Технология 3D-печати изменяет логику производства цифровым производством. From rapid prototyping of industrial gears and custom skeletons for medical use to lightweight components for racing engines, it continues to push the boundaries of Производство. как связь между проектированием и производственными моделями, 3D-принципиальными моделями становятся эффективными для действий. JS предоставляет профессиональные услуги печати. href = "https://jsrpm.com/blog/how-does-3d-printing-work"> FDM, SLA, SLS и процессы печати металлов , поддержка всего, от разработки прототипа до производства небольших партий и помогая инновациям.
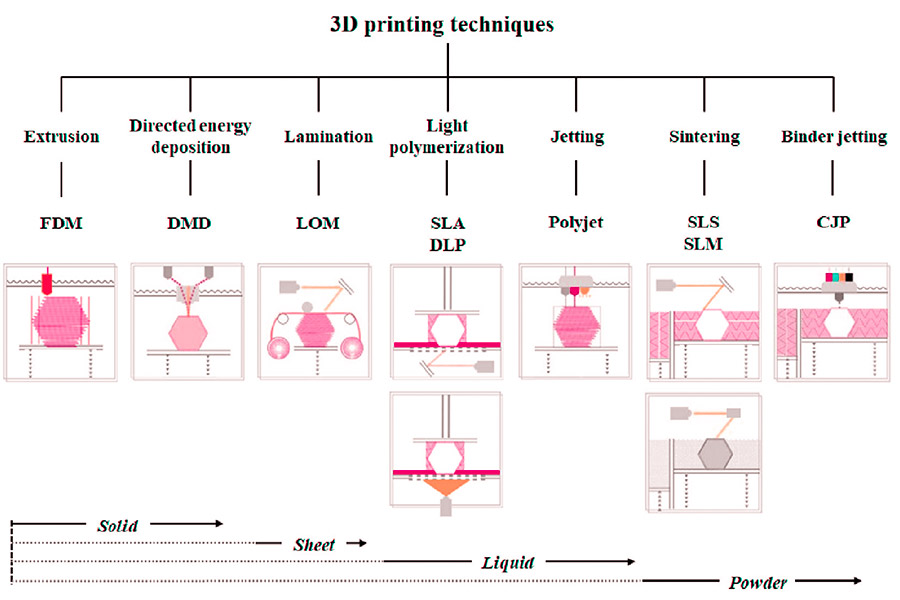
Каковы типы технологий 3D-печати?
1.fused Осаждение моделирование (FDM)
- Принцип: формование расплавленного осаждения, нагревающим слоем пластикового волокна при экструзии слоя.
- Особенности: низкая стоимость, подходит для быстрого прототификации , эффективный процесс производства JS может оптимизировать свою скорость.
2.sterolithography (sla)
- Принцип: Технология отверждения УФ, жидкая смола образуется путем отверждения УФ.
- Особенности: высокая точность (± 0,05 мм), гладкая поверхность, подходящая для сложных конструкций, удовлетворение требований к точке JS.
3. Селективное лазерное спекание (SLS)
- Как это работает: лазерный нилоновый порошок не требует структуры поддержки.
- Особенности: Высокая прочность, подходящая для функциональных деталей, совместимость металла/композитного материала JS может расширить свой диапазон применения.
4. data-translateid="674f16ec91bb64dd43699554f95f99f4" data-pos="2" data-len="23" data-v-7b79c893="">Multi Jet Fusion (MJF)
- Как это работает: Слияние струйного порошка, затвердевание слоя нейлонового порошка за слоем посредством плавления и инфракрасного нагрева.
- Поддержка. Быстрая оптимизация производства и затрат.
5.
- Как это работает: Металлическая порошковая лазерная плавление для высококачественного производства.
- Особенности: высокая точность (± 0,02 мм), высокая температурная сопротивление, технология точной обработки JS может еще больше улучшить качество продукта.
Relationship between layer thickness and mechanical strength 1. Чем толще слой, тем слабее межслойная адгезия
Тип техники
speed
Стоимость
Тип материала
Возможность обработки сложности
связанные преимущества компании JS
fdm
medium
low
пластмассы, такие как PLA и ABS.
★★★ ☆
Эффективная скорость оптимизации производственных процессов.
sla
Fast (dlp)
center
фоточувствительная смола.
★★★★ ☆
Высокая точность, соответствующая js ± 0,005 мм.
sls
medium
center
Нейлон, TPU и другие порошки.
