CNC-machining, with its high accuracy and efficiency, has become the core technology in aerospace, automobile manufacturing, medical devices and other fields. Whether it is precision rotational shaping of metal parts in lathe machining or efficient forming of complex surfaces in mill machining processing, the selection of materials is always the key factor that determines the quality and processing cost of products. From aluminum alloy to stainless steel to carbon fiber composites, the hardness, toughness and thermal conductivity of each material directly affect tool's service life, cutting parameters and even the ultimate surface quality.
In this paper, the characteristics and selection logic of mainstream materials in CNC machining will be systematically analyzed to provide comprehensive guidance to practitioners from design to implementation.
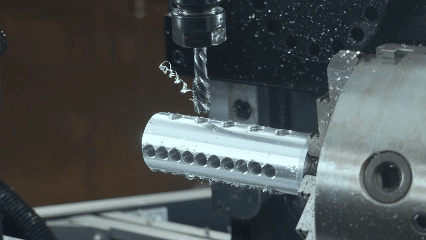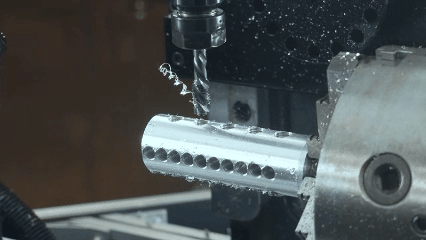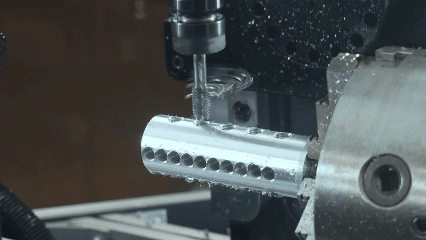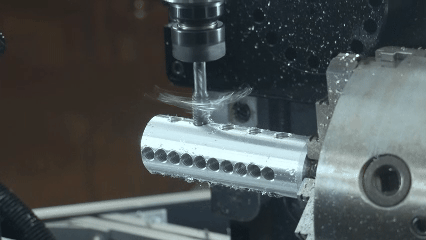
What is CNC machining?
CNC machining is a technology that realizes high precision automatic machining through computer numerical control. Its core lies to use pre programmed instructions to control the movement of the machine tool, lathe machining, mill machining, grinding machining and other machining forms. When milling, the tool can realize the formation of complex surface and precision structures by multiaxial axis linkage the workpiece. The machining is suitable not only for metal materials such as aluminum alloy and stainless steel, but also for non-metal materials such as plastics and composites. Whether mass production or small batch customization, CNC machining can optimize tool paths and cutting parameters and improve efficiency while ensuring surface quality and dimension consistency of parts.
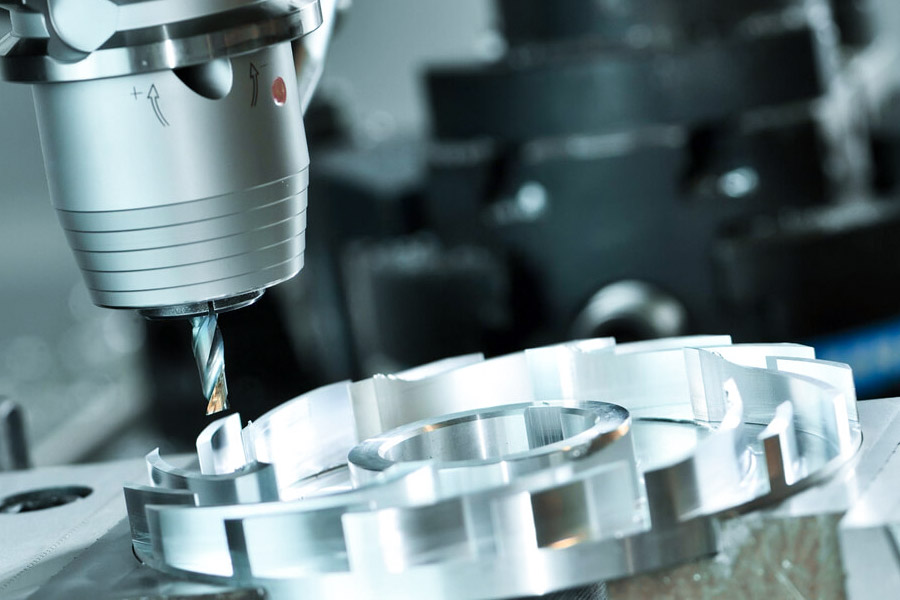

What are the most commonly used metal materials in CNC machining?
