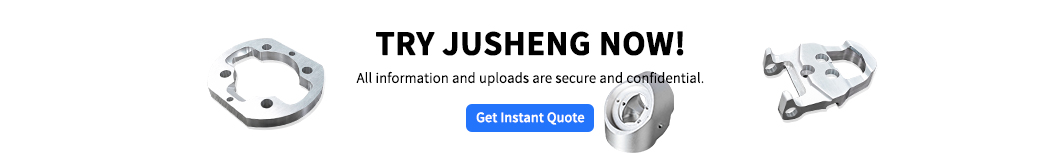
La tecnología de impresión 3D está remodelando la lógica de producción con la fabricación digital. FDM, SLA, SLS y procesos de impresión de metales , admitiendo todo, desde el desarrollo de prototipos hasta la producción de lotes pequeños y ayudar a las innovaciones a tierra.
1.Fused modelado de deposición (FDM) 2.stereolitography (sla) 3. sinterización láser selectiva (SLS) Cómo funciona: fusión del lecho de polvo de inyección, solidificación de la capa de polvo de nylon mediante la capa a través del calentamiento por fusión e infrarrojos.
5. fusión láser selectiva (slm) Comparación de 3D Printenting Tecnologías  ¿Cuáles son los tipos de tecnologías de impresión 3D?
¿Cuáles son los tipos de tecnologías de impresión 3D?
Tipo de técnica
velocidad
costo
tipo de material
Capacidad de procesamiento de complejidad
ventajas asociadas de la compañía JS
fdm
Medium
Low
plásticos como PLA y ABS.
★★★ ☆
Velocidad de optimización de proceso de producción eficiente.
sla
rápido (dlp)
Center
resina fotosensible.
★★★★ ☆
JS de alta precisión JS ± 0.005 mm.
sls
Medium
Center
nylon, tpu y otros polvos.
★★★★ ☆
Soporte de la expansión de aplicaciones de metal/compuesto.
mjf
extremadamente rápido
medianos-High
nylon (pa12/pa11).
★★★★★
Mejora de la eficiencia de producción por lotes para una entrega rápida.
slm
lento
tall
polvo de metal (titanio, acero inoxidable).
★★★★★
La tecnología de mecanizado de precisión garantiza una alta complejidad de las piezas.
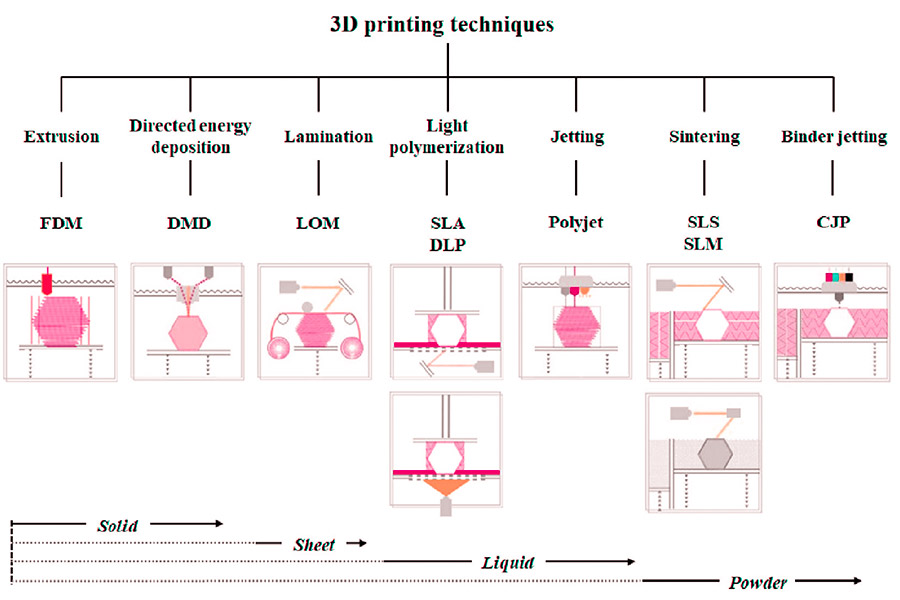
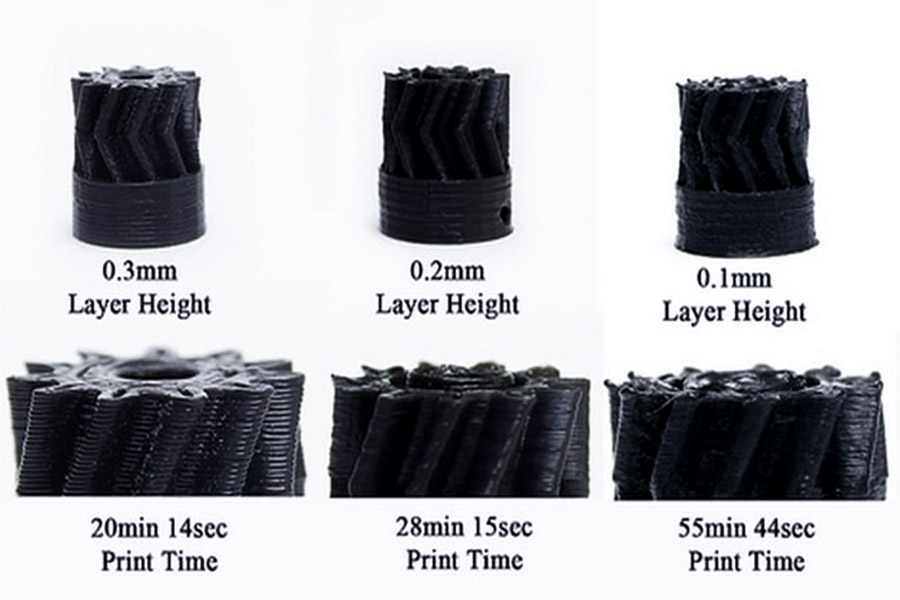
¿Cuál es el efecto del grosor de la capa de impresión FDM sobre la resistencia?
1. Cuanto más gruesa sea la capa, más débil es la adhesión entre capas