★★★★ ☆
Поддержка расширения металлических/композитных приложений.
mjf
Чрезвычайно быстро
средний
Нейлон (PA12/PA11).
★ ★ ★ жела
Повышение эффективности производства партий для быстрой доставки.
slm
медленный
Tall
Металлический порошок (титан, нержавеющая сталь).
★ ★ ★ жела
Технология точной обработки обеспечивает высокую сложность деталей.
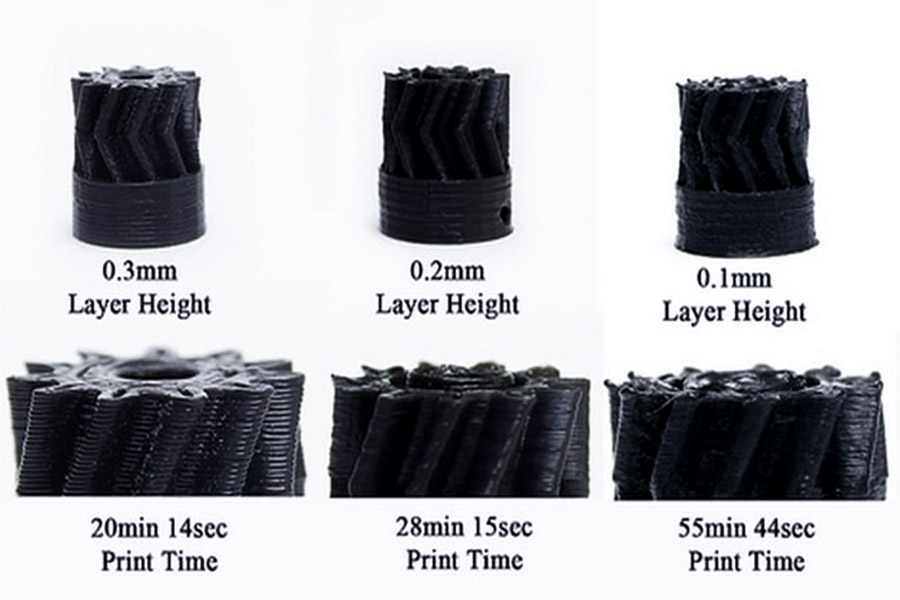
 Каково влияние толщины слоя печати FDM на прочность?
Каково влияние толщины слоя печати FDM на прочность?
- Маленькая толщина слоя, такая как 0,05 мм, уменьшайте зазор между слоями, что делает поверхность более гладкой и внутренней структурой более равномерной. Diseser Diseserse и Disperse Spasseres и Diseserse Specesse и Span Data-V-7B79C893 = "> Таким образом, увеличение воздействия.
- JS Case: во время печати Service аэрокосмических частей, JS управляет толщиной слоя печати.
Effect of layer thickness on printing direction
- Прочность деталей FDM является анизотропным, то есть вдоль направления печати (ось Z) обычно более сильнее, чем вертикальное направление (ось XY). If the loading direction is perpendicular to the layer, thin layer Печать снижает риск наслоения, в то время как толстые слои могут сломаться из -за слабых соединений между тонкими слоями.
- Решение: Профессиональная команда JS Professional Will рекомендую наиболее оптимальную комбинацию направления печати и толщины, чтобы максимизировать силу конструкции, основанную на требованиях проекта продукта.
баланс между толщиной слоя и свойствами материала
1. Слои.
Выбор толщины слоя в реальных приложениях 1. Функциональные части против отображения деталей 2. Материальная адаптация class = "предложение". Data-TransLateId = "67A9AA2DE38208C3575FD6CDDE054B37" DATA-POS = "0" DATA-LEN = "49" DATA-V-7B79C893 = "">

Какие параметры определяют разрешение печати SLA?
- Источник лазерного света: точечный диаметр, как правило, 10-100 микрон, подходящий для ювелирных изделий, стоматологии и других модели с высокой предпринимательской.
- DLP Источник света: спеку света прогнозируется через цифровой проектор, а размер пикселей определяет разрешение (например, 50-100 микрон для проекции 2K/4K).
.- Воздействие: чем меньше размер спеклей, тем лучше детали оси x/y, но время печати может увеличиться.