In CNC machining, the selection of metal materials directly determines the machining efficiency, precision and cost control of the finished product. The most commonly used classifications and characteristics of metallic materials are as follows:
1.Aluminum alloy (e.g. 6061, 7075)
Aluminum alloy has the advantages of light weight, high heat conductivity and excellent cutting performance, and has become the preferred material for machining CNC. Its low hardness characteristics reduces tool wear, making it particularly suitable for aerospace components such as brackets and housings, as well as light car parts such as wheels and hood. During processing, attention should be paid to the protection of oxide layer to avoid surface scratches.
2.Stainless steel (e.g. 304, 316L)
Stainless steel is commonly used in CNC machining for high corrosion resistance, such as medical devices (surgical instruments), food processing equipment, etc. Its high toughness may lead to a tendency to harden work, requiring a combination of high speed (1,000-2,000rpm) and low feed rate (0.05-0.2mm/r) parameters, as well as coolant, to reduce frictional heat.
3.Mold steel (e.g. S136, P20)
Mold steel is widely used in injection molding and die casting in machining CNC due to its high abrasion resistance and size stability. S136 is suitable for high mirror polishing requirements and P20 is suitable for rough machining of complex structures. Care should be taken to preheat during processing in order to reduce internal stress and avoid the risk of cracking.
4.Titanium alloy (e.g. Ti6Al4V)
Titanium alloy have become the core material of aircraft engine blades and orthopaedic implants due to their high weight ratio and high temperature resistance. In CNC-machining, specialized tools such as PCD or diamond coated milling cutters tools are needed and cutting parameters (speed<800rpm, feed rate<0.1mm/r) are optimized to inhibit tool choking.
5.Copper alloys (e.g. C18150)
Copper alloys have thermal conductivity and are ideal for 5G RF components copper heat sinks. During CNC machining, the cutting speed (200-400m/min) needs to be controlled to avoid oxidation of the material, and high pressure cooling technology is used to improve surface smoothness.
Technical point: The adaptability of different metal materials in CNC machining depends on the matching of physical properties and technological parameters. For example, aluminum alloys seek efficient cutting, while titanium alloys require a balance between accuracy and tool life. By using material databases and intelligent selection systems,such as the AI recommendation module developed JS company, most optimal processing solutions can be quickly matched.