- En la impresión FDM, cada capa de plástico fundido debe estar completamente unido a la capa anterior. si el letrero (e.g. Más), el área de contacto entre la capa y la capa disminuye, lo que puede conducir a una disminución de la adhesión, especialmente cuando la dirección de fuerza es paralela al patrón de la capa (por ejemplo, pruebas de tracción).
- Sugerencia de optimización: JS Company predetermina un grosor de capa delgada de 0.1-0.2 mm en el servicio de impresión para 2. Cuanto más gruesa es la capa, la estructura más densa
- Espesor de capa más pequeño, como 0.05 mm, reduce el espacio entre las capas, lo que hace que la superficie sea más suave y la estructura interna más uniforme.
- JS Caso: durante la impresión Servicio de piezas aeroespaciales, JS controla el grosor de la capa de impresión el nivel de micrómetro para garantizar que los componentes cumplan con los estándares de resistencia aeroespacial.
La resistencia de las partes FDM es anisotrópica, es decir, a lo largo de la dirección de impresión (eje z), generalmente es más fuerte que la dirección vertical (eje xy). Solución: el equipo de ingeniería profesional de JS será recomendar la combinación más óptima de la dirección de impresión y grosor para maximizar la fuerza estructural basada en los requisitos de diseño de productos.
Balance entre el grosor de la capa y las propiedades del material
1. Las capas de espesas guardan material pero sacrifican la fuerza
- Las capas gruesas imprimen rápidamente y usan menos consumibles, haciéndolos adecuados para la prototipos rápidos, pero pueden carecer de fuerza debido a los defectos entre capas. Por ejemplo, al imprimir plástico ABS con un espesor de capa de 0.3 mm, la resistencia a la tracción puede ser 15% -20% menor que la de un espesor de capa de 0.1 mm.
