing toward precision and customization, such as rapid mass production of Tesla panels.
- Policy and logistics: California's strict air pollution control regulations restrict traditional welding processes and promote laser welding. As a major global hub, Port of Los Angeles has shortened the import and export cycles for raw materials and products, but also faces the risk of delivery delays caused by port congestion.
3.Industry Future Trends
Digitization and data-driven approach:
Deploy sensors to monitor device status in real time and perform predictive maintenance to reduce downtime. At the same time, machine learning algorithms are used to balance order priorities and maximize equipment utilization.
Deepening sustainable manufacturing:
- Recycled aluminum Application: Companies Los Angeles use 60% recycled aluminum to produce auto parts and receive tax incentives from the state.
- Zero waste target: Using powder metallurgy technology to produce high performance composites from waste, reducing landfill volumes by 90%.
Trends in regional division of labour:
Offshore returns: Some companies are using their Mexican plants as satellite bases in Los Angeles, utilizing the North American Free Trade Agreement to reduce tariffs while maintaining supply chain agility.
Why invest in sheet metal manufacturing for your project?
Technical advantages of professional sheet metal manufacturer
1.Ultra precision machining capability: ±0.005mm tolerances were achieved using CNC laser cutting, CNC bending, robot welding, etc. (JS case: 95% of projects achieved this accuracy, reducing rework by 90%).
2.Automation and efficiency gains: Fully automated production lines, such as 300T bender unit, shorten production cycles and regular orders are delivered within 1-2 weeks (15% shorter on average JS project cycles).
3.Material and process compatibility: Optimize metal sheet selection, balance strength and cost based on sheet metal specifications, and provide custom finish.
Commercial value of working with sheet metal manufacturers
1.Accelerate product launch
- Rapid prototyping verification (3D printing/CNC sampling) shortens the design iteration cycle and supports a seamless transition from concept to mass production.
- JS undertakes to provide an offer within 24 hours of submitting CAD documents and to prioritize production upon confirmation.
2.Cost controllability and risk avoidance
- One-stop services include design optimization, process validation and delivery to reduce communication costs in outsourced processes.
- JS uses process databases to predict risks (such as white-edged bending of galvanized sheets) and provide solutions to reduce scrap rates.
3.Quality and Compliance Assurance
- The ISO 9001 certification system ensures product consistency by providing material reports, testing certificates and traceability records.
- JS Case: Medical equipment sheet metal parts are FDA-approved, with an error rate of less than 0.02%.
Summary
Sheet metal fabrication is a complete process of machining metal sheets into high-precision functional components. The core is to control the bending angle and clearance accurately according to the thickness of the metal plate by means of numerical control bending machine and laser cutting equipment to ensure that the finished product tolerance reaches ±0.005mm.
From car panels to medical equipment casings, sheet metal processing not only supports the precision development of modern manufacturing, but also promotes sustainable development through green manufacturing. JS Precision Manufacturing and other enterprises, with ultra-high precision, 98% on-time delivery and a global supply chain, continue to provide reliable solutions across industries to help customers grasp market opportunities.
Disclaimer
The content of this page is for informational purposes only.JS SeriesNo representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, are made as to the accuracy, completeness or validity of the information. It should not be inferred that the performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features,material quality and type or workmanship that the third-party supplier or manufacturer will provide through the jusheng network. This is the responsibility of the buyerAsk for a quote for partsto determine the specific requirements for these parts.please Contact us Learn more information.
JS Team
JS is an industry-leading companyFocus on custom manufacturing solutions. With over 20 years of experience serving more than 5,000 customers,we focus on high precisionCNC machining,Sheet metal fabrication,3D printing,Injection molding,metal stamping,and other one-stop manufacturing services.
Our factory is equipped with more than 100 state-of-the-art 5-axis machining centers and is ISO 9001:2015 certified. We provide fast, efficient and high-quality manufacturing solutions to customers in more than 150 countries around the world. Whether it's low-volume production or mass customization, we can meet your needs with the fastest delivery within 24 hours. chooseJS TechnologyIt means choosing efficiency, quality and professionalism.
To learn more, please visit our website:jsrpm.com
FAQs
1.What are the common methods of sheet metal surface treatment?
Spray, plating, anodic oxidation, passivation, wire drawing, sandblasting, chrome plating, electrophoretic coating, hot-dip galvanizing, chemical polishing.
2.How to eliminate the curved white edge of galvanized sheet?
This can be done by adjusting the bending radius, optimizing mold gap, using special lubricants or precoating with anti-oxidation coatings. Matching process parameters can effectively inhibit the shedding of zinc layer.
3.Why does sheet metal manufacturing require a gauge chart for sheet metal thickness?
It can guide the selection of plate processing parameters, guarantee the forming accuracy of different thickness sheets, avoid cracking and rebound deformation, and is the core of optimizing process efficiency and cost control.
4.How does sheet metal processing ensure environmental protection?
Green manufacturing and sustainable development using environmentally friendly materials (such as water-based paints), energy-efficient equipment, waste recycling systems, low-pollution processes (such as lead-free soldering), reduced energy consumption and waste emissions in conjunction with ISO 14001 certification standards.