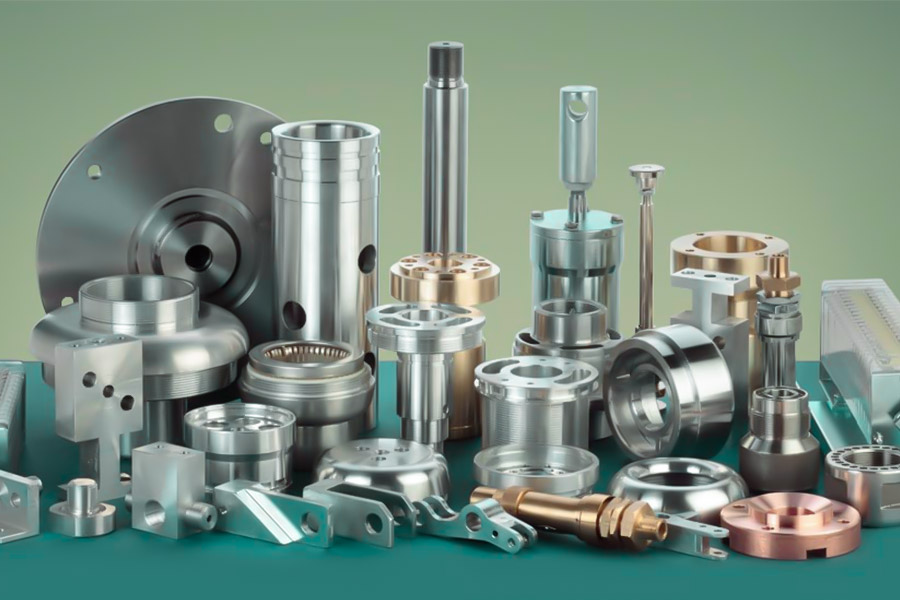

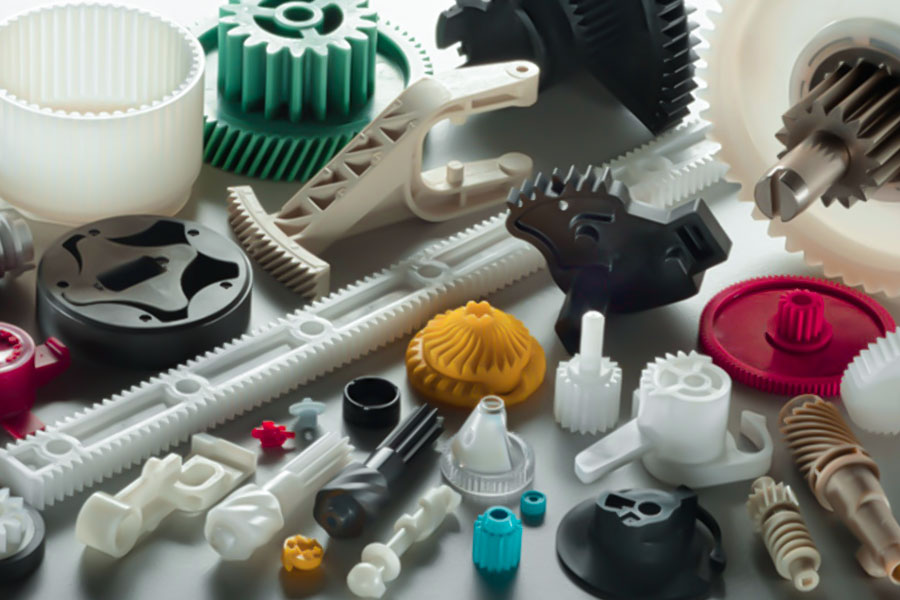
What are the basic classifications for common CNC machining of non-metallic materials?
In CNC machining, the classification of nonmetallic materials is mainly based on their chemical composition and physical properties. The basic classification and characteristics of common non-metallic materials are as follows:
1.Engineering plastics
- ABS: Good toughness, convenient processing, suitable for electronic shell, auto parts and so on. The cooling rate needs to be controlled during processing to prevent warping.
- PC (polycarbonate): High transmittance (over 90%), used in transparent shields and optical lenses to avoid stress cracking due to high temperatures.
- PEEK: High temperature resistance (above 250 °C) and good biocompatibility common to medical implants, as well as the need to control moisture absorption deformation during processing.
2.Composite materials
- Fiberglass reinforced nylon: Hard and lightweight, used in drone frames and car structures to avoid layering caused by direct contact between cutters and fibres.
- Carbon fiber epoxy: Excellent strength to weight ratio, suitable for aerospace components, requires diamond coated tools to reduce wear and tear during processing.
3.Ceramic materials
- Alumina ceramics: Good insulation and high hardness for electronic substrates and abrasionresistant cushions. Micrometer level precision required for grinding through diamond grinding wheels.
- Silicon nitride ceramics: Used for gas turbine blades high temperature resistance, high thermal shock resistance, processing needs to adopt ultrasonic assisted cutting technology.
4.Rubber and elastomers
- Silicone: High elasticity, anti-aging, used for sealing and medical catheters. Low speed (<500rpm) is required during processing to prevent material tearing.
- PU(Polyurethane): Abrasion and tear resistant, used in car floor mats and industrial cushioning components to avoid material deformation caused by high temperature.
Technical point: The processing of non-metallic materials needs to adjust process parameters according to material characteristics. engineering plastics, for example, need to control cutting heat to prevent deformation, while composite materials need to optimize tool paths to avoid layering. By using JS's material database and process simulation tools, the best processing scheme can be quickly matched.

