Im Bereich des modernen industriellen Designs Rapid Prototyping sind zur Kernbrücke zwischen konzeptioneller Innovation und körperlicher Überprüfung geworden. Im Wesentlichen ist die digitale Modellierung eine tiefe Verschmelzung der physikalischen Fertigungstechnologie, die abstraktes Design in greifbare und messbare physische Modelle umwandelt, um die Produktfunktionalität, Ästhetik und Praktikabilität in den frühen Stadien der Produktentwicklung schnell zu validieren. Dieser Prozess hängt nicht nur von hochprekusionsbearbeitungsgeräte ab, sondern erfordert auch ein tiefes Verständnis der Materialeigenschaften, Prozesslogik und iterativen Mechanismen. Integriert die additive Herstellung (z. B. SLA/DLP) und CNC-Bearbeitungs-Technologien und iteratiert rasant iteriert Metall-Komposit-Komponenten im Entwicklung von Robotic-Prototypen, das erfolgreiche Validierungszyklus von 60% des Branchendienstes erfolgreich komprimiert. JS stützt sich auf seine Erfahrungen mit mehr als 1.000 hochkomplexen Bestellungen pro Jahr und definiert die Rolle der schnellen Prototyping-Technologie in der High-End-Fertigung-nur als Laborwerkzeug, sondern auch als Infrastruktur für Innovation durch interdisziplinäre Zusammenarbeit.
Was ist die Kerndefinition des schnellen Prototyps?
Prototyping ist der Schlüsselprozess zur Umwandlung eines digitalen Designsystems in ein physikalisches Modell, um die Funktionalität, die Ästhetik und die praktische Praktikabilität zu verifizieren. Prototypen bedeuten nicht nur, dass physikalische Objekte hergestellt werden, sondern auch die Lücke zwischen Konzept und Realität durch physische Überprüfung überbrücken. Insbesondere im Prozess der komplexen Systementwicklung, strukturelle Defekte, Widersprüche der Menschen-Maschine-Wechselwirkung oder materielle Leistungsbeschränkungen, die nicht in Zeichnungen reflektiert werden können
modern Prototyping-Technologie kombiniert die additive Herstellung mit CNC-Bearbeitungstechnologie, bricht durch die Begrenzung von Einzelmaterialien, realisiert schnelle Formen von Metall-plastischen Hybrid-Struktur. Prototyping. 1. Data-V-7B79C893 = ""> Konzeptstufe: Klarheit der Anforderungen und Ziele mittels Marktforschung, Benutzerinterviews usw. werden die Kernanforderungen des Produkts bestimmt, und die Funktionen, Leistungs- und Kostengrenzen des Prototyps werden bestimmt. ", "Wie auch Prototypen ist erforderlich
2. Data-V-7B79C893 = ""> Designphase: Digitale Modellierung und Optimierung 3D-Modelle erstellen Verwenden von CAD-Software und Ausgabe von Dateien in Formaten wie STL/Step. The designer will optimize the design through parametric Anpassungen und Simulationsanalysen (z. B. Spannungstest, Dynamiksimulation) und zunächst beurteilen, ob dies durch schnelle Prototyping -Technologie erreicht werden kann. 3. Data-V-7B79C893 = ""> Konstruktionsphase: Rapid Prototyping Choose the appropriate process and material to make the prototype: 4. Data-Len = "62" Data-V-7B79C893 = ""> Testerphase: Mehrdimensionale Validierung und Datenerfassung Vollständige Tests von schnellen Prototypen: Testergebnisse müssen quantitativ aufgezeichnet werden (z.
