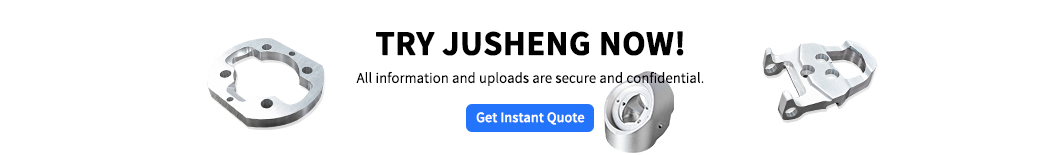
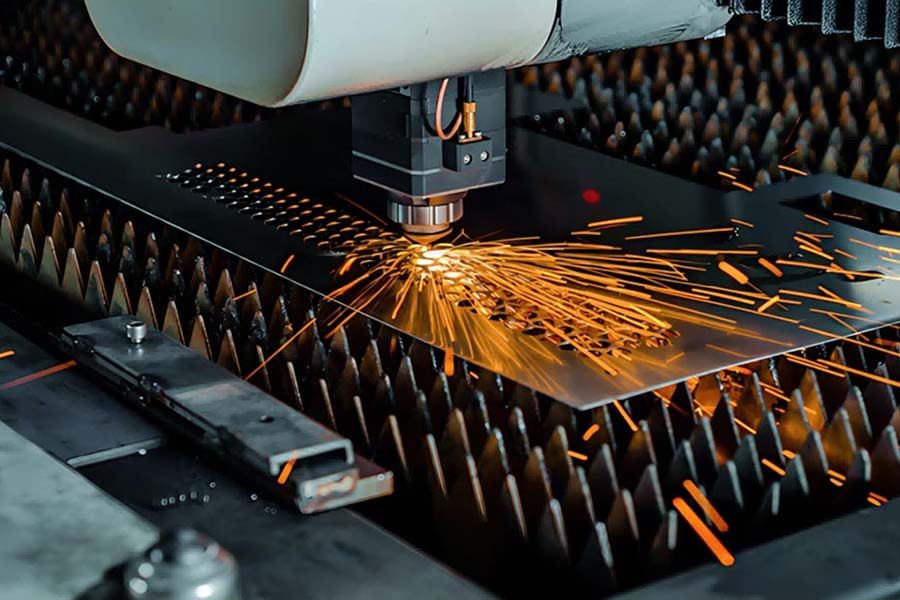
Sheet metal fabrication is widely used in automotive, electronics, aerospace, home appliances and other fields. Lightweight aluminum sheet metal and corrosion resistant galvanized sheet metal can be converted into industrial components to meet strict requirements through precise sheet metal fabrication. As an industry-leading company, JS is committed to providing customization solutions for sheet metal bending from design to production, helping enterprises achieve dual breakthroughs in efficiency and quality.

What is sheet metal fabrication?
Sheet metal fabrication is the process of cutting and bending metal plates into precise structural parts. It is widely used in automobile and electronics industries. The core is to use sheet metal fabrication molding products functional shape, such as through bending sheet metal adjustment performance and assembly accuracy. Sheet metal fabricators can accurately select materials, use CNC bending machines and other equipment, combined with rebound compensation algorithm, to achieve micrometer level bending forming, to ensure consistency of mass production. From design to mass production, sheet metal fabricators's ability to integrate the ductility of metal sheets into a lightweight, high-strength end product has become the key technology of modern industry.

What are the key methods for sheet metal fabrication?
