Stamp metal, as the core process of modern manufacturing industry, is constantly reshaping production methods in automobile, electronics, aerospace and other fields with its high efficiency, high precision and wide adaptability. Through the deep fusion of die design technology, stamping technology has advanced from traditional extensive manufacturing to precision intelligent manufacturing, from micrometer level precision precision complex curved surface forming to lightweight materials.
Its collaborative innovation with CNC machining, 3D printing and heat treatment not only overcomes the limitations of a single technology, but also gives rise to cutting-edge manufacturing models such as heterogeneous material integration and gradient functional structures, which provide the core for global manufacturing transformation and upgrading.
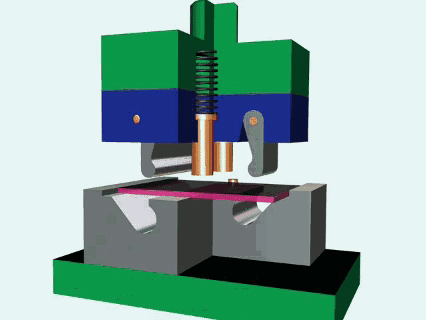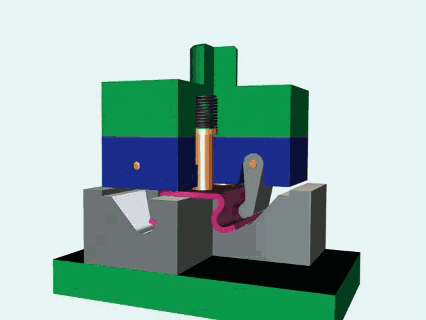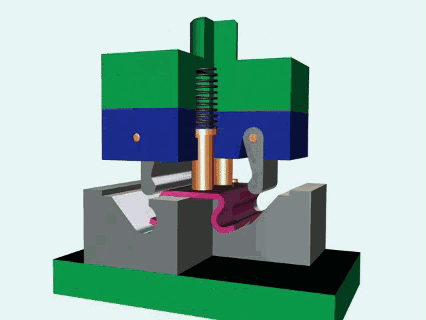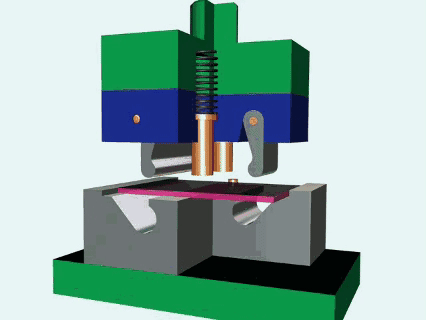
What is metal stamping?
Metal stamping is a kind of advanced manufacturing technology. By combining metal stamps with press, metal plate can be effectively processed into a specific shape. High hardness alloy steel is usually used to ensure consistency and surface quality of parts in mass production. The core of the die is to use the precise structure of the metal pressure, shear, bending, stretching and other deformation processes, widely used in automobiles, electronics, home appliances and other fields. Compared with traditional casting process, metal stamping has the advantages of high efficiency, energy saving and low cost, especially suitable for large-scale production. By optimizing mold design and stamping parameters (such as punch pressure and speed), material utilization can be greatly improved and subsequent processing steps can be reduced.