5. Data-Len = "58" Data-V-7B79C893 = ""> Verbesserungsphase: iterative Optimierung und Abschluss CAD-Modelle anhand von Testdaten anhand von Testdaten anpassen, um Schwachstellen zu optimieren (z. B. Strukturstärke und "> "> Das endgültige Prototypen. Formen oder technische Zeichnungen zu Gewährleistung der Konsistenz in der Massenproduktion . ">" Profitieren Sie die Data-V-7b79c89c893 ". Die Zyklen um über 50% und die einzelnen Iterationskosten um 80%. Sie eignen sich besonders für die schnelle Entwicklung von Projekten mit hochunsicheren Projekten wie Medizinprodukte und intelligente Hardware. 1. data-v-7b79c893="">Concept validation prototyping model: Core design concepts are validated by rapid prototyped models, which are often constructed quickly with low-cost materials (e.g. cardboard and foam) and focus on the feasibility of basic concepts such as product form and interactive logic. 2. CNC-Bearbeitung, um eine genaue Wiederherstellung von Schlüsselkomponenten zu erzielen. 3.visuelles Prototyping-Modell: Mit dem Aussehen als Core-Objektive wird das Prototyped durch oder CNC-Gravur-Technologie, die Produktfarbenanpassungen, materielle Textur und menschliches Maschinenverhältnis zeigt. is is ire in VISV-7B79C893 = "" wie Consumer Electronics und Car Interiors .
4.Interaktives Prototyping-Modell: integriert Hardwarekomponenten wie Sensoren und Motoren baut physische Modelle mit Basis-Betriebsfunktionen. Die Weitstufe und Basis-Sendern. Intelligente Hardwareentwicklung. 5. Benutzer-Testen Prototyp-Modell: Eine Versuchsversion eines Prototyps, das für eine Zielbenutzungsgruppe ausgelegt ist, die Benutzererfahrungsdaten durch A/B-Test, Szenario-Simulation und andere Methoden und andere Methoden sammelt, häufig, Szenario-Simulation und andere Methoden, und andere Methoden und andere Methoden, die Szenario-Szenarien und andere Methoden sammelt, kombiniert mit einer schnellen iterativen Optimierung zur Verbesserung der Produktsabilität . 2. Data-V-7b79c893 = ""> benötigtes Material 3. Data-V-7B79C893 = ""> Kostenbudget 4. data-len = "13" data-v-7b79c893 = ""> Lieferzeiten Im Bereich der schnellen Prototyping, 1. Data-V-7B79C893 = ""> Herstellungsprinzipien  Was sind die 5 Schritte des schnellen Prototyps?
Was sind die 5 Schritte des schnellen Prototyps?
Was sind die Arten von häufig verwendeten Prototyping -Modellen?
Wie wählt man eine geeignete schnelle Prototyping -Technologie?
Technischer Typ
Materialtyp
Genauigkeit
Kosten
Produktionsgeschwindigkeit
Typische Anwendung
fdm
± 0,1-0,3 mm
Low
Schnell
Funktionelle Prototypen und einfache strukturelle Komponenten.
SLA
Photosensitive Harz
± 0,05 mm
Zentrum
schneller
Aussehensprüfung, transparente Teile, Präzisionskomponenten .
SLS
Nylon/Verbundmaterial
± 0,1 mm
groß
Zentrum
Voll funktionsfähig und leicht.
CNC-Bearbeitung
Metall/Kunststoff
± 0,01-0,05 mm
höchstes
Slow
Tests mit hoher Intensität und endgültige Bestätigung vor Massenproduktion.
Silikonreplikationsform
Silikonform+Pu Resin
± 0,2-0,5 mm
Low (Batch)
Schnell
Prototypmodell und small-scale Pilotproduktion.
">
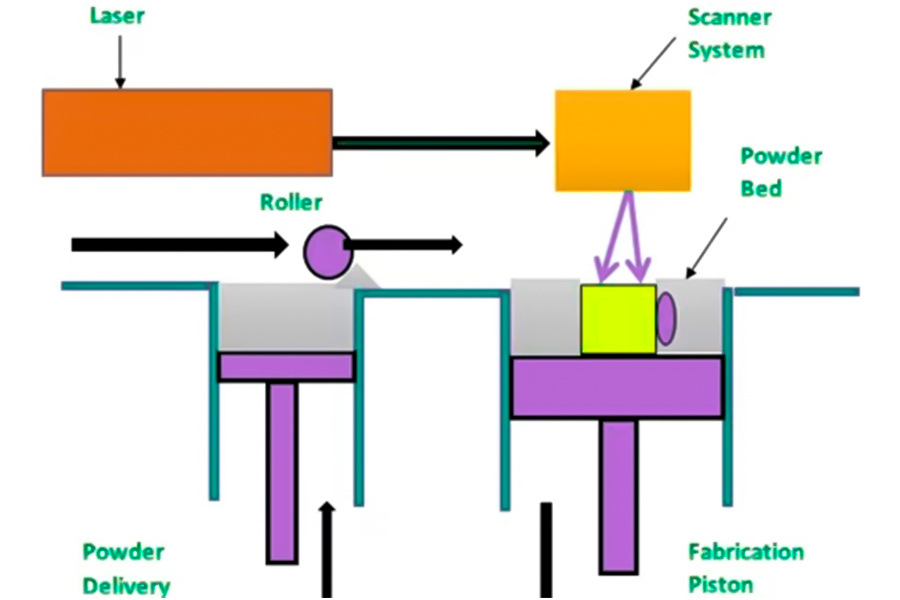
Was sind die Unterschiede zwischen 3D -Druck- und CNC -Prototyping?