1.Cutting
Common techniques to process and remove sheet metal parts include:
| Method | Principle | Applicable scenarios | Strengths and weaknesses |
| Laser cutting | High-energy laser beams melt material. | High precision, complex graphics. | It's expensive and slow. |
| Cutting | Mold pressure cut-off. | Linear cutting. | Fast, but limited to simple shapes. |
| Water jet cutting | High-pressure water mixed with abrasives. | Thin, heat-sensitive material. | No heat shock, but inefficient. |
2.Sheet metal bend
The core process of changing the angle of the plate through plastic deformation includes:
| Method | Principle | Applicable scenarios | Strengths and weaknesses |
| Brake bending | Apply pressure to the bending machine. | Accurate angles, mass produced. | Equipment is expensive but accurate. |
| Air bending | Apply local pressure to the mold. | Angles are complex. | No molds are needed, but the accuracy is low. |
| Roll Bending | Continuous plastic deformation of the roller. | Circular pipes and curved components. | Suitable for long strips and low efficiency. |
3.Stamping
Using molds to apply pressure to the sheet, creating features such as holes and grooves:
| Method | Principle | Applicable scenarios | Strengths and weaknesses |
| punching | Punch holes in molds. | Through holes and irregular holes. | High efficiency, but high mold cost. |
| forming | Plastic deformation of molds. | Complex structures (such as flanges). | Suitable for large quantities and low flexibility. |
4.Forming
Manufacturing complex geometries through plastic deformation:
| Method | Principle | Applicable scenarios | Strengths and weaknesses |
| deep drawing | Multiple stretching and forming. | Deep cavity container (such as battery case). | The material utilization rate is high, but the mold structure is complicated. |
| ironing | Localized thinning increases height. | Lampshade and tableware. | The uniformity of wall thickness needs to be controlled. |
5.Connect
Combine multiple sheet metal components into a complete structure:
| Method | Principle | Applicable scenarios | Strengths and weaknesses |
| welding | Melting material connection. | High intensity demand. | Deformation risk requires specialized equipment. |
| Welding | Mechanical fixation. | The scene needs to be disassembled. | Reversible, but less intense. |
| Adhesive | Chemical bonding. | Sealing or decoration. | No thermal deformation, but poor temperature resistance. |
The core of sheet metal processing lies in the flexible selection of cutting, bending, stamping and other methods, combined with process characteristics and production requirements, to achieve efficient and accurate parts manufacturing.
What are the mainstream process types for aluminum sheet metal stamping?
1.Aluminum sheet metal blanking
- Features: High-precision die and servo presses are used to achieve burr free and vertical cutting with tolerance of ±0.02mm.
- Technical highlights: It is necessary to control the gap between molds (0.01-0.03mm) and to use a CCD visual positioning system to increase production.
2.aluminum sheet metal deep drawing
- Features: Single punch box, depth>diameter (e.g. battery trays), tensile depth ratio ≤2.5.
- Difficulty: Aluminium rebound requires to be compensated (compensation coefficient 0.5° to 2°) and the die is coated with hard chromium to prevent adhesion.
3.Aluminum sheet metal bending
- V-shaped bending: Suitable for electrical housing of equal right angle structures, mold fillet radius ≥1.5 times plate thickness.
- Rolling bending: Continuous rolling of cylindrical/conical parts (e.g. lamp post bracket) with a minimum bending radius of R=2t.
- Technical core: The servo bending machine is equipped with real-time pressure feedback system by CAE simulation.
4.Aluminum sheet metal hydroforming
- Principle: Liquid media transfer pressure, reduce mold wear, suitable for complex hollow structure.
- Case: New energy vehicle battery pack, wall thickness uniformity error ≤0.1mm.
- Equipment requirements: Real-time monitoring of pressure fluctuations (accuracy ±0.5MPa) to prevent overstretching of aluminum plates.
Process Selection Comparison Table
| Process type | Core advantages | Aluminum adaptability | Typical applications |
| Blanking | High cross-sectional quality, suitable for thin plate. | 0.1-2.0mm aluminum sheet metal. | Precision electronics. |
| Deep drawing | Once molded, the material utilization rate is high. | 0.5-4.0mm ductile aluminum material. | Battery casing. |
| Bending | Customizable curvature and flexible production. | Thickness of all aluminum sheet metal. | Bracket, curved shell. |
| Hydroforming | Complex hollow structure with uniform wall thickness. | High-strength 6-series aluminum alloy. | New energy auto components. |
Main points of stamping process of aluminum sheet metal:
- Material adaptation: According to product requirements can be selected 1 series (pure aluminum), 5 series (rust proof), 6 series (high strength) aluminum sheet metal.
- Rebound control: The the elastic deformation of aluminum materials is offset by a mold compensation design (such as increasing prebend angle).
- Surface treatment: Anodized (hardness HV ≥150) or passivation treatment to improve corrosion resistance.