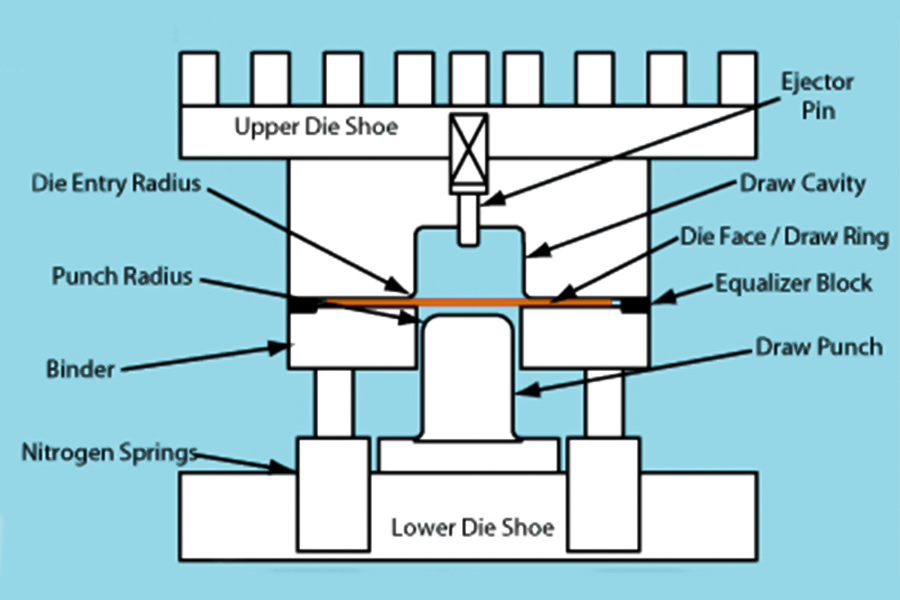
What are the processing steps for metal stamped?
Metal stamped is a process that effectively converts metal sheets into precision parts through a combination of die and press. Here are the core steps to take:
1.Preparation of materials
Select metal sheets (such as aluminum, steel, copper, etc.) according to product design requirements and determine thickness and specification. At this stage, the ductility, strength and surface condition of the material need to be considered to ensure the stability of the subsequent stamping process and the quality of the finished product. For example, car coverings typically use highly malleable alloy sheets, while electronic component casings prefer stainless steel to improve corrosion resistance.
2. Metal stamp design and fabrication
- Mold development: Engineers design metal stamps based on 3D drawings, including punch, die and guide mechanism. JS precision molds require CNC machining or wire cutting for precision ±0.005mm.
- Test die verification: Test die before formal production, adjust mold clearance, die speed and other parameters to ensure that die parts meet the size and surface quality requirements.
3. Stamping on Metal
This is a core process of applying pressure to the metal plate by using a press to drive the die to complete the following:
- Stamping: Separating materials, creating holes or contours (such as nameplates, terminals).
- Bending: Change the angle of the metal plate (e.g. U-shaped bracket).
- Drawing: To form a hollow or complex surface,such as car fuel tank.
- Joint stamping: Multiple processes (such as stamping and bending) are performed in a single molding to improve efficiency.
4.Post Processing Treatments
- Burr removal: To Eliminating sharp burrs from stamping edges by grinding, laser, or chemical treatment.
- Surface treatment: Select plating (rust prevention), spraying (decoration), anodic oxidation (enhanced wear resistance), etc.
- Heat treatment: Quenching or tempering of high strength steel parts to improve their mechanical properties.
5.Quality control
- Dimensional measurement: Critical size tolerances (± 0.01mm) were validated using CMM.
- Appearance inspection: Use manual or automatic equipment to detect scratches, deformation, color difference, etc.
- Functional test: Test insertion force, extraction force, conductivity of precision components (such as electronic connectors).
How to optimize stamping efficiency through mold design in metal stamping?
1.Selection and manufacture of High performance Metal Stamper material selection
- Material Upgrade: Adopting high hardness, high abrasion resistance resistance tool steel (e.g. SKD11, ASP23) or powder metallurgy mold steel, extending mold life (stamping cycle up to millions of times) and reducing downtime and maintenance time due to wear and tear.
- Modular design: Separate the die into independently replaceable inserts, maintain the fragile parts independently, avoid the whole scrap, and reduce maintenance cost.
- Heat Treatment Enhancement: The surface hardness of the die (HV>600) is improved by nitrogen extrusion and vacuum quenching, while the core toughness is maintained to prevent cracking.
2.Optimization of stamping metal in Composite Stamping Process Design
- Multi process integration: Integration Integrating punching, bending and stretching processes (such as feed molds), reduction of stamping frequency and manual intervention, and 30% -50% increase in productivity.