2. data-translateId = "9C8D0C9D004D7EAA4D3D8DB94A4466E7" data-pos = "3" data-len = "32" Data-V-7B79C893 = ""> скорость сканирования и время воздействия
3. толщина слоя (разрешение оси Z)
- Диапазон толщины слоя варьируется от 25 до 100 микрон. Например, 50 микрон для быстрого прототипа и 25 микрон.
4. Свойства смолы
5. Сложность геометрии модели
- Структуры и отверстия нависания требуют дополнительной поддержки или многоуровневых корректировок стратегии, которые могут быть за счет локального разрешения.
- Метод оптимизации: Структура адаптивной поддержки создается с помощью программного обеспечения для нарезки модели.
Сравнение параметров и таблица предложений оптимизации
<таблица стиля = "Пограничный коллапс: коллапс; ширина: 100,191%; ширина границы: 1px; пограничный цвет: #000000; высота: 434,547px;" border = "1">By properly selecting parameter combinations, the 3D printing model can achieve precise manufacturing from concept verification to functional prototypes.
Which printing technology is more stable in high temperature environments?
1.3D printing of metallic materials (high temperature environment preferred)
SLM/DMLS (selective laser melting/sintering)
- Heat resistance: Materials such as titanium alloy (Ti6Al4V, melting point 1668°C) and nickel-based superalloys (Inconel 718, melting point 1390°C) can withstand high temperatures for longer than 600° C.
- Stability: The laser melts the metal powder layer by layer, the tissue is compact, and the resistance to creep is strong.
- 3D printing service support: Printing shops reduce residual stress and prevent thermal deformation by optimizing laser power, scanning speed and cooling strategies.
2.Ceramic 3D printing technology (ultra-high temperature resistance potential)
SLA/DLP (light-curing ceramics)
- Heat resistance: Alumina (Al2O3, melting point 2050°C) and zirconium oxide (ZrO2, melting point 2700°C) ceramics can withstand temperatures above 1500°C.
- Stability: Ceramic blanks require high temperature sintering (above 1600°C), density is close to theoretical values, and thermal expansion coefficient low.
- 3D Printing Service Support: Printers provide a complete range of services from printing to degreasing and sintering to ensure that ceramic parts are fissure-free and size stable.
3.High-Performance engineering plastic 3D Printing
FDM (Molten deposition modeling)
- Heat resistant materials: PEEK (melting point 343°C), ULTEM (melting point 335°C) and other special engineering plastics.
- Stability: PEEK retains strength after prolonged use at 260°C, but printing temperature (280-320°C) and cooling conditions need to be optimized.
- 3D printing service support: Printing shops use industrial-grade FDM equipment (such as Stratasys Fortus series) with thermostats to reduce warping.
SLS (selective laser sintering)
- Heat resistance: Nylon + fiberglass/carbon fiber composites with a short-term temperature resistance of up to 180°C.
- Stability: Laser sintering is compact, but oxidizes easily at high temperature for a long time and requires surface coating protection.
- 3D printing service support: Printing shops provide material modification services (such as adding flame retardants) to improve temperature resistance.
- Advantages: Plastic 3D printing is low cost, short cycle time, suitable for medium and high temperature environments (e.g. automobile intake manifolds, electronic radiator, etc.).
Technology selection recommendations for high temperature scenarios
<таблица стиля = "Пограничный коллапс: коллапс; ширина: 100%; ширина границы: 1px; пограничный цвет: #000000;" border="1">How to achieve layered stacking in 3D ink jet printing?