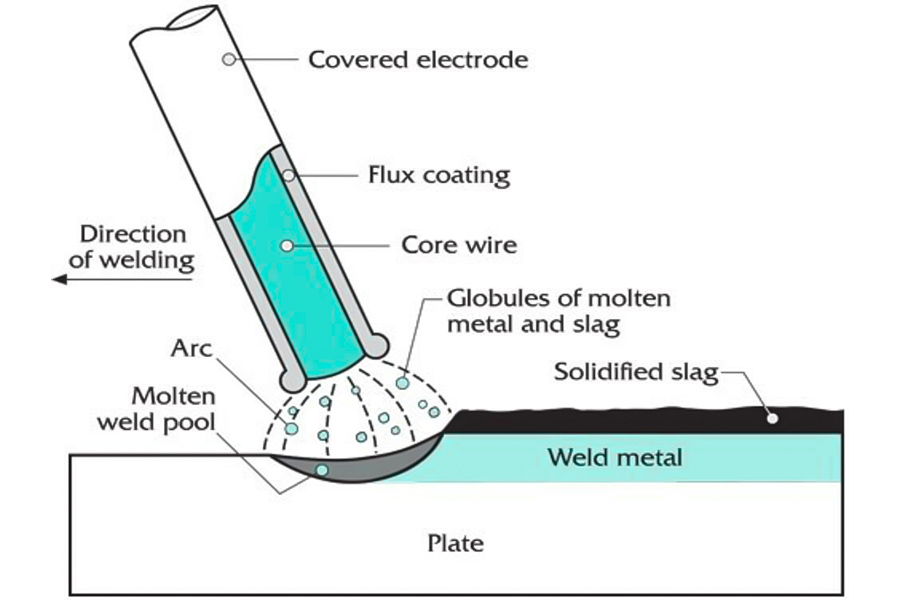
What welding process is suitable for galvanized sheet metal?
According to the technical ability of JS precision manufacturing and the characteristics of galvanized sheet metal, the following welding techniques are recommended:
1.Pulse MIG Welding
Zinc coating on galvanized steel metal is volatile, and traditional MIG welding can easily produce stomata. Pulse MIG reduces heat input and interference of zinc evaporation to the melt pool by controlling the current waveform while maintaining welding strength.
JS adopts advanced MIG equipment, supports pulse mode, adopts professional welding wires (containing silicon and aluminum), effectively suppresses zinc vapor and improves corrosion resistance of welds.
2.Laser Welding
High energy density laser beam can melt metal quickly, reduce heat effect zone and avoid large-scale oxidation of zinc layer. Suitable for welding precision galvanized steel metal components, such as automobile parts.
JS adopts high precision laser welding system, which can handle complex geometry, combine with real-time monitoring technology to ensure weld quality and meet strict tolerance requirement of ±0.005mm.
3.Resistance Spot Welding
Suitable for thin galvanized steel metal (e.g. 0.5-3mm), the metal melts in situ through the instantaneous action of electrode pressure and current, and the zinc layer is squeezed under pressure to form a reliable connection.
JS's automated resistance welding equipment can accurately control parameters, time and current, through electrode grinding system, prolong the service life of the equipment and adapt to efficient mass production of galvanized steel metal .
Extra advantages for JS company
- Pre-treatment and post-treatment: Provides surface cleaning (e.g. chemical zinc removal) and post-welding coating services for galvanized steel metal to improve corrosion resistance and extend the service life of components.
- Material diversification: More than 50 metal materials, including galvanized steel metal, are processed, supporting customization from prototype to mass production.
- Environmental process: Reduce zinc vapor emissions using low-pollution welding technology and exhaust gas recovery systems, in line with the 20% reduction target set by JS.
What is the impact of bending molds on machining accuracy?
The influence of bending mold on the machining accuracy of bend sheet metal is mainly reflected in the following aspects:
1.Design of mold fillet radius
- Impact angle accuracy: If mold fillet radius is too small, it will produce cracks in the plate at the crease. If the radius is too large, the theoretical bending angle may change (for example, the actual bending angle of a 90° mould may become 88 °-89 °).
- Rebound compensation: The mold needs to design a pre-bending angle (e.g. add 2-3° to compensate for rebound of aluminum plates) based on the ductility of the material.
2.Matching mold gaps
- Too small gap: Causing too much friction between the plate and mold, causing scratches or surface indentations, affecting the appearance quality.
- Excessive clearance: Results in plate sliding bias, resulting in bending angle deviation (error up to ± 1°-2°).
3.Mold surface roughness
- High precision mold: Surface roughness Ra≤ 0.8μm, can reduce plate scratching and improve surface smoothness.
- Rough: When Ra> 1.6μm, it is easy to cause metal debris to adhere to the surface of the plate, affecting subsequent spraying or welding processes.
4.Mold materials and heat treatment
- Mold hardness: Cr12MoV mold steel (HRC58-62) has a service life more than three times that of normal 45# mold steel and is not easily deformed after long use.
- Heat treatment defects: Mold quenching inhomogeneity will accelerate local wear and affect bending consistency.