- Path optimization: CAE CAE simulation the punch motion trajectory to avoid ineffectual travel and shorten the stamping cycle (e.g. from 2 seconds to 0.8 seconds).
- Synchronous engineering: Cooperate to optimize die design and stamping equipment parameters (such as slider speed and tonnage) to ensure smooth flow of metal sheets and reduce the risk of mold jamming.
3.Surface treatment and lubrication technology
- Mold surface coating: Using TICN, DLC and other coating technologies, reduce the friction coefficient (30% -40%) between metal plate and die, reduce burr, improve surface smoothness.
- Self-lubricating die: Embedding oil containing ceramic particles or PTFE coating into the die to achieve dry stamping, avoid lubricating oil pollution and improve stamping speed.
- Sheet metal Pre treatment: phosphodizing and galvanizing of stamping metal to improve lubrication performance and reduce die wear.
4.Intelligent mold monitoring and feedback
- Sensor integration: Embedding pressure and temperature sensors on metal stamper to monitor stress distribution during stamping in real time and to warn of abnormal deformation or fracture risks.
- Data-Driven Optimization: Collect stamping data via the Internet of Things (IoT), use artificial intelligence algorithms to analyze mold wear patterns and plan maintenance in advance to avoid sudden downtime.
- Adaptive adjustment: Utilizing the real-time feedback function of hydraulic press or servo presses, dynamic adjustment of punching force to adapt to the characteristics of different batches of metal materials.
5.High speed stamping and automation collaboration
- High-Speed Precision Mould: A lightweight punch heads designed for stamping metal such as aluminum foil and ultra-thin steel plates with a high speed punch (speed >1000 times/minute) for stable stamping of thousands of times per minute.
- Automatic loading and unloading system: Integrated robotic arm or AGV logistics vehicles to seamlessly interface die and stamping equipment, reducing manual refueling time (mold changing time <5 minutes).
- Waste recycling Design: The mould is equipped with waste guide slot or crushing device, which can transport waste products directly to recycling line, reduce manual cleaning time and improve the line continuity production line.

How to achieve burr free machining of complex curved stamping parts?
1.High-precision metallic stamp design
- Biomimetic mold contour: Based on product 3D surface data, die blades with arc transition (R ≥0.5mm) were designed to reduce stress concentration points and reduce the risk of material tearing.
- Dynamic pressure compensation: An array of sensors is embedded in the die to monitor the pressure distribution during stamping in real time. Pressure is dynamically regulated by a servo hydraulic system (accuracy +5%) to ensure uniform metal flow.
- Surface enhancement: TiAlN coating (3-5 μm thickness) or DLC coating (diamond-like carbon) is used to make the die surface hardness HV3000 or higher, increase abrasion resistance 5-8 times and reduce burrs caused by blade wear.
2.Lubrication and process synergy optimization
- Nano level lubricating film: Lubricated graphene (≤5 μm thickness) is sprayed on the surface of stamping the stampings before stamping, reducing friction coefficient to below 0.08 and effectively inhibiting metal adhesion.
- Isothermal stamping technology: The use of mold heating system (temperature control ±1℃) to maintain the material in an austenitic state (e.g. heating steel parts to 950°C) improves the plastic deformation ability and reduces bounce and burr.
- Multi process compound stamping: The stamping, bending and molding processes are integrated into the same set of die, and the stamping speed is controlled by CNC servo mold frame (adjustable 0.1-5m/s) to avoid positioning errors caused by multiple unloading.
3.Innovations in materials and processes
- High ductility alloys: DP780 dual-phase steel or 6061-T6 aluminum alloy is selected to reduce the risk of stamping fracture by increasing the plasticity of the material (elongation ≥15%) through heat treatment (e.g. solid solution+aging).
- Laser pre-forming technology: Laser microforming technology (5-20kW, 5-50mm/s scanning speed) involves pre-forming curvature profile on complex curved metal sheets, followed by stamping that only requires polishing to reduce burr generation.