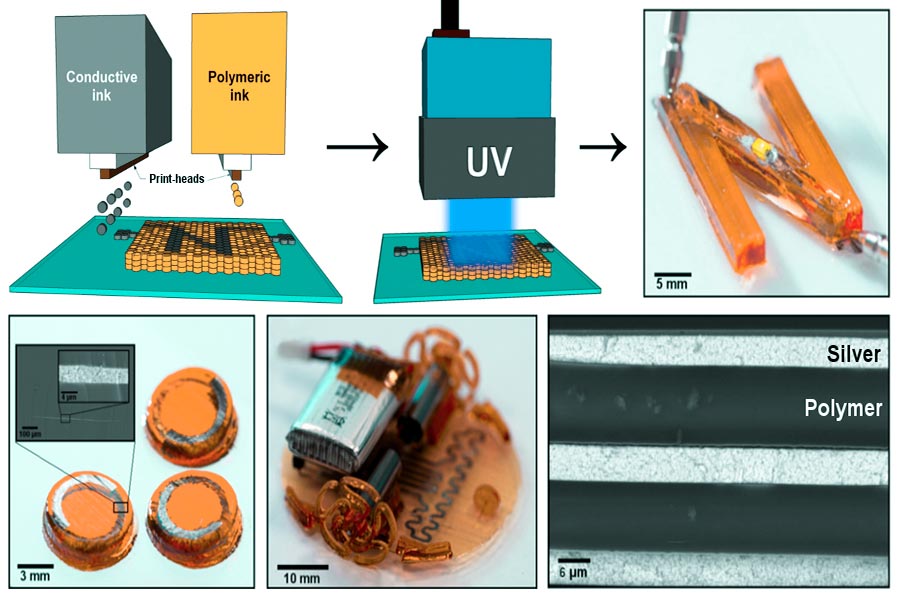
Ink jet printing technology is by layering liquid material on top of each other to create three-dimensional objects. Its core lies in high high-precision jetting and curing контроль. Specific implementation steps and key technologies are as Следует:
1.Preparation of materials: Adaptation of liquid media
- Photosensitive resin: The most commonly used material that requires fast curing and high viscosity stability.
- Support material: Water-soluble or fusible material used to temporarily support complex structures.
- Ink jet printing optimization: The injection accuracy of the nozzle (usually 20-100 microns in diameter, for example) needs to be adjusted by adjusting parameters such as viscosity of the material and surface tension.
2.Ink jet print head: Precision droplet injection
Piezoelectric drive or thermal foaming technology:
- Piezoelectric ceramics: The piezoelectric ceramic deformed by voltage changes, and ink cavity are compressed to produce tiny droplets.
- Thermal foaming: Local heating of ink to form bubbles, promote droplet spray.
- Multi-nozzle collaboration: Industrial-grade inkjet print heads integrate hundreds of nozzles to achieve a single sweep over a large area.
- Layered path planning: Software slices 3D models into 2D segments, and the inkjet head spray layers of material along the path.
3.Layer by layer stacking: droplet solidification molding
- Photocuring (UV/LED):
- After each layer of liquid resin is sprayed, solidify with UV light or LED light immediately to form a solid thin layer.
- Accurate control: Light intensity and exposure time need to be matched to the solidification characteristics of the material (e.g. SLA/DLP technology).
- Thermal curing: Some materials (such as some nylon powder binders) are heated to initiate cross-linking reactions.
- Multi-layer stacking: Repeat spray curing process until three-dimensional structure is complete (layer thickness is usually 20-100 microns).
4.Post-treatment: enhancement and surface optimization
- Support structure removal: Dissolve or melt temporary support material.
- Surface treatment: Grinding, sanding or chemical polishing to eliminate step effect.
- Late-stage maintenance: Some materials require secondary curing to improve mechanical performance.
How to choose supporting materials for complex 3D printing models?
1.Structural adaptation principle
Overhang structure (>45°):
- PVA/HIPS: Soluble scaffold for water solubility or solvent removal.
- Example: In 3D models printing of inclined bridges, PVA support can be removed by water solubility to prevent tool damage to detail.
Bridge structure (long span):
- ABS/nylon support rods: High temperature resistant to breakage during printing (such as robotic arm model).
- For example, HIPS support can withstand high temperatures when printing grids in 3D models printing to prevent breakage during printing.
2.Matching and separation of materials
Easy peel combination:
- PLA+PVA: Low adhesion, smooth finish.
- Example: The 3D models printing transparent resin model matched the PVA support and dissolved in water without residue.
Chemical dissolution combination:
ABS+HIPS: Lemonin is needed to dissolve the scaffold and is suitable for complex internal parts such as gear components.
3.Actual performance requirements
- Heat Scenario: Ceramic/metal supports: high temperature resistant (e.g. titanium alloy printing) requiring mechanical peeling.
- Shrinkage control: The material shrinkage rate of the supporting material is closer to that of the model material (e.g. PETG + PETG support).
4.Post-treatment efficiency
Quick removal:
- Water-soluble (PVA): Suitable for medium and small size printing, shortening post-treatment time (medium and small size preferred).
- Manual peeling (TPU): Low cost but requires fine handling.
Environmental Protection Plan: It is advisable to select biodegradable scaffolds (e.g. PBDE-based biodegradable materials) to reduce waste liquid treatment costs.