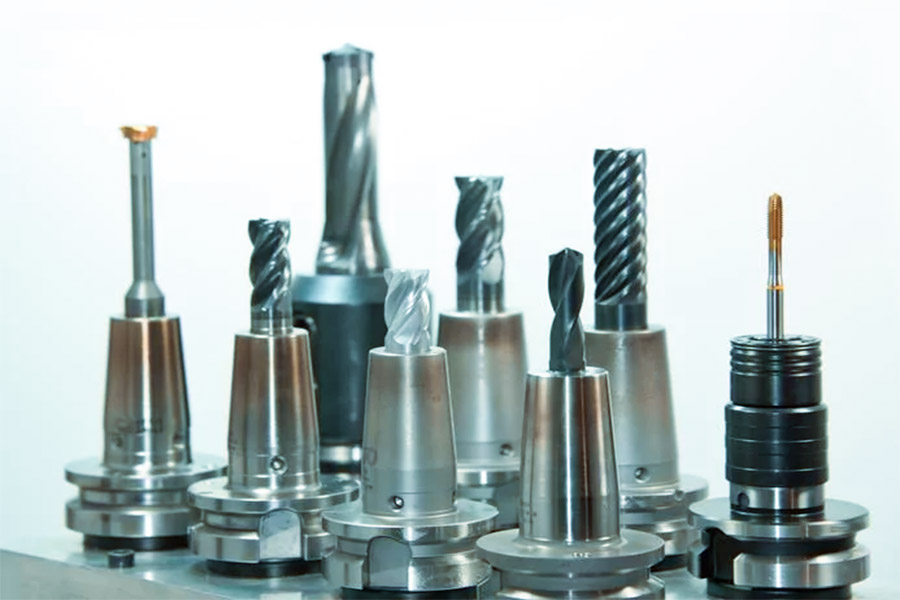
How to choose CNC cutting tools and machining parameters based on material hardness?
1.Classification of hardness and processing characteristics of materials
According to the material hardness (HRC Rockwell hardness), there are three kinds of processing objects. Different hardness has different effects on tool wear, cutting force and machining accuracy:
| Hardness Range (HRC) | Typical materials | Processing difficulties | JS technology response strategy |
| Low hardness (HRC<30) | Aluminum alloy, copper alloy, plastic. | Accumulation of cutting heat and surface oxidation. | Optimize coolant+high-speed cutting process. |
| Moderate hardness (HRC 30-50) | Stainless steel, quenched and tempered steel. | Cutlass and workpiece hardening. | Coated tools + Staging. |
| High hardness (HRC>50) | Hardened steel, cast iron, hard alloy. | Tools wear quickly and cutting force increases rapidly. | CBN cutting tool+specialized fixture design. |
2.Tool material and processing parameter matching table
Based on the summary of JS company long term practice, the following solutions are recommended in conjunction with machining lathe scenarios:
| Hardness grade | Recommended tool material | Cutting speed (m/min) | Feed rate (mm/r) | Cutting depth (mm) | JS Technology Highlights |
| Low hardness | Coated hard alloy (TiAlN) | 200-400 | 0.2-0.5 | 1-3 | Multi axis linkage control with surface roughness ≤0.8μm. |
| Medium hardness | Fine grained hard alloy (YG8) | 80-150 | 0.1-0.3 | 0.5-2 | Thermal deformation compensation technology with accuracy ±0.01mm. |
| High hardness | CBN cutting tools (cubic boron nitride) | 50-120 | 0.05-0.2 | 0.1-0.8 | Specialized fixtures can reduce vibration and prolong service life three times. |
3.Technical advantages and practical validations of JS
Tool customization:
- Provide nano-coated cutting tools (such as TiAlN, DLC) with up to over 50% wear resistance.
- Support customers to customize special geometry cutting tools (such as spiral blades, wavy blades, etc.).
Intelligent optimization of process parameters:
- Automatically avoid the risk of tool interference by using CAM software to simulate cutting process.
- machining lathe adaptive feed control is adopted to improve the efficiency by 20%.
Materials database support:
- There are 50+ material processing parameter libraries (including metals, plastics and composites).
- Real-time updates on industry-leading materials such as high-performance plastics such as PEKK and PEI.
Quality assurance system:
- CMM full inspection with size tolerance of ±0.005mm.
- Provide cutting parameter verification report to reduce customer trial and error cost.
4.Operational tips and caveats
- Cutting verification: Even if the parameters match, 200mm x 200mm cutouts still need to be processed to test surface quality.
- Tool life monitoring: Cutting force monitoring system (JS system alarm threshold adjustable) for tool wear alarm.
- Environmental control: In the process of processing high hardness materials, the temperature of the workshop (± 2℃) is stable to avoid the hot expansion and cold shrinkage affecting accuracy.

How to solve the tool wear problem of titanium alloy materials in CNC machining?
1.The main causes of wear of titanium alloy tool
- Hardness and work hardening tendency: Titanium alloys (such as Ti-6Al-4V) are prone to work hardening during cutting, resulting in rapid wear and tear tool edges.