2. Data-Len = "22" Daten-V-7b79c893 = ""> Materialanwendbarkeit
- 3D-Druck: Die Materialoptionen sind begrenzt (üblicherweise ABS, PLA, Titanlegierungen usw.) und einige Materialien haben schwache mechanische Eigenschaften.
- JS bietet mehr als 50 Materialien (Metalle, Plastik, Kompositionen) wie Aerospace-Grad-Grad-Grad-Grad-Grad-Grad-Grade-Größen und Legal-Legal-Legierungs-Alumin-Alumin-Alumin-Legierungs-Legierungs-Legierungs-Legierungs-Legierungs-Legierungs-Legierungs-Legierungs-Legierungs-Legierungs-Legierungs-Alumin-Alumin-Altics-Legierungs-Legierungs-Legierungs-Legierungs-Legierungs-Legierungs-Legierungs-Legierungs-Legierungs-Legierungs-Legierungs-Legierungs-Legierungs-Alumin-Alumin-Altics-Lengungen liefert. Anforderungen.
- CNC-Bearbeitung: Hat eine breite Palette an Materialanpassungsfähigkeit und kann Hartlegierungen (wie Edelstahl, Titanlegierungen) und High-Toughness-Materialien (z. B. Kohlefaser) verarbeiten.
- JS-Technologie Highlights: Its CNC-Geräte Komplexen Oberflächenbearbeitung Die materielle Verarbeitung zeigt. Funktionen.
| Dimensionen | Vorteile des 3D-Drucks | CNC-Vorteile | JS-Technologie-Balance-Punkt |
| Materialnutzungsrate | Reduce material waste (only what is needed). | High material waste (processing allowance required). | JS reduces CNC waste rate through smart path planning, and 3D printing supports metal powder recycling. |
| Surface quality | Surface roughness (Ra 50-200μm) requiring reprocessing. | Surface smoothness (Ra 0.8-3.2 μm). | JS's specialized post-processing equipment can optimize the surface roughness of 3D printed parts to Ra 1.6 μm. |
| Processing accuracy | ± 0.1-0.5mm (depending on model). | ± 0.02-0.1mm (up to ± 0.005mm high-precision machine tools). | Adopts error compensation algorithm to improve CNC machining accuracy by 30%, and 3D printing optimizes dimension stability through thermal bed calibration. |
| Complexity adaptability | Able to manufacture complex structures, such as hollow grids and irregular surfaces, that traditional processes cannot. | Suitable for general geometry and requires additional thin wall/suspension support. | JS Innovative hybrid manufacturing Model: CNC rough machining + 3D Printing Fine Features, Balanced Efficiency and Accuracy. |
- Choose 3D printing: When requirements focus on quick iterations, complex structure validation, or low-cost trial and error.
- Select CNC prototyping: When the goal is functional testing, high precision production preparation, or material performance validation.
Which industries rely the most on rapid prototyping technology?
According to the characteristics of online CNC processing and 3D printing business of JS, the application of rapid prototyping technology is analyzed below:
1.JS technology association:
- Lightweight aluminum alloy/carbon fiber prototypes available to support quick iterations of streamlined components.
- 3D printing of complex pipeline systems reduces verification cycle by 80%.