- Optimización de costos: el servicio de impresión de JS utiliza algoritmos inteligentes para Recomiendo automáticamente la solución de grosor de capa más económica Al asegurar la fuerza, ahorrar a los clientes más del 30% de los costos materiales.
2. Las capas delgadas agregan resistencia pero tardan más en imprimir
- La impresión de capa delgada puede mejorar la resistencia, pero el tiempo de impresión obviamente aumenta.
- Tiempo de servicio de impresión Garantizado: JS utiliza un clúster industrial de impresoras múltiples, por lo que incluso si opta por capas ultra delgadas, puede enviar dentro de las 1-2 semanas prometidas.
selección de espesor de capa en aplicaciones reales
1. Partes funcionales vs. Mostrar piezas
- Piezas funcionales (como manijas de herramientas, piezas mecánicas): se recomienda el espesor de la capa de 0.1-0.2 mm, teniendo en cuenta tanto la resistencia como la eficiencia.
- Piezas de visualización (como modelos de apariencia): se puede seleccionar un grosor de la capa de 0.3 mm para reducir los costos y acelerar la entrega.
- Servicio personalizado: JS proporciona una consulta técnica gratuita y ajusta dinámicamente los parámetros de grosor de la capa según las necesidades del cliente.
2. Adaptación de propiedades de materia
- PLA/ABS: el grosor de la capa convencional es 0.1-0.3 mm, y las capas delgadas pueden mejorar el rendimiento de detalles.
- Materiales de nylon/compuestos: se recomienda un grosor de la capa de 0.05-0.15 mm para mejorar la tenacidad.
- Biblioteca de material de servicio de impresión: JS admite la impresión de más de 50 materiales, y cada material ha sido probado para detectar grosor de la capa para garantizar un rendimiento óptimo de resistencia.

¿Qué parámetros determinan la resolución de impresión de SLA?
1. Tipo de fuente de luz y tamaño de moteos
- Fuente de luz láser: el diámetro de la mancha es generalmente de 10-100 micras, adecuado para joyería, dentistería y otros modelos de alta precisión. DLP Fuente de luz: una mota de luz se proyecta a través de un proyector digital, y el tamaño de píxeles determina la resolución (por ejemplo, 50-100 micras para una proyección 2k/4K).
- Impacto: cuanto más pequeño sea el tamaño de las motas, mejor son los detalles del eje x/y, pero el tiempo de impresión puede aumentar.
Layer thickness (Z-axis resolution) Viscosidad: las resinas de baja viscosidad tienen buena fluidez, fácil de llenar pequeñas estructuras, pero la velocidad de curado debe equilibrarse.
Model geometry complexity Tabla de comparación de parámetros y sugerencia de optimización By properly selecting parameter combinations, the 3D printing model can achieve precise manufacturing from concept verification to functional prototypes. 1.3D printing of metallic materials (high temperature environment preferred) SLM/DMLS (selective laser melting/sintering) 2.Ceramic 3D printing technology (ultra-high temperature resistance potential) SLA/DLP (light-curing ceramics) 3.High-Performance engineering plastic 3D Printing FDM (Molten deposition modeling) SLS (selective laser sintering) Technology selection recommendations for high temperature scenarios Ink jet printing technology is by layering liquid material on top of each other to create three-dimensional objects. Its core lies in high high-precision jetting and curing control. Specific implementation steps and key technologies are as Sigue: 1.Preparation of materials: Adaptation of liquid media 2.Ink jet print head: Precision droplet injection Piezoelectric drive or thermal foaming technology: 3.Layer by layer stacking: droplet solidification molding 4.Post-treatment: enhancement and surface optimization 1.Structural adaptation principle Overhang structure (>45°): Bridge structure (long span): 2.Matching and separation of materials Easy peel combination: Chemical dissolution combination: ABS+HIPS: Lemonin is needed to dissolve the scaffold and is suitable for complex internal parts such as gear components. 3.Actual performance requirements 4.Post-treatment efficiency Quick removal: Environmental Protection Plan: It is advisable to select biodegradable scaffolds (e.g. PBDE-based biodegradable materials) to reduce waste liquid treatment costs. 5.Printer adaptation FDM equipment: SLA/DLP equipment: 1.Multi-material printing technology support JS's 3D printing services include MJF and composite metal/ceramic printing technologies, which can switch different materials (e.g. metal-ceramic, carbide-polymer) during the same printing process to achieve continuous or segmented gradient changes in material composition. 