- Low heat conductivity: Heat is concentrated in the point of contact of the tool, which exacerbates high temperature softening and chemical wear.
- High chemical activity: Titanium alloy are prone to chemical reactions with tool materials, resulting in adhesive wear (adhesion phenomenon).
2.Targeted solutions and implementation approaches
Combining the technical points of different machining stages, the optimization strategy of JS titanium alloy machining tool wear is introduced below:
| Causes of wear | Solution | Implementation method | Effect evaluation |
| Work Hardening | Use superhard tool materials. | Use cubic boron nitride (CBN) or diamond coated cutting tools with hardness ≥ 40GPa were used. | Knife life is 2-3 times longer. |
| Low thermal conductivity |
Optimization of cooling process. |
High pressure micro lubrication + internal (MQL) + internally cooled cutting tools with coolant pressure ≥ 10MPa. | Reduce cutting temperature by -50%. |
| Chemical bonding wear | Coating technology. | TiAlN/TiCN composite coating thickness of 2-5 μm and friction coefficient <0.3. | The surface roughness ≤ 0.8μm decreased knife viscosity. |
| Unreasonable cutting parameters | Optimization. | Reduce spindle speed (200-400rpm), reduce feed speed (0.05-0.15mm/r) and increase the axial cutting depth (0.5-2mm). | Reduce cutting force fluctuations and improve processing stability. |
| The tool Insufficient geometric design | Improved blade shape and chip removal groove. | Spiral chip groove angles (30-45°) were optimized using large rake angles (15-20°) and negative blade inclination angle (-10-15°). | Smooth chip discharge reduces the risk of secondary cutting. |
3.Comparison of practical application cases
JS optimizes tool and process parameters, and the typical machining effect of titanium alloy is as follows:
| Indicator | Before optimization | JS optimized | Improvement range |
| Tool life (number of pieces) | 50-80 pieces | 150-200 pieces | ↑ 180%-250% |
| Surface roughness (Ra) | 1.6-3.2μm | ≤ 0.8μm | ↓ 50%-75% |
| Processing efficiency (pieces/hour) | 10-15 pieces | 25-30 pieces | ↑ 60%-100% |
| Cutting force (N) | 2,000-2,500 | 1,200-1,600 | ↓ 30%-40% |
4.Precautions and maintenance suggestions
- Periodically inspect tool wear: Changes in blade blade radius change when threshold ≥ 50μm) were monitored using an optical profilometer.
- Avoid the risk of tool breakage: When processing thin-walled parts to reduce feed speed, layered cutting strategy.
- Environmental control: Workshop temperature shall be stable at 20±2 °C and humidity ≤ 50% to prevent moisture absorption deformation of materials.
What are the effects of storage conditions for different materials on CNC machining?
1.Improper humidity control
- Metals (such as aluminum alloys and magnesium alloys): High humidity can easily lead to oxidation or corrosion of the material's surface, causing burrs or increasing surface roughness during processing. For example, if the oxide layer of aluminum alloy thickens in a humid environment, additional cutting depth or tool replacement is required.
- Engineering plastics (e.g. nylon, PC): After absorbing moisture, the material expands and the stability of the dimensions decreases, which may lead to deformation or size deviation of the processed parts.
2.Effects of temperature fluctuations
- Thermal expansion and shrinkage of sensitive materials (such as titanium alloys and Invar alloys): Temperature changes can lead to changes in material size, which can affect machining accuracy. titanium alloy, for example, expand at high temperatures, leading to tool path deviation during milling and requiring recalibration of machine tool parameters.
- Plastics (e.g. ABS, PEEK): Softens and deforms at high temperatures, increases brittleness at low temperatures, and is prone to cracking or layering during processing.
3.Insufficient packaging protection
- Surface scratches and contamination: If metal sheets are not coated with rust resistant paper or plastic sheeting, scratches during transport or storage can reduce the surface's smoothness and require additional polishing processes.
- Dust absorption: Carbon fiber composites are exposed to dust environments during processing. Impurities can become embedded inside the material and affect the strength of the structure.
4.Lack of anti oxidation measures
- Easily oxidizable metals (e.g. magnesium alloys and copper alloys): If not coated with rust oil or nitrogen protection, oxidation intensifies during processing and tool wear increases by 30%-50%.
- Solution: Use vacuum packaging or desiccant to absorb moisture from the environment and extend the material's shelf life.