- CNC precision machining of Automotive Electronic connector molds.
2.Industry demands:
- Structural verification of battery assembly of new energy vehicle.
- Rapid testing of self-driving sensor bracket.
- Conduct exterior reviews of internal parts prior to mass production.
1.JS technology association:
- Titanium alloy/ superalloy prototypes meet FAA certification requirements.
- Precision casting mold production reduces research and development cycle by 50%.
- Wind tunnel testing model of complex aerodynamic profile.
2.Industry demands:
- Verification of prototype engine turbine blades.
- Functional testing of satellite antenna deployment mechanism.
- Mechanical simulation of spacecraft docking mechanism.
Medical equipment
1.JS technology association:
- Biocompatible material Custom Implant Prototypes.
- Surgical simulator 3D printing (bone/organ models).
- Customized rehabilitation equipment for fast delivery.
2.Industry demands:
- Verification frictional properties of artificial joints.
- Dental implant bite test.
- Pressure Distribution Analysis customized orthotics.
1.JS technology association:
- 50+material libraries support concept validation.
- Full-color 3D-printed appearance evaluation model.
- Rapid casting master mold production (silicone mold/resin mold).
2.Industry demands:
- Home product ergonomics testing of household products.
- Verification the interior color scheme for transport vehicles.
- Robot joint motion simulation.

How to control the cost of prototype production?
Prototype production cost control requires comprehensive consideration of materials, production, post-production maintenance and other factors, the following are the main strategies:
| Indicators | Industry average | JS technical indicators | Increase amplitude |
| Single prototype cost | $120 | $72 | 40% ↓ |
| First time yield | 68% | 91% | 34% ↑ |
| Environmental impact factors | 0.72 (high energy consumption/pollution) | 0.35 (Green Manufacturing) | 51% ↓ |
| Material utilization rate | 45%-60% | 85%-92% | 35%-50% ↑ |
| Processing cycle | 12-24 hours | 6-18 hours | 30%-50% ↓ |
| Scrap rate | 8%-15% | ≤1% | 85%-94% ↓ |
| As a proportion of labour costs | 25%-35% | 12%-18% | 30%-45% ↓ |
| Maintenance costs (10,000/year) | 15-25 | 8-12 | 40%-55% ↓ |
Core Technical of Cost Control in JS Company
1.Material recycling system
- Metal powder recycling line established (92% SLM process waste powder reuse rate)
- Engineering Plastic Regeneration particle technology Developed (ABS/PC recycled material performance retention rate ≥90%)
2.Intelligent process optimization
- AI parameter recommendation system: Automatically selecting the optimal processing parameter combination based on historical data.
- Dynamic cutting force compensation: Reduce tool wear and prolong tool service life by 3 times.
3.Digital quality control
- Online Coordinate Measuring: First inspection time reduced from 2 hours to 15 minutes.
- Digital twin analogue: 87% of potential design defects identified early.
4.Green manufacturing technology
- Dry cutting techniques: 100% reduction in coolant usage and 28% reduction in energy consumption.
- Low temperature sintering process: Sintering temperature from traditional 1200°C to 600°C, energy saving 45%..
5.Flexible production system
- Fast die changing device: CNC die changing time from 4 hours to 30 minutes.
- Intelligent warehouse management: Material turnover efficiency increased by 60%.