2.Material compatibility and gradient design Through JS's 3D printing services, customers can choose from a variety of material combinations, including metals, ceramics and composites, and freely design the microstructure of functional gradient components (such as abrasionresistant + substrate layer). 3.Process optimization and performance assurance JS's industrial-grade equipment supports thickness control (±0.005mm) and temperature management to ensure uniform interface bonding strength and gradient transition across different materials and meet extreme working conditions such as high temperature and pressure. 4.Customized solutions For areas such as aerospace and medical devices, JS's team can provide a full range of services, from material selection and gradient structure design to reprocessing, such as: As a disruptive technology, 3dprinting continues to drive change in manufacturing with its diverse process types (e.g. FDM, SLA, metal printing, etc.) and a wide range of application scenarios (from industrial manufacturing to medical innovation). Whether it is the efficient production of complex functionally gradient parts or the rapid iteration of custom models, 3D printing services demonstrate irreplaceable flexibility and economy. Technology service providers represented by JS have further lowered the technology threshold by integrating multi-material printing, precision process control and industry-wide chain support, allowing businesses to focus on design innovation and value creation. El contenido en esta página es solo para referencia general. js series No hace garantías expresas o implícitas con respecto a la precisión, puntualidad o aplicabilidad de la información proporcionada. Los usuarios no deben asumir que las especificaciones del producto, los parámetros técnicos, los indicadores de rendimiento o los compromisos de calidad de los proveedores de terceros son completamente consistentes con el contenido que se muestra en esta plataforma. La característica de diseño específica, los estándares de material y los requisitos de proceso del producto deben basarse en el acuerdo de pedido real. Se recomienda que el comprador solicite proactivamente una cotización formal y verifique los detalles del producto antes de la transacción. Para una confirmación adicional, Póngase en contacto con nuestro equipo de servicio al cliente para obtener soporte profesional. JS es un proveedor líder de la industria de servicios de fabricación personalizados, dedicado a proporcionar a los clientes soluciones de fabricación de una alta precisión y alta eficiencia. Con más de 20 años de experiencia en la industria, hemos proporcionado con éxito el profesional CNC Meckining, Manufacturing de metales, Tenemos una fábrica moderna certificada con ISO 9001: 2015, equipado con más de 100 centros avanzados de mecanizado de cinco eje para garantizar que cada producto cumpla con los estándares de la más alta calidad. Nuestra red de servicios cubre más de 150 países en todo el mundo, proporcionando una respuesta rápida las 24 horas tanto para la producción de prueba a pequeña escala como para la producción a gran escala, lo que garantiza un progreso eficiente de su proyecto. eligiendo js equipo significa elegir socios de fabricación con excelente calidad, entrega precisa y confiabilidad. 1.Does SLS printing require support? SLS printing usually does not require support. The unsintered nylon powder will naturally envelop the model to avoid collapsing in the air. Only a few complex designs require a small amount of ancillary support, which greatly simplifies the reprocessing process. 2.Which technology is suitable for printing transparent parts? SLA technology is suitable for printing transparent parts. It uses photosensitive resin that hardens under UV luz. The surface is smooth and transparent. Suitable for making high precision transparent model (such as optical parts). 3.What does the layer thickness of FDM affect? The thickness of FDM layer influences surface smoothness, printing time and printing strength. The thicker the layer, the more visible the pattern, the faster the printing, but the intensity may be reduced. 4.How big a part can 3D printing make? Industrial-grade 3D-printing devices can manufacture large parts of meters (such as aerospace parts), while desktop devices are usually limited to a few dozen centimeters and are suitable for small models or prototypes.
parámetros
impacto en la resolución
dirección de optimización
valor típico
tipo de fuente de luz
láser> dlp (el láser tiene mayor precisión en la misma resolución).