5.Misclassification and storage
- Risk of cross-contamination: Mixing hard materials (e.g. tungsten carbide) with soft materials (e.g. polyethylene) may cause scratches on the surface and require separate storage in different areas.
- Physical damage: Excessive pile bar height may cause gravitational bending and affect the clamping stability during lathe machining.
The development trend of future CNC machining materials
1.Accelerate the popularization lightweight materials.
Aluminum alloy and magnesium alloy:
- Continue to replace traditional steel in automotive, aerospace and other fields by optimizing components such as high-strength aluminum alloy, magnesium alloys, and achieve 30%-50% weight loss.
- The improvement of CNC machining processes such as high-speed cutting and micro lubrication has further improved their machining efficiency.
Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer (CFRPs):
- It combines with a metal matrix to form a sandwich structure (such as carbon fiber+aluminum alloy) that balances strength and weight and is widely used in areas such as drones and racing cars.
- CNC machining needs to solve the problems of decolletage and burr, and promote the development of multi-axis coupling and special cutting tools.
2.Surge in demand for high-performance engineering materials
- Titanium alloy and superalloys: core materials used in extreme working conditions such as aviation engines and gas turbines. CNC machining needs to break through the bottleneck of high hardness and low thermal conductivity and promote the upgrading of CBN tool and cooling technology.
- Ceramic based composite materials: For semiconductor equipment and nuclear power components, specialized grinding processes and superhard cutting tools (such as diamond coatings) require to be developed.
3.The rise of sustainable and environmentally friendly materials
- Recycled metal materials: Improve the proportion of aluminum, copper and other metal shavings to be recycled and reused, and reduce the waste of raw materials through CNC netting.
- The biodegradable materials: PLA and PHA in consumer packaging is expanding. CNC machining needs to adapt to its low melting point and good moisture absorption characteristics.
Summary
In the field of CNC machining, material selection and application have always been the key factors to determine product performance and machining efficiency. From traditional aluminum alloys and titanium alloys to emerging carbon fiber composites, CNC machining has diversified the manufacture of precision parts by adapting to the physical properties of different materials. Metallic materials dominate industrial applications due their high strength and thermal conductivity, while non-metallic materials appear in light and extreme environmental scenarios.
In the future, with the increasing demand for lightweight, sustainable, and intelligent CNC machining will further integrate AI-driven material databases, multi-axis coupling processes, and green manufacturing technologies to drive breakthroughs in nano-precision and cross-material integration of machining lathe and machining mill, reshaping the boundaries of manufacturing in the future.
Disclaimer
The content of this page is for informational purposes only.JS SeriesNo representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, are made as to the accuracy, completeness or validity of the information. It should not be inferred that the performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features,material quality and type or workmanship that the third-party supplier or manufacturer will provide through the jusheng network. This is the responsibility of the buyerAsk for a quote for partsto determine the specific requirements for these parts.please Contact us Learn more information.
JS Team
JS is an industry-leading companyFocus on custom manufacturing solutions. With over 20 years of experience serving more than 5,000 customers,we focus on high precisionCNC machining,Sheet metal fabrication,3D printing,Injection molding,metal stamping,and other one-stop manufacturing services.
Our factory is equipped with more than 100 state-of-the-art 5-axis machining centers and is ISO 9001:2015 certified. We provide fast, efficient and high-quality manufacturing solutions to customers in more than 150 countries around the world. Whether it's low-volume production or mass customization, we can meet your needs with the fastest delivery within 24 hours. chooseJS TechnologyIt means choosing efficiency, quality and professionalism.
To learn more, please visit our website:jsrpm.com
FAQs
1.What should be paid attention to when processing plastic parts?
When processing plastic parts, cutting speed and feeding force must be reduced to avoid overheating and deformation. Compressed air is recommended for cooling to avoid cracking or discoloration caused by liquid residues.
2.How to determine when to replace CNC tools?
See if the color of the chip darkens, if the finish is rough, if there is a noise. If the tool is badly worn, it needs to be replaced to avoid chippings or reduce accuracy.
3.Why is it necessary to clean the material surface before CNC machining?
Remove oil stains or impurities from the surface of the material to prevent any impact on accuracy or damage to the tool during processing and to ensure smooth finish and accurate dimensions.
4.What to do if CNC machining aluminum parts is easy to stick to a knife?
Use coated cutting tools (such as TiN) to speed up and reduce feed rates and use a highly lubricating coolant to reduce friction and heat accumulation.
Resources