Zusammenfassung
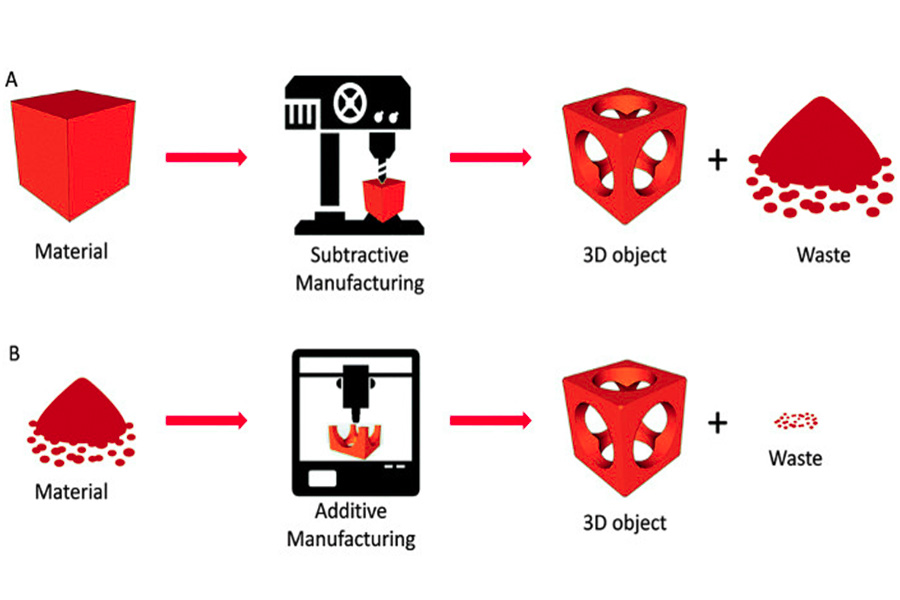
In the process of modern product development, rapid prototyping redefine the transformation path from concept to reality by iterating the prototyping model. Whether additive manufacturing or subtractive processes, the core prototyping meaning is to verify the feasibility of design with the most minimum cost and shortest cycle, and accelerate innovation loop cycle. From the sleek appearance of consumer electronics to high-performance components in aerospace, rapid prototype technology continues to push the boundaries of materials and processes, visualizing complex structures and making functionality testable. In the future, with the deep integration of intelligent algorithms and green manufacturing, prototyping models will be more deeply integrated into the life cycle of enterprise development, becoming a strategic tool for enterprises to deal with market uncertainty and continuously push industry innovation to agility and precision.
Disclaimer
The content of this page is for informational purposes only.JS SeriesNo representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, are made as to the accuracy, completeness or validity of the information. It should not be inferred that the performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features,material quality and type or workmanship that the third-party supplier or manufacturer will provide through the jusheng network. This is the responsibility of the buyerAsk for a quote for partsto determine the specific requirements for these parts.please Contact us Learn more information.
JS Team
JS is an industry-leading companyFocus on custom manufacturing solutions. With over 20 years of experience serving more than 5,000 customers,we focus on high precisionCNC machining,Sheet metal fabrication,3D printing,Injection molding,metal stamping,and other one-stop manufacturing services.
Our factory is equipped with more than 100 state-of-the-art 5-axis machining centers and is ISO 9001:2015 certified. We provide fast, efficient and high-quality manufacturing solutions to customers in more than 150 countries around the world. Whether it's low-volume production or mass customization, we can meet your needs with the fastest delivery within 24 hours. chooseJS TechnologyIt means choosing efficiency, quality and professionalism.
To learn more, please visit our website:jsrpm.com
FAQs
1.Does prototype production require the addition of supporting structures?
Whether to add support structures to prototype production depends on the type of process. For example, when FDM and SLA are used to print suspension structures, temporary brackets need to be added to prevent deformation and should be removed and polished upon completion. Due to the self-supporting nature of the powder, SLS technology usually does not require additional support, but it can affect the smoothness of the surface and requires reprocessing.
2.What should we do if the surface of the rapid prototyping is rough?
rapid prototyping rough surfaces can be treated by grinding, sandblasting or chemical polishing. For example, 3D-printed parts use sandpaper or chemicals to remove layered patterns, CNC machining and polishing to improve smoothness and ensure that functional or appearance requirements are met.
3.How long does it take for prototype production?
prototype production time vary according to process and complexity: simple plastic components (e.g. FDM) can be completed in a matter of hours, metal components or precision structures (e.g. CNC) require 1-3 days, and post-processing (polishing/coating) takes 1-2 days. Small batch customization or complex design may prolong the cycle, and advance communication of specific requirements is recommended.
4.Can prototypes be used directly in mass production?
Prototypes usually need to be adjusted before mass production can begin. For example, 3D-printed parts may need to replace mass-produced materials,such as metals, while CNC prototypes may need to optimize molds. Direct conversion may cause performance or cost problems, and gradual verification is recommended.