5.Mould wear and maintenance
- Wear threshold: When the mold blade wears more than 0.1mm, the stability of the bending angle decreases significantly (e.g. from ±0.5° to ±2°).
- Maintenance cycle: It is recommended that mold size be checked every 5,000 processing cycles and repair or replaced in a timely manner.
6.Match of mold thickness and plate thickness
- Thin plate mold (≤ 1mm): Alloy inserts are required to prevent breakage of the mold due to excessive punching force.
- Thick plate mold ≥ 3mm: It is necessary to add a gasket design to the bottom of the mold to disperse pressure and avoid plate layering.

How to choose the material thickness of sheet metal parts?
The selection of sheet metal part material thickness requires comprehensive consideration of function requirements, process limitations and economy. Sheet metal gauge chart is the core tool to guide selection. Here are the key steps and highlights:
1.Clarify application scenarios and load requirements
- Static loads (such as brackets and shells): The yield strength of a sheet metal gauge chart, select the minimum thickness that can withstand the expected load.
- Dynamic load (e.g. car chassis): Fatigue strength needs to be calculated, usually 20% to 30% more than static load.
- For example, if the electrical casing is subjected to a concentrated load of 50kg, according to the gauge chart, SPC steel 1.5mm thick meets the bending strength requirements.
2.Matching thickness range of manufacturing process
| Process type | Applicable gauge range | Process limitations |
| Laser cutting | 0.1mm-20mm | The cutting speed of thick plate is reduced and the risk of thermal deformation is great. |
| Bending | 0.5mm-6mm | The angle of the V-mold needs to be adjusted to the thickness (e.g. using the 80° V-mold to make a 6mm plate). |
| Deep stamping | 0.6mm-3mm | The material elongation rate should be ≥20% (such as aluminum alloy 5052). |
The sheet metal gauge chart will indicate the recommended thickness range for different processes, such as 0.8mm-3mm for aluminum sheet metal (1060) bending.
3.Balance cost and material utilization
- Thin plates (≤1mm): Low cost but easily deformed, suitable for large quantity of load bearing components (e.g. computer chassis).
- Thick plates (≥4mm): Material costs and processing difficulty are high and require optimal selection through gauge chart (e.g. replacement of 4mm plates with 3mm plates and reinforcement).
- Economic Thickness: Refer to industry-standard sheet metal specifications, such as the commonly used 1.0mm-1.5mm galvanized sheet metal in the automotive industry, to balance strength and cost.
4.Consider the impact of connectivity technology
- Welding: When plate thickness difference is more than 30%, step welding or groove treatment is required (e.g. cross-welding between 2mm and 1.5mm plates).
- Riveting: The total thickness of the plate ≤3 times the riveting diameter (e.g. M5 riveting for aluminum plates ≤1.5mm in thickness).
Sheet metal gauge chart application
| Material type | Gauge number | Actual thickness (mm) | Typical use |
| SPCC cold rolled steel | 18 | 1.2 | Electrical enclosures and shelves. |
| AL1100 aluminum sheet metal | 20 | 0.9 | Heat sink, electronic device casing. |
| SUS304 stainless steel | 16 | 1.0 | Medical equipment, food equipment. |
What are the reasons for choosing JS sheet metal fabrication?
1.Production accuracy and quality control
JS uses imported laser cutting equipment with accuracy of ±0.005mm, far exceeding industry standards (traditional sheet metal fabricators is typically ±0.02mm), especially for precision electronics (such as cell phone heat sinks) and aerospace components, and solves the deformation problem of high-strength steel and aluminum alloys.
| Comparison items | JS sheet metal fabrication | Other sheet metal fabricators |
| Cutting accuracy | ±0.005mm (laser cutting) | ±0.02mm-0.05mm (traditional CNC stamping machine) |
| Rebound compensation accuracy | AI algorithm compensation, error ±0.01mm. | Manual adjustment, error> 0.1mm. |
| Surface quality | Thermal effect zone<0.1mm, no burrs. | The burrs were obvious and needed polishing. |
2.Speed of delivery and productivity
JS standardized orders can be delivered within 1-2 weeks and urgent orders can be returned within 24 hours, with a 30% reduction in wait times. Multi process collaboration (cutting+bending+welding) is achieved synchronously, increasing overall efficiency by 30% -50%.