- Metal Additive manufacturing molds: For small batches of complex parts, 3D-printing metal molds (e.g. SLM technology with density ≥99.5%) are used to quickly respond to design changes and reduce the cost of trial mold.
4.Core technology of closed loop control for detection and reprocessing
- Online vision inspection system: Equipped with high-resolution industrial cameras (resolution 5 μm/pixel) and artificial intelligence algorithms, stamped parts surface defects (burrs, scratches, etc.) are detected in real time and defective products are automatically classified.
- Magnetorheological polishing: After micro scale burrs treatment, magnetorheological fluid (viscosity 10-1000cP) is controlled to achieve non-contact polishing (surface roughness Ra ≤0.05 μm).
- Data traceability platform: Records each batch of stamping parameters (pressure, speed, temperature) and test results, generates quality reports through MES system, and supports continuous process improvement.

Why is metal stamping important in the manufacturing industry?
Metal stamping, as a fundamental and efficient metal forming process, provides an irreplaceable solution for complex structural manufacturing, cost control and material optimization. Its core advantages and values are as follows:
| Importance | Core strengths | Typical application scenarios | Comparison with traditional craftsmanships |
| Efficient mass production | A single stamping can produce thousands to tens of thousands of parts and is 10-20 times more efficient than cutting. | Car body coverings, consumer electronics shell. | Traditional casting/welding processes are inefficient and costly. |
| High material utilization rate | Through precise typesetting and recycling, the material waste rate is controlled at below 5%, far lower than for castings (15-20 per cent). | Aircraft wing reinforcement ribs and energy storage battery casing. | Reduce raw material consumption and reduce carbon emissions. |
| Accuracy and consistency | Mold replication is ±0.01mm and batch products consistency is over 99.9%. | Medical titanium alloy bone plates and spacecraft fasteners. | It is difficult to ensure consistency in the cutting process of complex parts. |
| Manufacture of complex structures | Parts that cannot be processed by traditional methods, such as deep drawing and curved surface molding. | Automobile battery pack shell, hydraulic forming deep-pull parts. | Multiple processes or expensive equipment are required. |
| Cost-effective | The one-time investment in molds is high, but the cost of a single piece after scaling is extremely low (for example, the stamping cost of a car stand is only athird of the cost of injection molding). | Household appliance shell, industrial equipment components. | Suitable for large-scale production, quick result. |
| Adaptable | It can process various materials such as aluminum, steel and titanium alloys, and supports process expansion such as hot stamping and laser preforming. | High-strength automotive components (hot stamping), magnesium alloy consumer electronics components. | Material selection is limited by process (e.g. casting). |
| Rapid iteration capability | The die development cycle is short (7-10 days), supporting agile design changes and small-scale pilot production. | New energy auto components and consumer electronics Rapid prototyping. | Casting/welding process die cycle is long, flexibility is poor. |
How does JS company's metal stamping service collaborate with other processes?
1.Stamping+CNC precision machining
Technology Collaboration Logic:
- Stamping First: Using stamping to quickly form complex parts basic structure (such as contours and holes), shortening the processing cycle.
- CNC precision machining: Accuracy precision assembly requirements micron scale (such as thread holes and irregular grooves 0.1mm in diameter) is achieved through CNC machining.
JS company's advantages:
- Integrated production line: stamping machine and CNC machining centers to achieve physical connection, shortening workpiece transfer time (60% faster than traditional model).
- Intelligent scheduling system: dynamic configuration of stamping and CNC machining resources according to order priorities, reducing delivery time by 15%-20%.
2.Stamping+3D printing
Technology Collaboration Logic:
- Stamping reinforcement structure: Metal stamping is used to form a high rigidity main frame such as the frame of the drone fuselage.
- 3D Printing Filling Function Parts: Embed 3D printed plastic/metal parts (such as sensor compartments and movable hinges) are embedded in the reserved interface of stamped parts.
LS company's advantages:
- Cross-material database: An adaptive model of metal-plastic composites developed by ourselves, which automatically matches the optimum collaborative process parameters.