5.Printer adaptation
FDM equipment:
- Co-Supported: PLA/PVA/HIPS, optimize separation effect, optimized separation by adjusting nozzle temperature.
- Example: 3D models printing hollow spheres with HIPS support, acetone vapor smooth surface.
SLA/DLP equipment:
- Supported by soluble resin, it was cured by ultraviolet light and then soaked and removed directly.
- For example, when 3D models printing precision gears, resin supports retain microscopic detail.
Can JS achieve functionally graded components through multi material 3D printing?
1.Multi-material printing technology support
JS's 3D printing services include MJF and composite metal/ceramic printing technologies, which can switch different materials (e.g. metal-ceramic, carbide-polymer) during the same printing process to achieve continuous or segmented gradient changes in material composition.
2.Material compatibility and gradient design
Through JS's 3D printing services, customers can choose from a variety of material combinations, including metals, ceramics and composites, and freely design the microstructure of functional gradient components (such as abrasionresistant + substrate layer).
3.Process optimization and performance assurance
JS's industrial-grade equipment supports thickness control (±0.005mm) and temperature management to ensure uniform interface bonding strength and gradient transition across different materials and meet extreme working conditions such as high temperature and pressure.
4.Customized solutions
For areas such as aerospace and medical devices, JS's team can provide a full range of services, from material selection and gradient structure design to reprocessing, such as:
- Aerospace engine parts: Titanium alloy substrate gradient structure + ceramic thermal barrier coating.
- Orthopedic implants: Metal skeleton biomimetic design + bioactive ceramic coating.
Summary
As a disruptive technology, 3dprinting continues to drive change in manufacturing with its diverse process types (e.g. FDM, SLA, metal printing, etc.) and a wide range of application scenarios (from industrial manufacturing to medical innovation). Whether it is the efficient production of complex functionally gradient parts or the rapid iteration of custom models, 3D printing services demonstrate irreplaceable flexibility and economy. Technology service providers represented by JS have further lowered the technology threshold by integrating multi-material printing, precision process control and industry-wide chain support, allowing businesses to focus on design innovation and value creation.
Disclaimer
The content on this page is for general reference only. JS Series makes no express or implied warranties regarding the accuracy, timeliness, or applicability of the information provided. Users should not assume that the product specifications, technical parameters, performance indicators, or quality commitments of third-party suppliers are completely consistent with the content displayed on this platform. The specific design feature, material standards, and process requirements of the product should be based on the actual order agreement. It is recommended that the purchaser proactively request a formal quotation and verify product details before the transaction. For further confirmation, please contact our customer service team for professional support.
JS Team
JS is an industry leading provider of customized manufacturing services, dedicated to providing customers with high-precision and high-efficiency one-stop manufacturing solutions. With over 20 years of industry experience, we have successfully provided professional CNC machining, sheet metal manufacturing, 3D printing, injection molding, metal stamping and other services to more than 5000 enterprises, covering multiple fields such as aerospace, medical, automotive, electronics, etc.
We have a modern factory certified with ISO 9001:2015, equipped with over 100 advanced five axis machining centers to ensure that every product meets the highest quality standards. Our service network covers over 150 countries worldwide, providing 24-hour rapid response for both small-scale trial production and large-scale production, ensuring efficient progress of your project.
Choosing JS Team means choosing manufacturing partners with excellent quality, precise delivery, and trustworthiness.
For more information, please visit the official website: jsrpm.com
FAQs
1.Does SLS printing require support?
SLS printing usually does not require support. The unsintered nylon powder will naturally envelop the model to avoid collapsing in the air. Only a few complex designs require a small amount of ancillary support, which greatly simplifies the reprocessing process.
2.Which technology is suitable for printing transparent parts?
SLA technology is suitable for printing transparent parts. It uses photosensitive resin that hardens under UV light. The surface is smooth and transparent. Suitable for making high precision transparent model (such as optical parts).
3.What does the layer thickness of FDM affect?
The thickness of FDM layer influences surface smoothness, printing time and printing strength. The thicker the layer, the more visible the pattern, the faster the printing, but the intensity may be reduced.
4.How big a part can 3D printing make?
Industrial-grade 3D-printing devices can manufacture large parts of meters (such as aerospace parts), while desktop devices are usually limited to a few dozen centimeters and are suitable for small models or prototypes.