| Comparison items | JS sheet metal fabrication | Other sheet metal fabricators |
| Standard delivery times | 1-2 weeks. | 3-4 weeks. |
| Small batch response | 24-hour express delivery. | Mold replacement takes 1-2 hours and is only suitable for mass replacement. |
| Process collaboration | Multi process parallel processing. | A single process is produced in stages. |
3.Material selection and cost optimization
There are more than 50 kinds of metallic and non-metallic materials in JS, and the material utilization rate is over 92%.
| Comparison items | JS sheet metal fabrication | Other sheet metal fabricators |
| Number of material warehouse | More than 50 varieties (including special boards). | 10-20 types(conventional metals only). |
| Material utilization rate | 92% + (remaining material intelligently matched). | 80-85% (depending on fixed-specification procurement). |
| Cost control | Recycling excess materials can reduce costs by 15%. | Material waste is widespread and systematic optimization is lacking. |
4.Technological innovation and process upgrading
JS introduces artificial intelligence vision correction system and self-bending devices to support complex surface shaping and provide integrated solutions.
| Comparison items | JS sheet metal fabrication | Other sheet metal fabricators |
| Technical Capability | AI corrects + automatically bends. | Manual adjustment is the main focus. |
| Process innovation | Support irregular parts/surfaces. | For flat/simple bending only. |
| Simulation verification | Built-in CAE simulation system. | No simulation capability, by trial and error. |
5.Global service capability
JS supports multilingual drawings and global logistics tracking (DHL/UPS dedicated line) and serves clients in more than 30 countries.
| Comparison items | JS sheet metal fabrication | Other sheet metal fabricators |
| Scope of services | Global delivery (more than 30 countries). | Local or regional markets only. |
| Communications support | Multilingual drawing and technical team. | English documents rely on third-party translation. |
| Delivery times | International orders take 4 to 6 weeks. | Subcontracting causes delays to third parties. |
Summary
In the field of industrial manufacturing, sheet metal fabrication has become an indispensable technical pillar in modern industrial system due to its diverse process and extensive application scenarios. Sheet metal processing involves cutting, sheet metal bend, stamping, welding and other core processes, sheet metal sheets into a functional and aesthetic combination of structural components. Whatever the material, the perfect balance can be achieved through process optimization and material selection.
JS Precision Manufacturing has 20 years of industry experience and an intelligent production system that pushes traditional sheet metal processing to a new level. It redefines the technical boundaries and value standards of sheet metal processing by providing global customers with one-stop solutions ranging from prototype design to mass production with extreme precision, adequate material adaptability and green manufacturing concepts.
Disclaimer
The content of this page is for informational purposes only.JS SeriesNo representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, are made as to the accuracy, completeness or validity of the information. It should not be inferred that the performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features,material quality and type or workmanship that the third-party supplier or manufacturer will provide through the jusheng network. This is the responsibility of the buyerAsk for a quote for partsto determine the specific requirements for these parts.please Contact us Learn more information.
JS Team
JS is an industry-leading companyFocus on custom manufacturing solutions. With over 20 years of experience serving more than 5,000 customers,we focus on high precisionCNC machining,Sheet metal fabrication,3D printing,Injection molding,metal stamping,and other one-stop manufacturing services.
Our factory is equipped with more than 100 state-of-the-art 5-axis machining centers and is ISO 9001:2015 certified. We provide fast, efficient and high-quality manufacturing solutions to customers in more than 150 countries around the world. Whether it's low-volume production or mass customization, we can meet your needs with the fastest delivery within 24 hours. chooseJS TechnologyIt means choosing efficiency, quality and professionalism.
To learn more, please visit our website:jsrpm.com
FAQs
1.What is the general accuracy of sheet metal processing?
Laser cutting up to ±0.005mm, CNC bending up to ±0.02mm, traditional stamping up to ±0.1mm. High-end equipment combined with AI algorithms can break through micron level accuracy and meet high-demand scenarios such as precision electronics and aerospace.
2.What's the difference between laser cutting and traditional stamping?
High precision Laser cutting (±0.02mm), no mold required, suitable for irregular holes. Punching depends on die, low cost, suitable for large-scale wire cutting.
3.Why does the automotive industry heavily use sheet metal fabrication?
With its lightweight, high strength and high efficiency, the automobile industry relies on sheet metal processing to quickly form complex components such as bodywork and chassis, while taking into account cost control and large-scale production needs.
4.Why is sheet metal fabrication considered green manufacturing?
Sheet metal processing reduces pollution and waste by increasing material utilization (waste), low energy consumption and environmental protection measures. Realize resource recycling and cleaner production in conjunction with ISO 14001 certification.
Resources
Digital modeling and fabrication