- Online collaboration platform: Customers can preview the stamping+3D printing combination design scheme real time, supporting parameterized adjustments (e.g. interface tolerances, material thickness, etc.).
3.Stamping + Thermal Forming
Technology Collaboration Logic:
- Stamping pre-forming: Complex shapes (such as pre-bending B-pillar parts for automobiles) are initially formed by cold stamping.
- Thermal pressure secondary reinforcement: Grain refinement and microstructure reconstruction are carried out under high temperature and pressure conditions, which greatly improve strength and toughness of the premade parts.
LS company's advantages:
- Patent technology hot press die: Using gradient cooling channel design, die life increases by 3 times, the thermal deformation rate is less than 0.02%.
- Material database linkage: Built in more than 200 metal sheet thermopress process parameters library, a key to obtain optimization solutions.
4.Stamping+surface treatment
Technology Collaboration Logic:
- Stamping: Complete the basic structure and dimension precision of the parts.
- Surface treatment: Adopt plating, anodic oxidation, PVD coating and so on, give stamping parts anticorrosion, abrasion resistance, decoration and other functions.
LS company's advantages:
- Whole process quality control: Optimize surface treatment process parameters (such as pretreatment cleanliness which directly affects coating adhesion) in combination with stamping process parameters.
- Green process certification: Provides compliant electroplating solutions with over over 95% recovery rate.
Summary
Metal stamping is not only a process choice in manufacturing, but also a technological driver for industrial upgrading. Through efficient production and precision manufacturing of metal stampings, enterprises can achieve differentiation advantages in the fierce market competition. Mastering hardware stamping technology has become the key to improve core competitiveness, whether it is a carmaker pursuing scale or a consumer electronics company focusing on innovation. With its high precision die development capabilities, intelligent production systems, and stamping+combination process experience, JS provides customers with a one-stop shop for everything from prototype verification to mass production delivery, making it an important partner in enhancing global manufacturing competitiveness.
Disclaimer
The content of this page is for informational purposes only.JS SeriesNo representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, are made as to the accuracy, completeness or validity of the information. It should not be inferred that the performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features,material quality and type or workmanship that the third-party supplier or manufacturer will provide through the jusheng network. This is the responsibility of the buyerAsk for a quote for partsto determine the specific requirements for these parts.please Contact us Learn more information.
JS Team
JS is an industry-leading companyFocus on custom manufacturing solutions. With over 20 years of experience serving more than 5,000 customers,we focus on high precisionCNC machining,Sheet metal fabrication,3D printing,Injection molding,metal stamping,and other one-stop manufacturing services.
Our factory is equipped with more than 100 state-of-the-art 5-axis machining centers and is ISO 9001:2015 certified. We provide fast, efficient and high-quality manufacturing solutions to customers in more than 150 countries around the world. Whether it's low-volume production or mass customization, we can meet your needs with the fastest delivery within 24 hours. chooseJS TechnologyIt means choosing efficiency, quality and professionalism.
To learn more, please visit our website:jsrpm.com
FAQs
1.Can complex curved parts be manufactured by stamping?
Sure! Through advanced die or hydraulic forming technology, stamping can manufacture complex structures with deep tensile and curvature changes, such as car battery pack housing.
2.What are the types of metal stamping molds?
According to the complexity of parts, it is divided into punch die (cutting shape), bending die (bending shape), stretching die (hollow part forming) and composite die (multi-process integration).
3.What is the difference between hot stamping and cold stamping?
Cold stamping, normal temperature processing, high efficiency, but limited material ductility, suitable for thin steel plates. Hot stamping, where metal is heated to a high temperature (say, 900°C) and pressed, can manufacture high-strength steel structural elements that increase tensile strength by more than 50%.
4.What is the service life of metal stamping?
Metal stamping molds typically have a life span of 500,000 to 1 million stamping cycles, depending on material hardness (e.g. longer service life of aluminum molds), process parameters (punch pressure, speed) and maintenance.
Resource