Elija láser para modelos de precisión y DLP para la producción en masa.
láser: 50 μm / dlp: 100 μm
tamaño spot
cuanto más pequeño sea el lugar, más claros son los detalles.
Use cabezales láser de alta precisión o proyección DLP 4K.
50 μm (láser)
velocidad de escaneo
cuanto más lenta sea la velocidad, más completa es el curado.
Reducir la velocidad en áreas finas (por ejemplo, 0.1 mm/s) y acelerar en grandes áreas.
50-200 mm/s
grosor de la capa
El grosor de la capa se reduce a la mitad y la resolución del eje z aumenta 4 veces.
Use capas delgadas (25 μm) para piezas de precisión y capas gruesas (100 μm) para un aumento de velocidad.
50 μm (estándar)
viscosidad de resina
La baja viscosidad mejora la capacidad de llenado de fluidez y detalle.
Use special resins (e.g. transparent resins with viscosity ≤1500cP).
500-2000cP
Model overhang angle
If the angle is too small, dense support is required, and blocking the light affects the curing.
Avoid <45° overhangs or add auxiliary supports in the design.
≥60° (unsupported)
Which printing technology is more stable in high temperature environments?
Scene temperature
Recommended Technology
ventajas de núcleo
Key capabilities of printing shops
600-1000℃
Metal SLM/DMLS.
High strength and creep resistance.
Laser equipment, vacuum environment, heat treatment.
1000-1500℃
Ceramic SLA/DLP.
Ultra high temperature resistance and corrosion resistance.
Specialized ceramic materials and high-temperature sintering process.
200-600℃
PEEK FDM, Nylon SLS.
Economy and lightweight.
Industrial grade equipment and material modification.
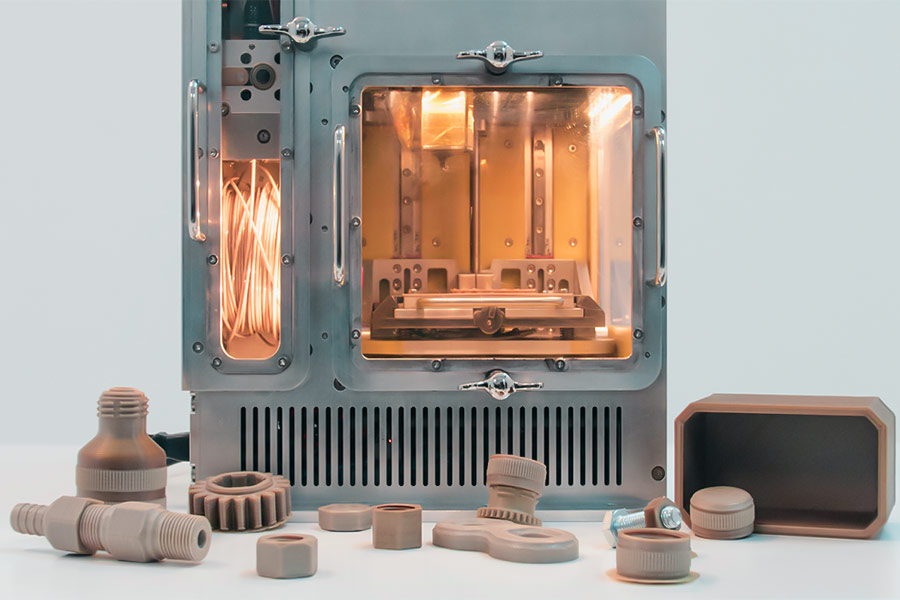
How to achieve layered stacking in 3D ink jet printing?
How to choose supporting materials for complex 3D printing models?
Can JS achieve functionally graded components through multi material 3D printing?
Summary
descargo de responsabilidad
JS Team
Para obtener más información, visite el sitio web oficial: jsrpm.com FAQs
Resources